Mad honey: Difference between revisions
SafariScribe (talk | contribs) Under discusioln Tags: New redirect Manual revert |
replacing redirect with new article Tag: Removed redirect |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Psychoactive type of honey}} |
|||
#redirect [[Grayanotoxin#Mad_honey_intoxication]] |
|||
[[File:Mad Honey.jpg|thumb|Mad honey]] |
|||
'''Mad honey''' is a type of [[honey]] that contains [[grayanotoxin]]s. The dark, reddish honey is produced from the nectar and pollen of ''[[Rhododendron]]'' species and has intoxicating effects. |
|||
Mad honey is produced principally in Turkey and Nepal, where it is used as a [[traditional medicine]] and [[recreational drug]]. In the [[Hindu Kush]] [[Himalayas|Himalayan]] range, it is produced by [[Apis laboriosa|Himalayan giant honey bees]] (''Apis laboriosa''). [[Honey hunting]] in Nepal has been traditionally performed by the [[Gurung people]]. The honey can also be found rarely in the eastern United States. |
|||
Historical accounts of mad honey are found in Ancient Greek texts. The Greek military leader [[Xenophon]] wrote in his ''[[Anabasis (Xenophon)|Anabasis]]'' about the effects of mad honey on soldiers in 401 BCE. In 65 BCE, during the [[Third Mithridatic War]], King [[Mithridates VI Eupator|Mithridates]] used mad honey as a biological weapon against Roman soldiers under General [[Pompey]]. During the 18th century, mad honey was imported to Europe where it was added to alcoholic beverages. |
|||
==Historical accounts== |
|||
Historical accounts of mad honey stretch back over two millennia. Early accounts by Ancient Greek historians noted the properties of the honey and its floral origins. There are a few accounts of its use as a biological weapon, usually as experienced by foraging soldiers.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
[[File:Zeus - a study in ancient religion (1914) (14782135992).jpg|thumb|upright=0.8|An [[amphora]] from [[Vulci]] depicting Laios, Keleos, Kerberos, and Aigolios being stung by bees in the [[Dictaean Cave]]]] |
|||
The 6th-century BCE ''Homeric Hymn to Hermes'', part of the ''[[Homeric Hymns]]'', may have indirectly alluded to the use of mad honey. The text refers to the ''melissai'' (bee-oracles) of Delphi's [[Mount Parnassus]] who could prophesy only after ingesting ''meli chloron'' (green honey), and may have been referring to [[Pythia]], the Oracle of Delphi.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Ott |first1=Jonathan |authorlink=Jonathan Ott|title=The Delphic Bee: Bees and Toxic Honeys as Pointers to Psychoactive and Other Medicinal Plants |journal=Economic Botany |date=1998 |volume=52 |issue=3 |pages=260–266 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/4256092 |issn=0013-0001}}</ref> |
|||
The Greek military leader and historian [[Xenophon]] wrote an account of a 401 BCE incident involving mad honey in his work ''[[Anabasis (Xenophon)|Anabasis]]'' about the expedition of the [[Ten Thousand (Greek)|Ten Thousand]]. In his account, he describes how Greek soldiers traveling near [[Trabzon]] (now part of Turkey) near the [[Black Sea]], ate mad honey and then became disoriented, suffering vomiting and diarrhea, and no longer able to stand. The soldiers recovered the following day.<ref name=Gunduz2013">{{cite book |last1=Gunduz |first1=Abdülkadir |last2=Ayaz |first2=Faik Ahmet |title=Honey in Traditional and Modern Medicine |date=2013 |publisher=CRC Press |isbn=978-1-4398-4016-0 |pages=360–376 |chapter-url=https://www.google.com.ar/books/edition/Honey_in_Traditional_and_Modern_Medicine/GXlFAQAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1&dq=%22mad%20honey%22&pg=PA360&printsec=frontcover |language=en |chapter=Mad Honey: The Reality}}</ref> |
|||
{{blockquote|The number of [[beehive|bee-hives]] was extraordinary, and all the soldiers that ate of the [[Honeycomb|combs]], lost their senses, vomited, and were affected with purging, and none of them were able to stand upright; such as had eaten only a little were like men greatly intoxicated, and such as had eaten much were like mad-men, and some like persons at the point of death.<br><br> |
|||
They lay upon the ground, in consequence, in great numbers, as if there had been a defeat; and there was general dejection. The next day no one of them was found dead; and they recovered their senses about the same hour that they had lost them on the preceding day; and on the third and fourth days they got up as if after having taken physic.<ref name="Big Think"/>}} |
