Camenellan
| Camenellan Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
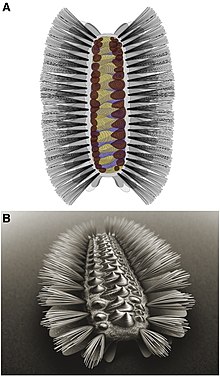
| Reconstruction and life restoration of the camenellan Wufengella | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Grade: | "Tommotiida" |
| Informal group: | †Camenellans |
| Genera | |
| |

The camenellans, consisting of the genera Camenalla, Dailyatia, Kennardia, Kelanella, Wufengella and Lapworthella, are a (probably monophyletic) group of Tommotiid invertebrates from the Cambrian period, reconstructed as sister to all others[clarification needed] (plus brachiopods and phoronids). They are primarily known from isolated sclerites, but are believed to have a scleritomous, Halkieria-like construction.[2][3] This was confirmed by the discovery of Wufengella, known from articulated remains, which showed camenellans to be mobile, worm-like animals.[4]
Dailyatia and Camenella have distinct dorsal (symmetrical) and lateral (asymmetric) sclerite morphologies. The same has been asserted for Lapworthella[5] even though that has not always been the common perception.[3]
It has been argued that Camenella, Kelanella and Lapworthella, assuming a slug-like anatomy, had an anterior 'head valve' followed by pairs of asymmetric valves running in pairs along their dorsal surface.[5]
The 'head valve' in Lapworthella - that is the bilaterally symmetric Morph A valve - is thought to have fused from two ontogenetically separate sclerites.[5] Dailyatia has a similar double-mounded structure at the tip of its A type sclerites.[2]
Growth rings in all are marked out by prominent external ridges.[2][5]
Taxonomy
[edit]Two families:[2]
Kennardiidae Laurie, 1986: three sclerite morphs, one of which (conventionally termed the A morph) is bilaterally symmetrical, the other two occurring in sinistral and dextral variants. Includes Kennardia and Dailyatia, and questionably Shetlandia
Lapworthellidae: sclerites occur in something of a morphological continuum, but essentially form a single type with a sinistral and dextral version, possibly with the anterior-most pair of sclerites fusing into a single bilaterally-symmetrical, dual-tipped sclerite.
Dailyatia species:[2]
- D. ajax Bischoff, 1976 (type)
- D. bacata Skovsted et al., 2015
- D. braddocki Evans & Rowell, 1990
- D. decobruta Betts, 2019[6]
- D. helica Skovsted et al., 2015
- D. macroptera (Tate, 1892)
- D. odyssei Evans & Rowell, 1990
References
[edit]- ^ Devaere, L. et al. The tommotiid Kelanella and associated fauna from the early Cambrian of southern Montagne Noire (France): implications for camenellan phylogeny. Palaeontology 57, 979–1002 (2014).
- ^ a b c d e Skovsted, C. B., Betts, M. J., Topper, T. P. & Brock, G. A. The early Cambrian tommotiid genus Dailyatia from South Australia. Mem. Assoc. Australas. Palaeontol. 48, 1–117 (2015).
- ^ a b Murdock, D. J. E., Donoghue, P. C. J., Bengtson, S. & Marone, F. Ontogeny and micro-structure of the enigmatic Cambrian tommotiid Sunnaginia Missarzhevsky, 1969. Palaeontology 55, 661–676 (2012).
- ^ Guo, Jin; Parry, Luke A.; Vinther, Jakob; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Wei, Fan; Zhao, Jun; Zhao, Yang; Béthoux, Olivier; Lei, Xiangtong; Chen, Ailin; Hou, Xianguang; Chen, Taimin; Cong, Peiyun (2022). "A Cambrian tommotiid preserving soft tissues reveals the metameric ancestry of lophophorates". Current Biology. Online: S0960–9822(22)01455–5. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2022.09.011. ISSN 1879-0445. PMID 36170853.
- ^ a b c d Devaere, L. & Skovsted, C. B. New early Cambrian sclerites of Lapworthella schodakensis from NE Greenland: advancements in knowledge of lapworthellid taxonomy, sclerite growth and scleritome organization. Geol. Mag. (2016). doi:10.1017/S0016756816000698
- ^ Betts, Marissa; Claybourn, Thomas; Brock, Glenn; Jago, James; Skovsted, Christian; Paterson, John (2019). "Early Cambrian shelly fossils from the White Point Conglomerate, Kangaroo Island, South Australia" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 64 (3). doi:10.4202/app.00586.2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-08-30. Retrieved 2019-08-30.
