Telosentis exiguus
| Telosentis exiguus | |
|---|---|
| |
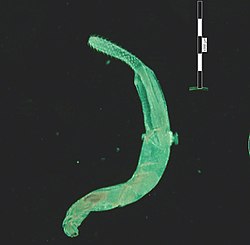
| Telosentis exiguus from the Big-scale sand smelt from France | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | T. exiguus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Telosentis exiguus (von Linstow, 1901)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Telosentis exiguus is a widespread intestinal parasitic worm. Its hosts are marine and brackish water fish of the Mediterranean basin.
Characteristics

T. exiguus' tegument is covered with spines in anterior and posterior parts. Its cerebral ganglion located in central part of the proboscis sac, sometime moved to anterior region. Its proboscis is cylindrical or club-shaped, armed with 12 longitudal rows of hooks of same type; the smaller hooks are in the posterior region of proboscis, larger is in its central part. The roots of the hooks have long forward-facing appendixes.[1]
Range
This species is found in the Mediterranean Sea[2] (near the coasts of France and Italy), in the Adriatic Sea (Italy, Montenegro), the Sea of Marmara,[3] the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov (near the coasts of Ukraine).
Hosts
T. exiguus is able to thrive in a variety hosts. It has been found as an intestinal parasite in anchovies, sand-smelts, shads, garfishes, eels, sticklebacks, pipe-fishes, grass gobies, some other gobies, blennies, and wrasses.
Life cycle
In the Black Sea the intermediate hosts of this acanthocephalan is the amphipod Apherusa bispinosa,[4] in the coelom of which the cystacanthes are located. Fish are infested by feeding on amphipods infected with larvae.
References
- ^ Kvach Y., Sasal P. (2010) Telosentis exiguus (von Linstow, 1901) (Palaeacanthocephala: Illiosentidae), a generalist parasite of fishes in the Mediterranean basin. Systematic Parasitology, 76(1): 9-18.[1]
- ^ Golvan Y.J. (1969) Systématique des acanthocéphales (Acanthocephala Rudolphi 1801). Première partie. L’ordre de Palaeacanthocephala Meyer 1931. Premier fascicule. La superfamille de Echinorhynchoidea (Cobbold 1876) Golvan et Houin 1963. Mémoires du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle (Série A), 57, 1–373.
- ^ Oğuz M.C. (1991) Ekınlı Lagnünüde yakalanan dere pısısı baliklari (Pleuronectus flesus luscus L. 1758) üzerıne parasıtolojık bır araştirma. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 15: 150–163.
- ^ Belofastova I.P., Grintsov V.A. (2003) On the Find of Acantellae of the Acanthocephalan Telosentis exiguus in Apherusa bispinosa (Amphipoda, Calliopiidae) in the Black Sea. Vestnik Zoologii, 37(4): 57–59. (in Russian)[2]
