Liebeskind–Srogl coupling
The Liebeskind–Srogl coupling reaction is an organic reaction forming a new carbon–carbon bond from a thioester and a boronic acid using a metal catalyst.[1] This reaction was invented by and named after Jiri Srogl from the Academy of Sciences, Czech Republic, and Lanny S. Liebeskind from Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, USA. The metal catalyst depicted below uses TFP = tris(2-furyl)phosphine as an additional ligand and CuTC = copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate as a co-metal catalyst. The overall reaction scheme is shown below.
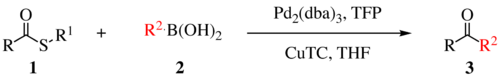
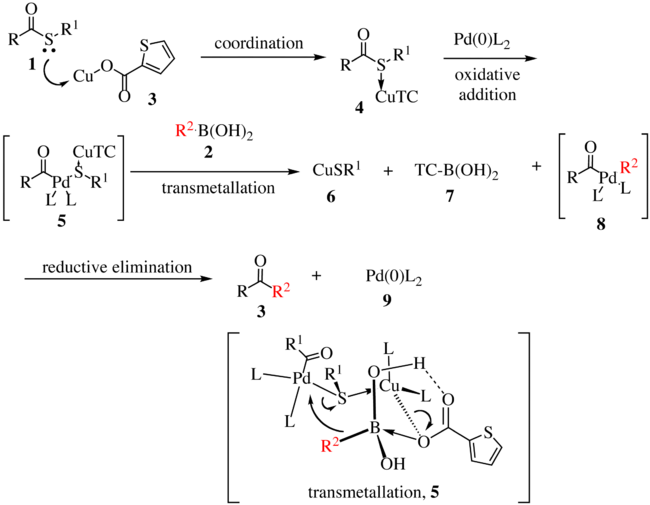
Mechanism
The proposed reaction mechanism is shown below.[2][3] The thioester 1 complexes with copper complex 3 to form compound 4. With the oxidative insertion of [Pd] into the carbon–sulfur bond, compound 5 is formed, and with transmetallation, organopalladium species 8 is formed. The transmetallation proceeds via the transfer of R2 to the palladium metal center with concomitant transfer of the sulfur atom to the copper complex. Reductive elimination gives ketone 3 with the regeneration of the active catalyst 9.
References
- ^ Liebeskind, L.; Srogl, Jiri (2000). "Thiol Ester−Boronic Acid Coupling. A Mechanistically Unprecedented and General Ketone Synthesis". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122: 11260–11261. doi:10.1021/ja005613q.
- ^ Yu, Y.; Liebeskind, L. S. (2004). "Copper-mediated, palladium-catalyzed coupling of thiol esters with aliphatic organoboron reagents". J. Org. Chem. 69 (10): 3554–3557. doi:10.1021/jo049964p. PMID 15132570.
- ^ ^ Villalobos, J. M.; Srogl, J.; Liebeskind, L. S. (2007). "A new paradigm for carbon–carbon bond formation: aerobic, copper-templated cross-coupling". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129 (51): 15734–15735. doi:10.1021/ja074931n. PMC 2561227. PMID 18047333.
