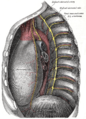
Thoracic ganglia
| Thoracic ganglia | |
|---|---|
 Lower half of right sympathetic cord. | |
| Details | |
| To | thoracic splanchnic nerves, stellate ganglion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglia thoracica |
| TA98 | A14.3.01.024 |
| TA2 | 6613 |
| FMA | 77577 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The thoracic ganglia are paravertebral ganglia. The thoracic portion of the sympathetic trunk typically has 12 thoracic ganglia. Emerging from the ganglia are thoracic splanchnic nerves (the cardiopulmonary, the greater, lesser, and least splanchnic nerves) that help provide sympathetic innervation to abdominal structures. The thoracic part of sympathetic trunk lies posterior to the costovertebral pleura and is hence not a content of the posterior mediastinum
Also, the ganglia of the thoracic sympathetic trunk have both white and gray rami communicantes. The white rami carry sympathetic fibers arising in the spinal cord into the sympathetic trunk.
Additional images
-
The thoracic aorta, viewed from the left side.
-
Sympathetic connections of the ciliary and superior cervical ganglia.