Thectardis
| Thectardis Temporal range: Ediacaran, 565-555 Ma
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Artist's reconstruction | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia (?)
|
| Phylum: | |
| Genus: | Thectardis Clapham et al. 2004
|
| Species: | T. avalonensis Clapham et al. 2004
|
Thectardis avalonensis is a triangular-shaped member of the Ediacara biota, dating from 575 to 565 million years ago. The organism took the form of an elongated cone with a central depression, and its apex was anchored to the substrate.
Morphology
The fossils take the form of a triangle with a central depression, suggesting that the original organism was conical. The diameter to height ratio of the organism is roughly constant in each location at 1 to 3 in the younger beds, and from 1 to 2.5 in the older beds. The constant ratio suggests that it grew by adding to its body at the base of the cone. The triangle has a raised margin about a quarter of the width of the triangle. The interior either is blank, depressed, or has some vague transverse markings. The impression occurs in the upper bed rather than the lower surface.
Occurrence
205 specimens of Thectardis are known, from two bedding surfaces, separated by 2 km and 10 million years at Mistaken Point, Newfoundland.
Thectardis bearing bedding surfaces also contain Charnia and Ivesheadia.
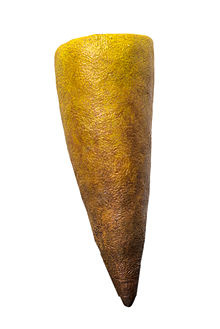
Ecology
Water currents knocked down the triangles in the same direction, and where they fall on top of other objects they flex over the top. When alive, the organism probably stuck to the microbial mats that bound the Ediacaran sea floor, standing on their tips like a pin in a pin cushion, so that the organism would have resembled an inverted cone. They probably fed on suspended particles. As there is no evidence for a holdfast anchoring them to the sea floor, it remains a matter of speculation how they were attached.
Etymology
The generic name Thectardis is derived from the Greek thektos, sharp-pointed, and ardis, arrow-point. The specific name derives from the Avalon Peninsula, where it was found. Thus, Thectardis avalonensis translates as "sharp arrow-point of Avalon (Peninsula)."
See also
References
- Clapham, Matthew E.; Narbonne, Guy M.; Gehling, James G.; Greentree, Carolyn; Anderson, Michael M. (2004). "Thectardis avalonensis: A New Ediacaran Fossil from the Mistaken Point Biota, Newfoundland" (PDF). Journal of Paleontology. 78 (6): 1031–1036. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2004)078<1031:TAANEF>2.0.CO;2.
