Megasthenes
Megasthenes | |
|---|---|
| File:Megasthenes arriving in Pataliputra artist impression.jpg Artistic impression of Megasthenes arriving in Pataliputra circa 300 BC. |
Megasthenes (/m[invalid input: 'ɨ']ˈɡæsθ[invalid input: 'ɨ']niːz/ mi-GAS-thi-neez; Ancient Greek: Μεγασθένης, c. 350 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period, author of the work Indika.[1] He was born in Asia Minor and became an ambassador of Seleucus I Nicator of the Seleucid dynasty possibly to Chandragupta Maurya in Pataliputra, India.[2] However the exact date of his embassy is uncertain. Scholars place it before 298 BCE, the date of Chandragupta's death.
Travel
Arrian explains that Megasthenes lived in Arachosia, with the satrap Sibyrtius, from where he visited India:
"Megasthenes lived with Sibyrtius, satrap of Arachosia, and often speaks of his visiting Sandracottus, the king of the Indians." Arrian, Anabasis Alexandri [3]
We have more definite information regarding the parts of India Megasthenes visited. He entered the subcontinent through the district of the Pentapotamia (modern day Punjab region[4]), providing a full account of the rivers found there (thought to be the five affluents of the Indus that form the Punjab region), and proceeded from there by the royal road to Pataliputra. There are accounts of Megasthenes having visited Mathura (Muttra), in Bihar, but he appears not to have visited any other parts of India.
Indica
Indika (Greek: Ἰνδικά; Latin: Indica) is an account of Mauryan India by Megasthenes. The original book is now lost, but its fragments have survived in later Greek and Latin works. The earliest of these works are those by Diodorus Siculus, Strabo (Geographica), Pliny, and Arrian (Indica).[5][6]
Reconstruction
Megasthenes' Indica can be reconstructed using the portions preserved by later writers as direct quotations or paraphrase. The parts that belonged to the original text can be identified from the later works based on similar content, vocabulary and phrasing, even when the content has not been explicitly attributed to Megasthenes. Felix Jacoby's Fragmente der griechischen Historiker contains 36 pages of content traced to Megasthenes.[7]
| Fragments used by John Watson McCrindle to reconstruct Megasthenes' Indica | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Work | Author / Editor | Section | Topic | Book number in Megasthenes' Indica |
| 1 | Bibliotheca historica | Diodorus Siculus | II.35-42 | Summary of India | Summary |
| 2 | Bibliotheca historica | Diodorus Siculus | III.63 | Three persons named Dionusos | Summary |
| 3 | The Anabasis of Alexander | Arrian | V. 6. 2-11 | Boundaries and rivers | I |
| 4 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | II. 1. 7 | Boundaries | I |
| 5 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.11 | Boundaries and extent | I |
| 6 | Geographica | Strabo | II.1.7 | Size of India | I |
| 7 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.12 | Size of India | I |
| 8 | Geographica | Strabo | II.1.4 | Size of India | I |
| 9 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | III. 7-8. | Size of India | I |
| 10 | Geographica | Strabo | II.1.19 | Ursa Major and shadows | I |
| 11 | Natural History | Pliny | VI. 22.6. | Ursa Major | I |
| 12 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.20 | Fertile soil | I |
| 13 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.37 | Wild animals | I |
| 14 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XVII 39. | Indian apes | I |
| 15 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XVI. 41 | Winged scorpions and serpents | I |
| 16 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.56 | Animals of India, and the Reed | I |
| 17 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XVI. 20.21 | Animals of India | I |
| 18 | Natural History | Pliny | VIII. 14. 1 | Boa constrictor | I |
| 19 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | VIII.7 | Of the Electric Eel. | I |
| 20 | Natural History | Pliny | VI.24.1 | Taprobane | I |
| 21 | Antigon. Caryst. | Antigonus of Carystus | 647 | Marine trees | I |
| 22 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | 4. 2-13. | Indus and Ganges | I |
| 23 | Natural History | Pliny | VI. 21.9-22. 1. | Indus and Ganges | I |
| 24 | Polyhistor | Gaius Julius Solinus | 52. 6-7. | Indus and Ganges | I |
| 25 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | 6. 2-3. | Silas river | I |
| 26 | Anecdota Graeca | Jean François Boissonade de Fontarabie | I. p. 419, | Silas river | I |
| 27 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.38 | Silas river | I |
| 28 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | 5. 2 | Number of Indian rivers | I |
| 29 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.35-36 | Pataliputra city | II |
| 30 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | 10 | Pataliputra and Indian manners | II |
| 31 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.53-56 | Indian manners | II |
