Lacuna (histology)
| Lacuna | |
|---|---|
 Section parallel to the surface from the body of the femur. X 100. a, Haversian canals; b, lacunae seen from the side; c, others seen from the surface in lamella, which are cut horizontally. | |
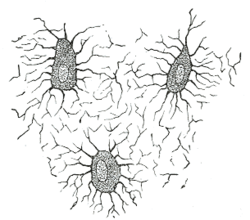 Nucleated bone cells and their processes, contained in the bone lacunæ and their canaliculi respectively. From a section through the vertebra of an adult mouse. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
In histology, a lacuna is a small space containing an osteocyte in bone or chondrocyte in cartilage.
Bone
The Lacunae are situated between the lamellae, and consist of a number of oblong spaces. In an ordinary microscopic section, viewed by transmitted light, they appear as fusiform opaque spots. Each lacuna is occupied during life by a branched cell, termed an osteocyte, bone-cell or bone-corpuscle. Lacunae are connected to one another by small canals called canaliculi. A lacuna never contains more than one osteocyte. Sinuses are an example of lacuna.
Cartilage
The cartilage cells or chondrocytes are contained in cavities in the matrix, called cartilage lacunae; around these the matrix is arranged in concentric lines, as if it had been formed in successive portions around the cartilage cells. This constitutes the so-called capsule of the space. Each lacuna is generally occupied by a single cell, but during the division of the cells it may contain two, four, or eight cells. Lacunae are found between narrow sheets of calcified matrix that are known as lamellae (lah-MEL-ah).
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 90 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 90 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- aplab[dead link] - BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System
- Bone histology photomicrographs
