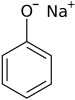
Sodium phenoxide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sodium phenolate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.862 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5NaO | |
| Molar mass | 116.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium phenoxide is an organic compound with the formula NaOC6H5. This white solid is the conjugate base of phenol. It is used as a precursor to many other organic compounds, such as aryl ethers.
Synthesis and structure
Most commonly, solutions of sodium phenoxide are produced by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide.[1] Anhydrous derivatives can be prepared from phenol and sodium:
- Na + HOC6H5 → NaOC6H5 + 1/2 H2
Like other sodium alkoxides, crystalline sodium phenolate adopts a complex structures involving multiple Na-O bonds. Solvent-free material is polymeric, each Na center being bound to three oxygen ligands as well as the phenyl ring. Adducts of sodium phenoxide are molecular, such as the cubane [NaOPh]4(HMPA)4.[2]
Sodium phenoxide is produced by the "alkaline fusion" of benzenesulfonic acid, whereby the sulfonate groups is displaced by hydroxide:
- C6H5SO3Na + 2 NaOH → C6H5ONa + Na2SO3
This route once was the principal industrial route to phenol.
Reactions
Sodium phenoxide is a moderately strong base. At low pH's gives phenol:[3]
- PhOH ⇌ PhO− + H+ (K = 10−10)
Sodium phenoxide can be used to prepare phenyl ethers and metal phenolates:[1]
- NaOC6H5 + RBr → ROC6H5 + NaBr
References
- ^ a b C. S. Marvel and A. L. Tanenbaum "γ-Phenoxypropyl Bromide" Org. Synth. 1929, vol. 9, pp. 72.
- ^ Michael Kunert, Eckhard Dinjus, Maria Nauck, Joachim Sieler "Structure and Reactivity of Sodium Phenoxide - Following the Course of the Kolbe-Schmitt Reaction" Chemische Berichte 1997 Volume 130, Issue 10, pages 1461–1465. doi:10.1002/cber.19971301017
- ^ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
External links
![]() Media related to Sodium phenoxide at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sodium phenoxide at Wikimedia Commons


