Knölker complex
Appearance
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Properties | |
| C17H28FeO3Si2 | |
| polar organic solvents | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
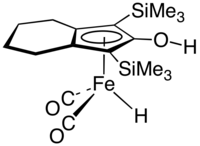
The Knölker complex is an organoiron compound, which is a catalyst for transfer hydrogenation. The complex features an hydroxycyclopentadienyl ligand bound to an Fe(CO)2H centre. It is generated by the corresponding cyclopentadienone tricarbonyl by treatment with base followed by acidification.[1] The compound is related to the organoruthenium compound called Shvo's complex, a hydroxycyclopentadienyl derivative that also functions as a catalyst for hydrogenation.[2]
References
- ^ Knölker, Hans-Joachim; Baum, Elke; Goesmann, Helmut; Klauss, Rüdiger (1999). "Demetalation of Tricarbonyl(cyclopentadienone)iron Complexes Initiated by a Ligand Exchange Reaction with NaOH—X-Ray Analysis of a Complex with Nearly Square-Planar Coordinated Sodium". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 38 (13–14): 2064. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990712)38:13/14<2064::AID-ANIE2064>3.0.CO;2-W.
- ^ Bullock, R. Morris (2007). "An Iron Catalyst for Ketone Hydrogenations under Mild Conditions". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 46 (39): 7360. doi:10.1002/anie.200703053.
