SR-142948
Appearance
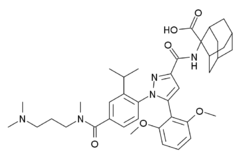 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C39H51N5O6 |
| Molar mass | 685.850 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
SR-142948 is a drug used in scientific research which is a non-peptide antagonist selective for the neurotensin receptors, although not selective between subtypes.[1] It has been used to study the role of neurotensin in the regulation of dopamine receptor activity[2][3][4][5] and glutamate signalling in the brain,[6][7] and in animal studies SR-142948 blocked the effects of stimulant drugs,[8] including MDMA.[9]
References
- ^ Nalivaiko E; Michaud JC; Soubrié P; Le Fur G (October 1998). "Electrophysiological evidence for putative subtypes of neurotensin receptors in guinea-pig mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons". Neuroscience. 86 (3): 799–811. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(98)00084-0. PMID 9692718.
- ^ Alonso R; Gnanadicom H; Fréchin N; Fournier M; Le Fur G; Soubrié P (March 1999). "Blockade of neurotensin receptors suppresses the dopamine D1/D2 synergism on immediate early gene expression in the rat brain". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 11 (3): 967–74. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00506.x. PMID 10103090.
- ^ Matsuyama S; Higashi H; Maeda H; Greengard P; Nishi A (April 2002). "Neurotensin regulates DARPP-32 thr34 phosphorylation in neostriatal neurons by activation of dopamine D1-type receptors". Journal of Neurochemistry. 81 (2): 325–34. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.00822.x. PMID 12064480.
- ^ Leonetti M; Brun P; Sotty F; Steinberg R; Soubrié P; Bert L; Renaud B; Suaud-Chagny MF (June 2002). "The neurotensin receptor antagonist SR 142948A blocks the efflux of dopamine evoked in nucleus accumbens by neurotensin ejection into the ventral tegmental area". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 365 (6): 427–33. doi:10.1007/s00210-002-0574-6. PMID 12070755.
- ^ Panayi F; Colussi-Mas J; Lambás-Señas L; Renaud B; Scarna H; Bérod A (May 2005). "Endogenous neurotensin in the ventral tegmental area contributes to amphetamine behavioral sensitization". Neuropsychopharmacology. 30 (5): 871–9. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300638. PMID 15637639.
- ^ Matsuyama S; Fukui R; Higashi H; Nishi A (September 2003). "Regulation of DARPP-32 Thr75 phosphorylation by neurotensin in neostriatal neurons: involvement of glutamate signalling". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 18 (5): 1247–53. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02859.x. PMID 12956723.
- ^ Yin HH; Adermark L; Lovinger DM (January 2008). "Neurotensin reduces glutamatergic transmission in the dorsolateral striatum via retrograde endocannabinoid signaling". Neuropharmacology. 54 (1): 79–86. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.06.004. PMC 2697967. PMID 17675102.
- ^ Reynolds SM; Geisler S; Bérod A; Zahm DS (July 2006). "Neurotensin antagonist acutely and robustly attenuates locomotion that accompanies stimulation of a neurotensin-containing pathway from rostrobasal forebrain to the ventral tegmental area". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (1): 188–96. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04791.x. PMID 16882016.
- ^ Marie-Claire C; Palminteri S; Romualdi P; Noble F (June 2008). "Effects of the selective neurotensin antagonist SR 142948A on 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine-induced behaviours in mice". Neuropharmacology. 54 (7): 1107–11. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.03.001. PMID 18410947.
Template:Neuropeptide agonists and antagonists
