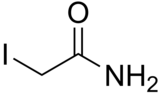
Iodoacetamide
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iodoacetamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.119 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H4INO | |
| Molar mass | 184.964 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow-brown crystals |
| Melting point | 94 °C (201 °F; 367 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2-Iodoacetamide is an alkylating agent used for peptide mapping purposes. Its actions are similar to those of iodoacetate. It is commonly used to bind covalently with the thiol group of cysteine so the protein cannot form disulfide bonds.[1][2] Also used in ubiquitin studies as an inhibitor of deubiquitinase enzymes (DUBs) because it alkylates the cysteine residues at the DUB active site. Like many other alkylating agents, iodoacetamide is highly toxic. In laboratory mice it has been shown to cause skin tumors and negatively affect reproductive ability. It may act as a human carcinogen, and may cause reproductive damage.[citation needed]
Peptidase inhibitor
Iodoacetamide is an irreversible inhibitor of all cysteine peptidases, with the mechanism of inhibition occurring from alkylation of the catalytic cysteine residue (see schematic). In comparison with its acid derivative, iodoacetate, iodoacetamide reacts substantially more slowly. This observation appears contradictory to standard chemical reactivity, however the presence of a favourable interaction between the positive imidazolium ion of the catalytic histidine and the negatively charged carboxyl-group of the iodoacetate is the reason for the increased relative activity of iodoacetamide.[3]

References
- ^ Smythe CV (1936). "The reactions of Iodoacetate and of Iodoacetamide with various Sulfhydryl groups, with Urease, and with Yeast preparations". J. Biol. Chem. 114 (3): 601–12.
- ^ Anson ML (1940). "The reactions of Iodine and Iodoacetamide with native Egg Albumin". J. Gen. Physiol. 23 (3): 321–31. doi:10.1085/jgp.23.3.321. PMC 2237930. PMID 19873158.
- ^ Polgar, L (1979). "Deuterium isotope effects on papain acylation. Evidence for lack of general base catalysis and for enzyme-leaving group. interaction". Eur. J. Biochem. 98 (2): 369–374. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13196.x. PMID 488108.
External links
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: Iodoacetamide

