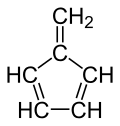
Fulvene
Appearance
(Redirected from Pentafulvene)
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Methylidenecyclopenta-1,3-diene[1] | |||
| Other names
Fulvene[1]
5-Methylene-1,3-cyclopentadiene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6 | |||
| Molar mass | 78.114 g·mol−1 | ||
| -42.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Fulvene (pentafulvene) is a hydrocarbon with the formula (CH=CH)2C=CH2. It is a prototype of a cross-conjugated hydrocarbon.[2] Fulvene is rarely encountered,[3] but substituted derivatives (fulvenes) are numerous. They are mainly of interest as ligands and precursors to ligands in organometallic chemistry.
Fulvene is an isomer of benzene, which when irradiated at 237 to 254 nm forms small amounts of fulvene along with benzvalene.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 379. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Preethanuj Preethalayam; Syam krishnan, K.; Sreeja Thulasi; Sarath Chand, S.; Jomy Joseph; Vijay Nair; Florian Jaroschik; K.V.Radhakrishnan (2017). "Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Pentafulvenes". Chemical Reviews. 117 (5): 3930–3989. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00210. PMID 28151643.
- ^ Bergmann, E. D. (1968). "Fulvenes and Substituted Fulvenes". Chemical Reviews. 68: 41–84. doi:10.1021/cr60251a002.
- ^ Kaplan, Louis; Wilzbach, K. E. (1968). "Photolysis of benzene vapor. Benzvalene formation at wavelengths 2537-2370 A". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 90 (12): 3291–3292. doi:10.1021/ja01014a086. ISSN 0002-7863.