Pegasus (satellite)
 Pegasus satellite, attached to the S-IV upper stage | |
| Manufacturer | Fairchild Hiller |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | United States |
| Operator | NASA |
| Applications | Micrometeoroid detection |
| Specifications | |
| Launch mass | 1,450 kilograms (3,200 lb) |
| Dimensions | 29 meters (96 ft) wide by 4.1 meters (13.6 ft) long |
| Power | Solar cells |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Production | |
| Status | retired |
| Built | 3 |
| Launched | 3 |
| Operational | 16 February 1965 |
| Retired | 29 August 1968 |
| Failed | 0 |
| Maiden launch | 16 February 1965 |
| Last launch | 30 July 1965 |
| Configuration | |
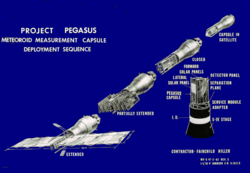 Deployment of a Pegasus Satellite | |
The Pegasus satellite program was a series of three American satellites launched in 1965 to study the frequency of micrometeorite impacts on spacecraft. All three Pegasus satellites were launched by Saturn I rockets, and remained connected with their upper stages.
The Pegasus satellite was named for the winged horse of Greek mythology and was first lofted into space by a NASA Saturn I rocket on February 16, 1965. Like its namesake, the Pegasus satellite was notable for its "wings", a pair of 96-foot (29 m)-long, 14-foot (4.3 m)-wide arrays of 104 panels fitted with sensors to detect punctures by micrometeoroids at high altitudes, in support of the Apollo Program to send manned lunar landing missions starting by 1970. Micrometeoroids were believed to be potentially hazardous to the Apollo crew if they could puncture the spacecraft skin. The sensors successfully measured the frequency, size, direction and penetration of scores of micrometeoroid impacts. The satellite also carried sample protective shields mounted on the arrays.
The NASA Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for the design, production and operation of the three Pegasus satellites which were launched by Saturn I rocket test flights in 1965. At launch, a boilerplate Apollo Command/Service Module and launch escape system tower were atop the Saturn I, with the Pegasus experiment folded inside the Service Module. After first stage separation and second-stage ignition, the launch escape system was jettisoned. When the second stage attained orbit, the 10,000-pound Apollo boilerplate Command and Service modules were jettisoned into a separate orbit. Then a motor driven device extended the winglike panels on the Pegasus to a span of 96 feet (29 m). The Pegasus wings remained attached to the Saturn I's second stage as planned.
A television camera, mounted on the interior of the Service Module adapter, provided pictures of the satellite deploying in space and as one historian[who?] has written, "captured a vision of the eerie silent wings of Pegasus I as they haltingly deployed." The satellite exposed more than 2,300 square feet (210 m2) of instrumented surface, with thickness varying up to 0.016-inch (0.41 mm).
Ernst Stuhlinger, then director of the MSFC Research Projects Laboratory, noted that all three Pegasus missions provided more than data on micrometeoroid penetration. Scientists also were able to gather data regarding gyroscopic motion and orbital characteristics of rigid bodies in space, lifetimes of electronic components in the space environment, and thermal control systems and the degrading effects of space on thermal control coatings. Space historian Roger Bilstein reported that for physicists the Pegasus missions provided additional knowledge about the radiation environments of space, the Van Allen radiation belts and other phenomena.
Orbits
- Pegasus 1
- Launched: 16 February 1965
- Launch vehicle: A-103
- Orbital inclination: 31.7 degrees.
- Perigee: 510 km
- Apogee: 726 km
- Launch weight: 10.5 tons.
- Dry weight: 1451.5 kg
- Decayed: 17 September 1978
- International Designator: 1965-009A
- Pegasus 2
- Pegasus 3
External links
- Encyclopedia Astronautica entry
- REDISCOVERED Pegasus test vehicle
- A film clip showing Pegasus 2 liftoff and animation (May 1965) is available for viewing at the Internet Archive
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