| 32 | Varia Historia | Claudius Aelianus | iv.1. | Indian manners | II |
| 33 | Nicol. Damasc. | Nicolaus of Damascus | 44 | Indian manners | II |
| 34 | Sermones | Stobaeus | 42 | Indian manners | II |
| 35 | Deipnosophistae | Athenaeus | iv. p. 153. | Indian suppers | II |
| 36 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.57 | Extraordinary tribes | II |
| 37 | Natural History | Pliny | VII. ii. 14-22 | Extraordinary races | II |
| 38 | Polyhistor | Gaius Julius Solinus | 52. 26-30 | Extraordinary races | II |
| 39 | On the Face in the Moon (de facie in orbe lunae) in Moralia | Plutarch | Opp. ed. Reisk, tom. ix. p. 701. | Race of mouthless humans | II |
| 40 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | Xl.l.-XII.-9 | 7 castes of India | III |
| 41 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.39-41 | 7 castes of India | III |
| 42 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.50-52 | Administration of public affairs; horses and elephants. | III |
| 43 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XIII. 10. | Horses and elephants | III |
| 44 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.41-43 | Elephants | III |
| 45 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | ch. 13-14. | Elephants | III |
| 46 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XII. 44. | Elephants | III |
| 47 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XIII. 7. | Of the diseases of Elephants. | III |
| 48 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.44 | Gold-digging ants | III |
| 49 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | XV.5-7. | Gold-digging ants | III |
| 50 | Orations | Dio Chrysostom | Or. 35 | Gold-digging ants | III |
| 51 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.58-60 | Indian philosophers | III |
| 52 | Stromata | Clement of Alexandria | I. p. 305 D | Indian philosophers | III |
| 53 | Praeparatio evangelica | Eusebius | IX. 6 | Indian philosophers | III |
| 54 | Contra Julianum (Against Julian) | Cyril of Alexandria | IV | Indian philosophers | III |
| 55 | Stromata | Clement of Alexandria | I | Indian philosophers | III |
| 56 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.68 | Indian philosophers: Kalanos (Calanus) and Mandanis | III |
| 57 | The Anabasis of Alexander | Arrian | VII ii. 3-9 | Indian philosophers: Kalanos (Calanus) and Mandanis | III |
| 58 | Geographica | Strabo | XV.1.68 | Indians had not attacked anyone or faced external attacks; Dionysos and Herakles | IV |
| 59 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | V. 4-12. | Indians had not attacked anyone or faced external attacks; Dionysos and Herakles | IV |
| 60 | Contra Apion | Josephus | I. 20 (T. II p. 451, Havere.) | King of the Babylonians surpassed Herakles in greatness | IV |
| 61 | Antiquitates Judaicae | Josephus | X. ii. 1 (T. I p. 533, Havere.) | King of the Babylonians surpassed Herakles in greatness | IV |
| 62 | Zonar. Annal. Basileae 1557 | King of the Babylonians surpassed Herakles in greatness | IV | ||
| 63 | G. Syncell. T. I. | George Syncellus??? | p. 419, ed. Benn. (p. 221 ed. Paris, p. 177 ed. Venet.) | King of the Babylonians surpassed Herakles in greatness | IV |
| 64 | Fragments of Abydenus's writings in Praeparatio evangelica | Eusebius | I. 41 (ed. Colon. 1688, p. 456 D) | King of the Babylonians surpassed Herakles in greatness | IV |
| 65 | Indica (Arrian) | Arrian | 7-9. | King of the Babylonians surpassed Herakles in greatness | IV |
| 66 | Natural History | Pliny | IX. 5 | Pearls | IV |
| 67 | Mirabilia | Phlegon of Tralles | 33 | Pandaian land | IV |
| 68 | Natural History | Pliny | VI. xxi. 4-5. | Ancient history of Indians | IV |
| 69 | Polyhistor | Gaius Julius Solinus | 52. 5. | Ancient history of Indians | IV |
| 70 | The Anabasis of Alexander | Arrian | VII. ii. 3-9. | Indian philosophers: Kalanos (Calanus) and Mandanis | IV |
| 71 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XII. 8. | Elephants | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 72 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | III. 46. | White elephant | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 73 | De Recta in Deum Fide | Adamantius (Pseudo-Origen) | vol. I. p. 904. | Brachhmans (Brahmins) and their philosophy | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 74 | Palladius De gentibus Indiae et Bragmanibus' | Palladius of Galatia | pp. 8, 20 et seq. ed. Londin. 1668. | Indian philosophers: Kalanos (Calanus) and Mandanis | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 75 | De Moribus Brachmanorum | Ambrosius | pp. 62, 68 et seq. ed. Pallad. Londin. 1668. | Calanus and Mandanis | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 76 | Natural History | Pliny | VI. 21. 8-23. 11. | Indian races | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 77 | Polyhistor | Gaius Julius Solinus | 52. 6-17. | Catalogue of Indian Races. | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 78 | Stratagems | Polyaenus | I. 1. 1-3. | Dionysos | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 79 | Stratagems | Polyaenus | I. 3. 4. | Hercules and Pandaea | (Doubtful fragments) |
