Tseytin transformation
The Tseitin transformation takes as input an arbitrary combinatorial logic circuit and produces a boolean formula in conjunctive normal form (CNF), which can be solved by a CNF-SAT solver. The length of the formula is linear in the size of the circuit. Input vectors that make the circuit output "true" are in 1-to-1 correspondence with assignments that satisfy the formula. This reduces the problem of circuit satisfiability on any circuit (including any formula) to the satisfiability problem on 3-CNF formulas.
Motivation
The naive approach is to write the circuit as a Boolean expression, and use De Morgan's law and the distributive property to convert it to CNF. However, this can result in an exponential increase in equation size. The Tseitin transformation outputs a formula whose size has grown linearly relative to the input circuit's.
Approach
The output equation is the constant 1 set equal to an expression. This expression is a conjunction of sub-expressions, where the satisfaction of each sub-expression enforces the proper operation of a single gate in the input circuit. The satisfaction of the entire output expression thus enforces that the entire input circuit is operating properly.
For each gate, a new variable representing its output is introduced. A small pre-calculated CNF expression that relates the inputs and outputs is appended (via the "and" operation) to the output expression. Note that inputs to these gates can be either the original literals or the introduced variables representing outputs of sub-gates.
Though the output expression contains more variables than the input, it remains equisatisfiable, meaning that it is satisfiable if, and only if, the original input equation is satisfiable. When a satisfying assignment of variables is found, those assignments for the introduced variables can simply be discarded.
A final clause is appended with a single literal: the final gate's output variable. If this literal is complemented, then the satisfaction of this clause enforces the output expression's to false; otherwise the expression is forced true.
Gate Sub-expressions
Listed is some of the possible sub-expressions that can be created for various logic gates.
| Type | Operation | CNF Sub-expression |
|---|---|---|
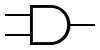 AND AND
|
||
 NAND NAND
|
||
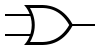 OR OR
|
||
 NOR NOR
|
||
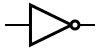 NOT NOT
|
||
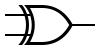 XOR XOR
|
Examples
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (March 2013) |
Simple combinatorial logic
The following circuit returns true when at least some of its inputs are true, but not more than two at a time. It implements the equation . A variable is introduced for each gates' output; here each is marked in red:

Notice that the output of the inverter with as an input has two variables introduced. While this is redundant, it does not affect the equisatisfiability of the resulting equation. Now substitute each gate with its appropriate CNF sub-expression:
| gate | CNF sub-expression |
|---|---|
The final output variable is so to enforce that the output of this circuit be true, one final simple clause is appended:
. Combining these equations results in the final instance of SAT:
|
One possible satisfying assignment of these variables is:
| variable | value |
|---|---|
| gate2 | 0 |
| gate3 | 1 |
| gate1 | 1 |
| gate6 | 1 |
| gate7 | 0 |
| gate4 | 0 |
| gate5 | 1 |
| gate8 | 1 |
| x2 | 0 |
| x3 | 1 |
| x1 | 0 |
The values of the introduced values are usually discarded, but they can be used to trace the logic path in the original circuit. Here, indeed meets the criteria for the original circuit to output true. To find a different answer, the clause can be appended and the SAT solver executed again.
Derivation
Presented is one possible derivation of the CNF sub-expression for some chosen gates:
OR Gate
The OR gate is operating properly when the following conditions hold:
- if the output C is true, then one (or both) of its inputs A, B is true
- if the output C is false, then both its inputs A, B are false
express these conditions as an expression that must be satisfied:
convert the implications to AND's and OR's
it's nearly CNF already; distribute the rightmost clause twice
associativity of conjunction
NOT Gate
The NOT gate is operating properly when its input and output oppose each other. That is:
- if the output C is true, the input A is false
- if the output C is false, the input A is true
express these conditions as an expression that must be satisfied:
NOR Gate
The NOR gate is operating properly when the following conditions hold:
- if the output C is true, then neither A or B are true
- if the output C is false, then at least one of A and B were true
express these conditions as an expression that must be satisfied:
References
- G.S. Tseitin: On the complexity of derivation in propositional calculus. In: Slisenko, A.O. (ed.) Studies in Constructive Mathematics and Mathematical Logic, Part II, Seminars in Mathematics, pp. 115–125. Steklov Mathematical Institute (1970). Translated from Russian: Zapiski Nauchnykh Seminarov LOMI 8 (1968), pp. 234–259.



















































