Picein
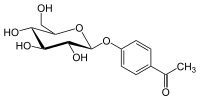 Chemical structure of picein
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-[4-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyphenyl]ethanone
| |
| Other names
L-Picein
Ameliaroside | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.704 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H18O7 | |
| Molar mass | 298.291 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Picein is a phenolic compound found in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces (Picea abies).[1] It is the glucoside of piceol.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Münzenberger, Babette; Heilemann, Jürgen; Strack, Dieter; Kottke, Ingrid; Oberwinkler, Franz (1990). "Phenolics of mycorrhizas and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruce". Planta. 182 (1): 142–8. doi:10.1007/BF00239996. PMID 24197010.
- ^ Løkke, Hans (1990). "Picein and piceol concentrations in Norway spruce". Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 19 (3): 301–9. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(90)90032-Z. PMID 2364913.