| 80 | De Natura Animalium | Claudius Aelianus | XVI. 2-22. | Beasts of India | (Doubtful fragments) |
India according to the reconstructed text
According to the text reconstructed by J. W. McCrindle, Megasthenes' Indica describes India as follows:
Geography
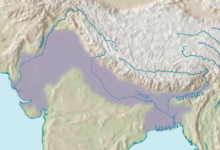
India is a quadrilateral-shaped country, bounded by the ocean on the southern and the eastern side.[8] The Indus river forms the western and the north-western boundary of the country, as far as the ocean.[9] India's northern border reaches the extremities of Tauros. From Ariana to the Eastern Sea, it is bound by mountains that are called Kaukasos by the Macedonians. The various native names for these mountains include Parapamisos, Hemodos and Himaos (the Himalayas).[10] Beyond Hemodos, lies Scythia inhabited by the Scythians known as Sakai.[11] Besides Scythia, the countries of Bactria and Aryans bordered India.[12]
At the extreme point of India, the gnomon of the sundial often casts no shadow, and the Ursa Major is invisible at night. In the remotest parts, the shadows fall southward, and even Arcturus is not visible.[11]
India has many large and navigable rivers, which arise in the mountains on its northern border. Many of these rivers merge into Ganges, which was 30 stadia wide at its source, and runs from north to south. The Ganges empties into the ocean that forms the eastern boundary of Gangaridai.[13] Other nations feared Gangaridai's huge force of the biggest elephants, and therefore, Gangaridai had never been conquered by any foreign king.[14] Indus also runs from north to south, and had several navigable tributaries. The most notable tributaries are Hupanis, the Hudaspes, and the Akesines.[15] One peculiar river is Sillas, which originates from a fountain of the same name. Everything cast into this river sinks down to the bottom - nothing floats in it.[12] In addition, there are a large number of other rivers, supplying abundant water for agriculture. According to the native philosophers and natural scientists, the reason for this is that the bordering countries are more elevated than India, so their waters run down to India, resulting in such a large number of rivers.[16]
History

In the primitive times, the Indians lived on fruits and wore clothes made of animal skin, just like the Greeks. The most learned Indian scholars say that Dionysus invaded India, and taught Indians several things including how to grow plants, make wine and worship. He founded several large cities, introduced laws and established courts. For this reason, he was regarded as a deity by the Indians. He ruled entire India for 52 years, before dying of old age. His descendants ruled India for several generations, before being dethroned and replaced with democratic city-states.[17]
The Indians who inhabit the hill country also claim that Herakles was one of them. Like the Greeks, they characterize him with the club and the lion's skin. According to them, Herakles was a powerful man who subjugated evil beasts. He had several sons and one daughter, who became rulers in different parts of his dominion. He founded several cities, the greatest of which was Palibothra (Pataliputra). Herakles built several places in this city, fortified it with water-filled trenches and settled a number of people in the city. His descendants ruled India for several generations, but never launched an expedition beyond India. After several years, the royal rule was replaced by democratic city states, although there existed a few kings at the time Alexander's invasion of India.[18]
Flora and fauna
India has several mountains with fruit trees of every kind.[11] There are a large number of animal species in India. The Indian elephants are far stronger than the Libyan elephants, because of the abundance of food on the Indian soil. The elephants are domesticated in large numbers, and trained for war.[19] The gestation period of the elephants ranges from 16 to 18 months, and the oldest of the elephants live up to 200 years.[20]
Economy
Gold, silver, copper and iron are abundant on Indian soil. Besides tin and other metals are used for making a number of tools, weapons, ornaments, and other articles.[19]
India has very fertile plains, and irrigation is practised widely.[19] The main crops include rice, millet, a crop called bosporum, other cereals, pulses and other food plants.[21] There are two crop cycles per year, since rain falls in both summer and winter. At the time of summer solstice, rice, millet, bosporum and sesamum are sown. During winter, wheat is sown.[21]
No famines have ever occurred in India because of the following reasons:[22]
- The Indians are always assured of at least one of the two seasonal crops
- There are a number of spontaneously growing fruits and edible roots available.
