Xenotosuchus
| Xenotosuchus Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
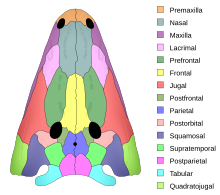
| |
| Xenotosuchus skull, showing the full complement of tetrapod skull roof bones | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Temnospondyli |
| Suborder: | †Stereospondyli |
| Clade: | †Capitosauria |
| Family: | †Mastodonsauridae |
| Genus: | †Xenotosuchus Morales and Shishkin, 2002 |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Xenotosuchus is an extinct genus of mastodonsaurid temnospondyl within the family Mastodonsauridae known from the Triassic of South Africa. The genus is based on a skull originally described as Parotosuchus, an animal which it resembled in general build and habit.[1]

Description
[edit]Like many mastodontosaurids, it was a large animal with a large head. Its amphibian life history meant that the distinct shape of the skull roof would change from a generalized tadpole-like skull type through to the distinct adult shape.[2] The head bones are covered in large pits and grooves, indicating extensive dermal armour on the head. Both the upper and lower jaw had tusks, those of the upper jaw being situated on a 2nd row of teeth on the vomer and palatine bone. Contrary to related forms like Mastodonsaurus, the tusks of the lower jaw were of moderate size and did not penetrate the premaxilla.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Morales, M.; Shishkin, M. A. (2002). "A Re-Assessment of Parotosuchus africanus (Broom), a Capitosauroid Temnospondyl Amphibian from the Triassic of South Africa". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 22 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2002)022[0001:araopa]2.0.co;2. JSTOR 4524188.
- ^ Damiani, R. (2008). "A giant skull of the temnospondyl Xenotosuchus africanus from the Middle Triassic of South Africa and its ontogenetic implications" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 53 (1): 75–84. doi:10.4202/app.2008.0104.


