RG-59
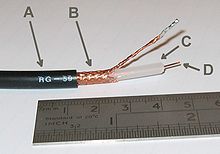
- Outer plastic sheath
- Copper braid shield
- Inner dielectric insulator
- Copper-plated core (sometimes solid core)
RG-59/U is a specific type of coaxial cable, often used for low-power video and RF signal connections. The cable has a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms, and a capacitance of around 20pF/ft (60pF/m).[1] The 75 ohm impedance matches a dipole antenna in free space. RG (for radio guide) was originally a unit indicator for bulk radio frequency (RF) cable in the U.S. military's Joint Electronics Type Designation System. The suffix /U means for general utility use. The number 59 was assigned sequentially. The RG unit indicator is no longer part of the JETDS system (MIL-STD-196E) and cable sold today under the RG-59 label does not necessarily meet military specifications.
RG-59 is often used at baseband video frequencies, such as composite video. It may also be used for broadcast frequencies, but its high-frequency losses are too high to allow its use over long distances; in these applications, RG-6 or RG-11 is used instead. In cases where the transmission distance is too long for these media, such options as UTP (unshielded twisted pair) or fiber optic can be used.
RG-59 coaxial cable is commonly packed with consumer equipment, such as VCRs or digital cable/satellite receivers. Manufacturers tend to include only RG-59 cables because it costs less than RG-6 does. However, given the short lengths provided (usually 4–6 ft or 1.2–1.8 m), this is generally sufficient for its typical use.
RG-59 is frequently used to synchronize two digital audio devices, such as ADAT optical devices. This is called word clock.
The higher breakdown voltage of RG-59 allows for higher voltage use in scientific experiments.
See also
- BNC connector
- Coaxial cable
- RG-58 — A similar cable but with an impedance of 50 or 52 ohms