- The Indian warriors regard those engaged in agriculture and animal husbandry as sacred. Unlike the warriors in other countries, they do not ravage farms during war conquests. Moreover, the warring sides never destroy the enemy land with fire or cut down its trees.
Society
Because of its large size, India is inhabited by many diverse races, all of which are indigenous. India has no foreign colony, and Indians have not established any colonies outside India.[12] The Indians are of above average stature, because of abundant food, fine water and pure air. They are well-skilled in art.[19]
A law, prescribed by ancient Indian philosophers, bans slavery. The laws treats everyone equally, but allows the property to be unevenly distributed.[23]
The population of India is divided into 7 endogamous and hereditary castes:[24]
- Philosophers
- Not numerous compared to other castes, but most prominent
- Exempted from all public duties
- Neither masters, nor servants
- "believed to be most dear to the gods, and to be the most conversant with matters pertaining to Hades"
- Engaged by others to offer sacrifices and perform funerary rites, for which they received valuable gifts and privileges
- At the beginning of the year, they make prophecies about droughts, rain storms, propitious winds, diseases and other topics. Based on these prophecies, the citizens and the rulers make adequate preparations. A philosopher whose prophecy fails receives strong criticism and has to observe silence for the rest of his life, but otherwise incurs no penalty.
- Farmers
- Most numerous of all castes
- Live in villages, and avoid visiting towns
- Exempted from fighting and other public duties
- Regarded as public benefactors, and protected from damage during wars, even by enemy warriors
- Pay a land tribute to the ruler, the official land owner
- In addition, they remit 1/4th of their produce to the state treasury
- Herders
- Live in tents, outside villages and towns
- Hunt and trap crop-destroying birds and animals
- Artisans
- Create weapons as well as tools for farmers and others
- Exempted from paying taxes, and receive a maintenance from the state exchequer
- Military
- Second most numerous among the castes
- Well-organized and equipped for war
- Indulge in amusements and idleness during peaceful times
- Maintained at state expense, along with war horses and elephants
- Overseers
- Carry out administrative tasks
- Report to the king or (in states not ruled by kings) magistrates
- Councillors and Assessors
- Composed of wise people with good character
- Deliberate on public affairs; included the royal advisers, state treasurers, dispute arbitrators; the army generals and chief magistrates also usually belonged to this class.
- Least numerous, but most respected
Administration
The foreigners are treated well. Special officers are appointed to ensure that no foreigner was harmed, and judges handed out harsh punishment to those who took unfair advantage of the foreigners. Sick foreigners are attended by physicians and taken care of. Foreigners who died in India are buried, and their property is delivered to their relatives.[25]
Historical reliability
Later writers such as Arrian, Strabo, Diodorus, and Pliny refer to Indika in their works. Of these writers, Arrian speaks most highly of Megasthenes, while Strabo and Pliny treat him with less respect.
