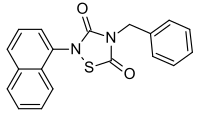
Tideglusib
Appearance
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H14N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 334.392 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Tideglusib (NP-12, NP031112) is a potent, selective and irreversible[1] small molecule non-ATP-competitive glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) inhibitor.
Potential applications
Tideglusib is under investigation for multiple applications:
- Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. As of 2017 it was undergoing Phase IIa[2] and IIb clinical trials.[3][4][5][6] The first trial to be published (in English) was Phase II and demonstrated that tideglusib was well tolerated, except for some moderate, asymptomatic, fully reversible increases in liver enzymes (≥2.5x ULN; where ULN=Upper Limit of Normal).[4]
- Tooth repair mechanisms that promotes dentine reinforcement of a sponge structure until the sponge biodegrades, leaving a solid dentine structure. In 2016 it was successfully trialled for permanently filling 0.14mm holes in mouse teeth.[7]
- Autism spectrum disorders in adolescents.
Furthermore, recent research has shown Tideglusib to be a promising treatment for Congenital/Juvenile-Onset Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy Type I, with Phase II clinical trials (under the aegis of AMO Pharmaceuticals) nearing completion.[8]
References
- ^ Domínguez, JM; Fuertes, A; Orozco, L; del Monte-Millán, M; Delgado, E; Medina, M (January 2012). "Evidence for Irreversible Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 by Tideglusib" (PDF). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (2): 893–904. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.306472. PMC 3256883. PMID 22102280.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Teodoro Del Ser (2010). "Phase IIa clinical trial on Alzheimer's disease with NP12, a GSK3 inhibitor". Alzheimer's & Dementia. 6 (4): S147. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2010.05.455.
- ^ Eldar-Finkelman, H; Martinez, A (2011). "GSK-3 Inhibitors: Preclinical and Clinical Focus on CNS". Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 4: 32. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2011.00032. PMC 3204427. PMID 22065134.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Del Ser, T; Steinwachs, KC; Gertz, HJ; Andrés, MV; Gómez-Carrillo, B; Medina, M; Vericat, JA; Redondo, P; et al. (2013). "Treatment of Alzheimer's disease with the GSK-3 inhibitor tideglusib: A pilot study". Journal of Alzheimer's disease. 33 (1): 205–15. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-120805. PMID 22936007.
- ^ "FDA Grants Fast Track Status to Tideglusib (ZentylorTM) for Progressive Supranuclear Palsy". PR Newswire Europe Including UK Disclose. 10 September 2010. Retrieved 11 August 2013.
- ^ Dominguez, JM; Fuertes, A; Orozco, L; Del Monte-Millan, M; Delgado, E; Medina, M (2011). "Evidence for Irreversible Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 by Tideglusib". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (2): 893–904. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.306472. PMC 3256883. PMID 22102280.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Gallagher, James (2017-01-09). "'Tooth repair drug' may replace fillings". BBC News. Retrieved 2017-01-09.
- ^ "AMO-2". AMO Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 9/21/2017.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
