Trachyteuthis
| Trachyteuthis Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
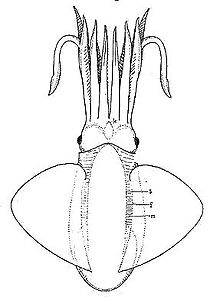
| |
| Reconstruction of Trachyteuthis hastiformis | |

| |
| Trachyteuthis hastiformis, Jura Museum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | Trachyteuthidinae Naef, 1921
|
| Genus: | Trachyteuthis Meyer, 1846
|
| Species | |
| |
Trachyteuthis is a genus of fossil teuthid, comprising four species: T. hastiformis, T. nusplingensis, T. teudopsiformis,[1] and T. covacevichi.[2]
Taxonomy
The taxonomic placement of Trachyteuthis is uncertain. Though often assigned to the order Vampyromorphida, the discovery of fossilised Trachyteuthis beaks in the Upper Jurassic limestone of Germany suggests a close phylogenetic relation to the Octopoda.[3][4] It is clear that it does at least belong in the Coleoidea.[1] It is thought to be very closely related to Teudopsis.[2]
Distribution
Fossils are scarce but have been reported from the Kimmeridge clay of the UK; the Solnhofen limestone of Germany, Jurassic deposits in Antarctica,[5] and Oxfordian deposits in Chile.[2]
History

First described in 1773 as the remnants of a fish, Trachyteuthis was considered comparable to a Sepia cuttlebone by Rüppell in 1829. A separate genus was erected for the material in 1846 by Meyer.[1] English material discovered in 1855 was termed Coccoteuthis latipinnis; this was later synonymised with the identical Solnhofen deposits. A 2007 survey of museum collection established that there were ground for the erection of three species within the genus.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d
Fuchs, D.; Engeser, T.; Keupp, H. (2007). "Gladius shape variation in coleoid cephalopod Trachyteuthis from the Upper Jurassic Nusplingen and Solnhofen Plattenkalks" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 52 (3): 575–589.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c
Fuchs, D.; Schultze, H.-P. (2008). "Trachyteuthis covacevichin. Sp., a Late Jurassic Palaeopacific coleoid cephalopod". Fossil Record. 11 (1): 39. doi:10.1002/mmng.200700012.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^
Klug, C.; Schweigert, G.; Dietl, G.; Fuchs, D. (2005). "Coleoid beaks from the nusplingen Lithographic Limestone (Upper Kimmeridgian, SW Germany)". Lethaia. 38 (3): 173. doi:10.1080/00241160510013303.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^
Fischer, J.; Riou, B. (2002). "Vampyronassa rhodanica nov. gen. nov sp., vampyromorphe (Cephalopoda, Coleoidea) du Callovien inférieur de la Voulte-sur-Rhône (Ardèche, France)". Annales de Paléontologie. 88 (1): 1. doi:10.1016/S0753-3969(02)01037-6.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Doyle, P. (1991). "Teuthid cephalopods from the Upper Jurassic of Antarctica" (PDF). Palaeontology. 34 (1): 169–178.
