Scalding
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (November 2014) |
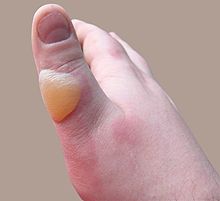
Scalding (from the Latin word calidus, meaning hot[1]) is a form of thermal burn resulted from heated fluids such as boiling water or steam. Most scalds are considered first or second degree burns, but third degree burns can result, especially with prolonged contact.
Causes
Most scalds result from exposure to high-temperature water such as tap water in baths and showers or cooking water boiled for the preparation of foods. Another common cause of scalds is spilled hot drinks, such as coffee. Scalds are typically far more severe when caused by steam, because it has absorbed a great amount of latent heat, and is therefore far more effective at heating objects.
Scalds are generally more common in children, especially from the accidental spilling of hot liquids.
Treatment
Applying first aid for scalds is the same as for burns. First, the site of the injury should be removed from the source of heat, to prevent further scalding. If the burn is at least second degree, remove any jewelry or clothing from the site, unless it is already stuck to the skin. Cool the scald for about 20 minutes with cool or lukewarm water, such as water from a tap.[2]
With second-degree burns, blisters will form, but should never be popped, as it only increases chances of infection. With third-degree burns, it is best to wrap the injury very loosely to keep it clean, and seek expert medical attention.
Treatments to avoid
Ice should be avoided, as it can do further damage to area around the injury,[3] as should butter, toothpaste, and specialized creams.
Scalding in food production
Beef, poultry and pork

The carcasses of beef, poultry and pigs are commonly scalded after slaughter to facilitate the removal of feathers and hair. Methods including immersion in tanks of hot water or spraying with steam. The scalding may either be hard or soft in which the temperature or duration is varied. A hard scald of 58 °C (136.4 °F) for 2.5 minutes will remove the epidermis of poultry, and this is commonly used for carcasses that will be frozen so that their appearance is white and attractive.[4]
Scalding milk
Scalded milk is milk that has been heated to 82 °C (180 °F).[5] At this temperature, bacteria are killed, enzymes in the milk are destroyed, and many of the proteins are denatured.
In cooking, milk is typically scalded to increase its temperature, or to change the consistency or other cooking interactions due to the denaturing of proteins.
Recipes that call for scalded milk include café au lait, baked milk, and ryazhenka. Scalded milk is used in yogurt to make the proteins unfold, and to make sure that all organisms that could out-compete the yogurt culture's bacteria are killed.
Milk is both scalded and also cooled in many recipes, such as for bread and other yeast doughs, as pasteurization does not kill all bacteria, and the wild yeasts that may also be present can alter the texture and flavor. In addition, scalding milk improves the rise due to inhibition of bread rise by certain undenatured milk proteins.[6]
References
- ^ Mosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary, Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book Inc., 1994, p. 1395.
- ^ Burns and scalds - NHS Choices, Treating Burns and Scalds.
- ^ The Dos and Don'ts of Burns, What's the best way to treat a burn?
- ^ "Scalding", Microbial ecology of food commodities, 2005, p. 113, ISBN 978-0-306-48675-3.
- ^ Rombauer, Irma and Marion Rombauer Becker. The Joy of Cooking. New York: Signet, 1973. ISBN 0-451-07166-2.
- ^ Corriher, Shirley. CookWise: The Hows & Whys of Successful Cooking, The Secrets of Cooking Revealed. New York: William Morrow Cookbooks, 1997. ISBN 978-0-688-10229-6.
External Links
- Burns at MedlinePlus
