Piston pump

A piston pump is a type of positive displacement pump where the high-pressure seal reciprocates with the piston[1]. Piston pumps can be used to move liquids or compress gases. They can operate over a wide range of pressures. High pressure operation can be achieved without a strong effect on flow rate. Piston pumps can also deal with viscous media and media containing solid particles [2].
Types
The two main types of piston pump are the lift pump and the force pump.[3] Both types may be operated either by hand or by an engine.
-
Lift pump
-
Force pump
Lift pump
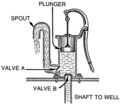
In a lift pump, the upstroke of the piston draws water, through a valve, into the lower part of the cylinder. On the downstroke, water passes through valves set in the piston into the upper part of the cylinder. On the next upstroke, water is discharged from the upper part of the cylinder via a spout.
Force pump
In a force pump, the upstroke of the piston draws water, through an inlet valve, into the cylinder. On the downstroke, the water is discharged, through an outlet valve, into the outlet pipe.