Jacobi integral
In celestial mechanics, Jacobi's integral (named after Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi) is the only known conserved quantity for the circular restricted three-body problem problem [1]; unlike in the two-body problem, the energy and momentum of the system are not conserved separately and a general analytical solution is not possible. The integral has been used to derive numerous solutions in special cases.
Definition
Synodic system

One of the suitable coordinates system used is so called synodic or co-rotating system, placed at the barycentre, with the line connecting the two masses μ1, μ2 chosen as x-axis and the length unit equal to their distance. As the system co-rotates with the two masses, they remain stationary and positioned at (−μ2, 0) and (+μ1, 0)1.
In the (x, y)-coordinate system, the Jacobi constant is expressed as follows:
where:
- is the mean motion (orbital period T)
- , for the two masses m1, m2 and the gravitational constant G
- are distances of the test particle from the two masses
Note that the Jacobi integral is minus twice the total energy per unit mass in the rotating frame of reference: the first term relates to centrifugal potential energy, the second represents gravitational potential and the third is the kinetic energy. In this system of reference, the forces that act on the particle are the two gravitational attractions, the centrifugal force and the Coriolis force. Since the first three can be derived from potentials and the last one is perpendicular to the trajectory, they are all conservative, so the energy measured in this system of reference (and hence, the Jacobi integral) is a constant of motion. For a direct computational proof, see below.
Sidereal system
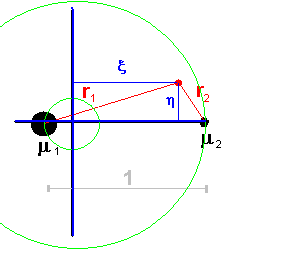
In the inertial, sidereal co-ordinate system (ξ, η, ζ), the masses are orbiting the barycentre. In these co-ordinates the Jacobi constant is expressed by:
Derivation
In the co-rotating system, the accelerations can be expressed as derivatives of a single scalar function
Using Lagrangian representation of the equations of motion:
[Eq.1]
[Eq.2]
[Eq.3]
Multiplying [Eq.1], [Eq.2] and [Eq.3] by and respectively and adding all three yields
Integrating yields
where CJ is the constant of integration.
The left side represents the square of the velocity v of the test particle in the co-rotating system.
1This co-ordinate system is non-inertial, which explains the appearance of terms related to centrifugal and Coriolis accelerations.
See also
References
- Carl D. Murray and Stanley F. Dermot Solar System Dynamics [Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1999], pages 68–71. (ISBN 0-521-57597-4)
- [1] Original research article: Jacobi, Carl Gustav Jacob (1836) "Sur le movement d'un point et sur un cas particulier du problème des trois corps," Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences de Paris, vol. 3, pages 59–61. (Available on-line at: http://visualiseur.bnf.fr/StatutConsulter?N=VERESS3-1201640420309&B=1&E=PDF&O=NUMM-90217 .)













