Spence (tugboat)

| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Owner | TransAtlantic Lines[1] |
| Builder | Bollinger Machine Shop & Ship Yard Inc.[1] |
| Completed | 1 September 1974[1] |
| Identification |
|
| General characteristics | |
| Tonnage | 189 GT[1] |
| Length | 27.78 m (91.1 ft)[1] |
| Beam | 7.92 m (26.0 ft)[1] |
| Depth | 3.50 m (11.5 ft) molded depth[1] |
| Capacity | 129 DWT[1] |

| |
| Name |
|
| Owner | TransAtlantic Lines[3] |
| Builder | Misener Industries Inc.[3] |
| Completed | 1 September 1983[3] |
| General characteristics | |
| Tonnage | 2,529 GT[3] |
| Length | 76.2 m (250 ft)[3] |
| Beam | 21.95 m (72.0 ft)[3] |
| Depth | 4.88 m (16.0 ft) molded depth[3] |
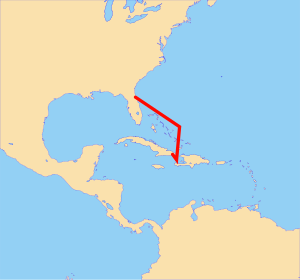 Approximate route of the tugboat Spence and barge Guantanamo Bay Express
| |
Tugboat Spence and her barge Guantanamo Bay Express are owned by the American shipping company TransAtlantic Lines LLC. Together, they make a twice-monthly trip between Naval Station Mayport; near Jacksonville, Florida; and Naval Station Guantanamo Bay in Cuba.[4] Each leg of the trip takes approximately 4+1⁄2 days and covers approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 km). Unloading the barge can take up to five days.
History
On 13 June 2001, TransAtlantic Lines won a contract with an estimated cumulative value of $16,738,001 for dedicated ocean liner cargo service to US military installations in Guantanamo Bay, Cuba.[5] This contract extended until 30 June 2004.[5] The government announced the requirements for the charter on the World Wide Web on 4 December 2000, and seven bids were received.[5] Military Traffic and Management Command in Alexandria, Virginia, is the contracting activity.[5]
On 14 February 2002 the Department of Defense announced an award of contract DAMT01-02-D-0025, a $17,923,770 firm-fixed-price contract for the tug and barge combination.[6] The contract required provision of international cargo transportation services using ocean common or contract carrier offering regularly scheduled commercial liner service for requirements that may arise in any part of the world.[6] Contract requirements included provision of dedicated ocean, inter-modal, and related transportation services primarily between the Continental United States and Naval Station Guantanamo Bay, Cuba.[6] There were seven bids solicited on 26 September 2001, and seven bids received.[6] The Military Traffic Management Command located in Alexandria, Virginia was the contracting activity.[6]
On 11 November 2004, while leaving Mayport, Florida en route to Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, the tow wires connecting the tug and barge parted, causing the barge to run aground.[7] At the time of the accident, the vessels were experiencing 30-knot (56 km/h; 35 mph) wind gusts and 12-foot (3.7 m) seas.[7] Extensive bottom damage and breaches to all port side voids were reported.[7] The barge was refloated and delivered to the owners the following day.[7] The vessels were owned by Pac-Atlantic Marine Leasing, LCC at the time.[8]
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Spence (7420037)". ABS Record. American Bureau of Shipping.[dead link]
- ^ a b "Spence (130659)". Port State Information Exchange. United States Coast Guard. Retrieved 4 May 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Guantanamo Bay Express (8305329)". ABS Record. American Bureau of Shipping.[dead link]
- ^ Morris, Joseph A.; Pisano, Chris S. (5 July 2002). "Living and dying by the barge" (PDF). The Wire. pp. 6, 7. Archived from the original (pdf) on 9 May 2009. Retrieved 26 September 2007.
- ^ a b c d US Department of Defense (14 June 2001). "Contract". DefenseLink (Press release). US Department of Defense. 268-01.
- ^ a b c d e US Department of Defense (14 February 2002). "Contract". DefenseLink (Press release). US Department of Defense. 072-02.
- ^ a b c d "Titan Beats Time Before Barge Breaks Up". Maritime Journal. Mercator Media. 1 January 2005. Retrieved 26 September 2007.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)[dead link] - ^ "Guantanamo bound barge grounds". MarineLog. 12 November 2004.
- "Guantanamo Bay Express (218595)". Port State Information Exchange. United States Coast Guard. Retrieved 4 May 2008.
