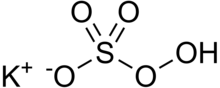
Potassium peroxymonosulfate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium peroxysulfate
| |
| Other names
Caroat
Oxone potassium monopersulfate MPS | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.158 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KHSO5 | |
| Molar mass | 152.2 g/mol (614.76 as triple salt) |
| Appearance | off-white powder |
| decomposes | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Oxidant, Corrosive |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Degussa Caroat MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Potassium persulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium peroxymonosulfate (also known as MPS, potassium monopersulfate, potassium caroate, and the trade names Caroat and Oxone) is widely used as an oxidizing agent. It is the potassium salt of peroxymonosulfuric acid.
The triple salt 2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4 (known by the tradename Oxone) is a form with higher stability.[2] The standard electrode potential for this compound is +1.81 V with a half reaction generating the hydrogen sulfate (pH=0).[3]
- HSO5− + 2 H+ + 2 e− → HSO4− + H2O
Reactions
MPS is a versatile oxidant. It oxidizes aldehydes to carboxylic acids; in the presence of alcoholic solvents, the esters may be obtained.[4] Internal alkenes may be cleaved to two carboxylic acids (see below), while terminal alkenes may be epoxidized. Thioethers give sulfones, tertiary amines give amine oxides, and phosphines give phosphine oxides.
Illustrative of the oxidation power of this salt is the conversion of an acridine derivative to the corresponding acridine-N-oxide.[5]

MPS will also oxidize a thioether to a sulfone with 2 equivalents.[6] With one equivalent the reaction converting sulfide to sulfoxide is much faster than that of sulfoxide to sulfone, so the reaction can conveniently be stopped at that stage if so desired.

MPS can also react with ketones to form dioxiranes, with the synthesis of dimethyldioxirane (DMDO) being representative. These are versatile oxidising agents and may be used for the epoxidation of olefins. In particular, if the starting ketone is chiral then the epoxide may be generated enantioselectively, this forms the basis of the Shi epoxidation.[7]

Uses
Potassium peroxymonosulfate can be used in swimming pools to keep the water clear, thus allowing chlorine in pools to work to sanitize the water rather than clarify the water, resulting in less chlorine needed to keep pools clean.[8] One of the drawbacks of using potassium peroxymonosulfate in pools is it can cause the common DPD #3 water test for combined chlorine to read incorrectly high.[9]
References
- ^ "DuPont MSDS" (PDF).
- ^ Crandall, Jack K.; Shi, Yian; Burke, Christopher P.; Buckley, Benjamin R. (2001). Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1002/047084289x.rp246.pub3. ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8.
- ^ Spiro, M. "The standard potential of the peroxosulphate/sulphate couple". Electrochimica Acta. 24 (3): 313–314. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(79)85051-3. ISSN 0013-4686.
- ^ Benjamin R. Travis; Meenakshi Sivakumar; G. Olatunji Hollist; Babak Borhan (2003). "Facile Oxidation of Aldehydes to Acids and Esters with Oxone". Organic Letters. 5 (7): 1031–4. doi:10.1021/ol0340078. PMID 12659566.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Thomas W. Bell, Young-Moon Cho, Albert Firestone, Karin Healy, Jia Liu, Richard Ludwig, and Scott D. Rothenberger (1993). "9-n-Butyl-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-Octahydroacridin-4-ol". Organic Syntheses
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collected Volumes, vol. 8, p. 87. - ^ James R. McCarthy, Donald P. Matthews, and John P. Paolini (1998). "Reaction of Sulfoxides with Diethylaminosulfur Trifluoride". Organic Syntheses
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collected Volumes, vol. 9, p. 446. - ^ Frohn, Michael; Shi, Yian (2000). "Chiral Ketone-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins". Synthesis. 2000 (14): 1979–2000. doi:10.1055/s-2000-8715.
- ^ "Benefits of Using a Non-Chlorine Shock Oxidizer Powered by DuPont Oxone" Dupont.com Archived 2011-07-15 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed July 2011.
- ^ "How to accurately measure chlorine levels in water shocked with potassium monopersulfate". Tech note from water test maker Taylor Technologies, originally appeared in Aquatics International. Accessed November 2011

