Lesser petrosal nerve
| Lesser petrosal nerve | |
|---|---|
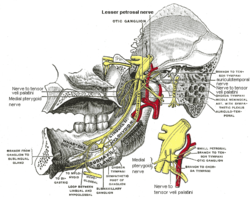 Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve, seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. (Small petrosal labeled at center top and bottom right.) | |
 Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves. | |
| Details | |
| From | tympanic plexus |
| To | otic ganglion |
| Innervates | parotid gland |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus petrosus minor |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.149 |
| TA2 | 6326 |
| FMA | 53491 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The lesser petrosal nerve (also known as the small superficial petrosal nerve) is the General visceral efferent (GVE) component of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), carrying parasympathetic fibers from the tympanic plexus to the parotid gland.
Structure
After arising in the tympanic plexus, the lesser petrosal nerve passes forward and then through the hiatus for lesser petrosal nerve on the anterior surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone into the middle cranial fossa. It travels across the floor of the middle cranial fossa,[1] then exits the skull via foramen ovale to reach the infratemporal fossa. The fibres synapse in the otic ganglion, and post-ganglionic fibres then travel briefly with the auriculotemporal nerve (a branch of V3) before entering the body of the parotid gland.
The facial nerve gives off a branch at the geniculate ganglion for communication with the otic ganglion which joins the lesser petrosal nerve.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Kakizawa Y. et al., "The course of the lesser petrosal nerve on the middle cranial fossa." Neurosurgery. 2007 Sep; 61(3 Suppl): 15-23. PMID 17876229
External links
- Lesser petrosal nerve diagram
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (IX)
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (midearcavity) (#7)
- MedEd at Loyola grossanatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cn9.htm
- Template:YaleCranialNerves