The first century Greek writer Strabo called both Megasthenes and his succeeding ambassador Deimachus liars, and stated that "no faith whatever" could be placed in their writings.[26] The Indika itself contained numerous fantastical stories of people with backwards feet, ears large enough to sleep in, no mouths, or other strange features. Strabo directly contradicted these descriptions, assuring his readers that Megasthenes' stories, along with his recounting of India’s founding by Hercules and Dionysus, were mythical with little to no basis in reality.[27]
According to Paul J. Kosmin, Indica depicts contemporary India as an unconquerable territory, in order to justify Seleucus's retreat from India. Megasthenes tries to argue that Dionysus was able to conquer India, because before his invasion, India was a primitive rural society. Dionysus' urbanization of India makes India a powerful, impregnable nation. The later ruler — the Indian Herakles — is presented as a native of India, despite similarities with the Greek Heracles. This, according to Kosmin, is because now India is shown as unconquerable.[28] Megasthenes emphasizes that no foreign army had been able to conquer India (since Dionysus) and Indians had not invaded a foreign country either. This representation of India as an isolated, invincible country is an attempt to vindicate Seleucus' peace treaty with the Indian emperor.[29]
Legacy
Megasthenes' Indica, along with Ctesias' book of the same name, is among the earliest well-known Western accounts of India and he is regarded as one of the founders of the study of Indian history in the West. He is also the first foreign Ambassador to be mentioned in Indian history.
Megasthenes also comments on the presence of pre-Socratic views among the Brahmans and Jews. Five centuries later Clement of Alexandria, in his Stromateis, may have misunderstood Megasthenes to be responding to claims of Greek primacy by admitting Greek views of physics were preceded by those of Jews and Indians. Megasthenes, like Numenius of Apamea, was simply comparing the ideas of the different ancient cultures.[30]
See also
References
- ^ "Realty to broaden horizon".
- ^ Mookerji 1988, p. 38.
- ^ Arrian. "Book 5". Anabasis.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|titlelink=ignored (|title-link=suggested) (help) - ^ "History of West Punjab (Pakistan)". World History at KMLA.
- ^ Upinder Singh (2008). A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India. Pearson Education India. p. 324. ISBN 9788131711200.
- ^ Christopher I. Beckwith (2015). Greek Buddha: Pyrrho's Encounter with Early Buddhism in Central Asia. Princeton University Press. p. 62. ISBN 9781400866328.
- ^ Kosmin 2013, p. 99.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 49.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 46.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, pp. 48–49.
- ^ a b c McCrindle 1877, p. 30.
- ^ a b c McCrindle 1877, p. 35.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 33.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 33-34.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 34.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 34-35.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 35-38.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 39-40.
- ^ a b c d McCrindle 1877, p. 31.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 44.
- ^ a b McCrindle 1877, p. 32.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 32-33.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 40.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 40-44.
- ^ McCrindle 1877, p. 44-45.
- ^ Dahlaquist 1996, p. 28.
- ^ Strabo, Geography, Book XV, Chapter 1
- ^ Kosmin 2013, p. 98-100.
- ^ Kosmin 2013, p. 103-104.
- ^ Bezalel Bar-Kochva (2009). The Image of the Jews in Greek Literature: The Hellenistic Period.
He does not respond to the implied claim of Greek primacy, presumably because he did not have, and could not have had, hard information about the beginnings of "parallel" opinions among the Brahmans.
Bibliography
- McCrindle, J. W. (1877). Ancient India As Described By Megasthenes And Arrian. London: Trübner & Co.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kosmin, Paul J. (2013). "Apologetic Ethnography: Megasthenes' Indica and the Seleucid Elephant". In Eran Almagor, Joseph Skinner (ed.). Ancient Ethnography: New Approaches. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 9781472537607.
- Dahlaquist, Allan (1996). Megasthenes and Indian Religion- Volume 11 of History and Culture Series. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. p. 386. ISBN 81-208-1323-5.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Vassiliades, Demetrios (2000). The Greeks in India: A survey in Philosophical Understanding. New Delhi: Munshiram Manoharlal Publ. ISBN 81-215-0921-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Megasthenes (1846), E. A. Schwanbeck (ed.), Indica, Sumptibus Pleimesii, bibliopolae (Original Oxford University)
- Mookerji, Radha Kumud (1988) [first published in 1966], Chandragupta Maurya and his times (4th ed.), Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 81-208-0433-3
External links
- Fragments of Indika, as reconstructed from later accounts
- Ancient India as described by Arrian based on accounts by Megasthenes
