Tivantinib
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ARQ197; ARQ-197 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.231.891 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
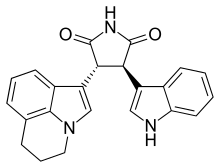
| Formula | C23H19N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 369.42 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Tivantinib (ARQ197; by Arqule, Inc.) is an experimental small molecule anti-cancer drug. It is a bisindolylmaleimide that binds to the dephosphorylated MET kinase in vitro. (MET is a growth factor receptor.) Tivantinib is being tested clinically as a highly selective MET inhibitor.[1] However, the mechanism of action of tivantinib is still unclear.[citation needed]
Tivantinib displays cytotoxic activity via molecular mechanisms that are independent from its ability to bind MET, notably tubulin binding, which likely underlies tivantinib cytotoxicity.[2]
Possible applications include non-small-cell lung carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and oesophageal cancer.[3]
In 2017, it was announced that a phase III clinical trial for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma had failed to meet the primary endpoint.[4][5]
References
- ^ "ArQule Announces Commencement of Phase 3 Clinical Trial with Tivantinib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Partner Kyowa Hakko Kirin in Japan - WSJ.com". online.wsj.com. Retrieved 2014-02-09.
- ^ Basilico, C; Pennacchietti, S; Vigna, E; Chiriaco, C; Arena, S; Bardelli, A; Valdembri, D; Serini, G; Michieli, P (2013). "Tivantinib (ARQ197) displays cytotoxic activity that is independent of its ability to bind MET". Clinical Cancer Research. 19 (9): 2381–92. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3459. PMID 23532890.
- ^ H. Spreitzer (24 November 2014). "Neue Wirkstoffe – Tivantinib". Österreichische Apothekerzeitung (in German) (24/2014): 30.
- ^ ArQule, Daiichi Sankyo Say Cancer Candidate Tivantinib Fails Phase III Trial. Feb 2017
- ^ https://www.arqule.com/pipeline/tivantinib-arq-197/
See also