|||
[[File:The Bee & The Rhododendron (18759766132).jpg|thumb|''[[Rhododendron]]'' species are a source of the [[grayanotoxin]]s that give mad honey its properties.]] |
|||
Roman and Greek authorities believed mad honey could cure [[insanity]].<ref name="Mayor1995"/> [[Aristotle]] noted that "at Trapezus honey from boxwood has a heavy scent, and they say that healthy men go mad, but that [[Epilepsy|epileptics]] are cured by immediately".<ref name="Silici2015"/> Roman naturalist [[Pliny the Elder]] referred to mad honey as ''meli mænomenon'' and was among the first to recognize that the toxicity was linked to [[oleander]], [[azalea]], and ''Rhododendron'' species.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
Historians also noted that mad honey's potency or intoxicating effects varied seasonally or cyclically. Pliny noted that the honey was most hazardous after wet springs, while Greek physician [[Pedanius Dioscorides]] noted that the honey was only dangerous in certain seasons.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
Mad honey was used as an early [[biological weapon]] in the [[Black Sea region]]. In 65 BCE, during the [[Third Mithridatic War]],<ref name="Turner2023"/><ref name=Gunduz2013"/> King [[Mithridates VI Eupator|Mithridates]] staged a strategic withdrawal from Roman soldiers under General [[Pompey]]. Possibly under the counsel of Greek botanist Kateuas, Mithridates had the withdrawing soldiers place combs of mad honey on their path. The Roman soldiers who ate the honey succumbed to mad honey intoxication and were slain.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Bryce |first1=Emma |title=The Strange History of 'Mad Honey' |url=https://modernfarmer.com/2014/09/strange-history-hallucinogenic-mad-honey/ |work=Modern Farmer |date=4 September 2014}}</ref> The Greek geographer [[Strabo]] described the incident as having wiped out three [[Maniple (military unit)|maniples]] of Romans, which could mean anywhere from 480 to 1,800 soldiers.<ref name="Mayor1995">{{cite journal |last1=Mayor |first1=Adrienne |authorlink=Adrienne Mayor |title=Mad Honey! |journal=[[Archaeology (magazine)|Archaeology]] |date=1995 |volume=48 |issue=6 |pages=32–40 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/41771162 |issn=0003-8113}}</ref><ref name="Turner2023">{{cite journal |last1=Turner |first1=Matthew D |title=Mad Honey and the Poisoner King: A Case of Mass Grayanotoxin Poisoning in the Roman Military |journal=Cureus |date=29 April 2023 |doi=10.7759/cureus.38289 |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10226383/}}</ref> |
|||
Other incidents of honey poisonings may have been caused by mad honey. In 946, allies of Queen [[Olga of Kyiv]] sent several tons of fermented honey to her Russian foes. 5,000 Russians were massacred as they lay in a stupor.<ref name="Mayor1995"/><ref name="HSW">{{cite news |title=Ridiculous History: Ancient Armies Waged War With Hallucinogenic Honey |url=https://history.howstuffworks.com/historical-events/history-hallucinogenic-mad-honey-warfare.htm |work=HowStuffWorks |date=27 February 2017 |language=en-us}}</ref> Later in 1489, in the same region, [[Tatars]] consumed casks of mead that had been left in an abandoned camp. 10,000 of the Tatars were slaughtered by Russians.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
During the 18th century, around 25 tons of mad honey were exported from the Black Sea Region to Europe every year.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> It was known then in France as ''miel fou'' (crazy honey) and was added to beer and other alcoholic drinks to give them extra potency.<ref name="McKernan2020"/><ref name="Assimon-2012"/><ref name="Mayor1995"/> American botanist [[Benjamin Smith Barton]] observed that [[beekeeper]]s in [[Pennsylvania]] became intoxicated by mad honey. They added the honey to liquor and sold the concoction in [[New Jersey]] as an elixir they named 'metheglin'. Barton noted that the inebriation began pleasantly, but could suddenly turn "ferocious".<ref name="Mayor1995"/> Former [[Confederate States of America|Confederate]] surgeon J. Grammer described in 1875 in ''Gleanings in Bee Culture'' that there were several incidents with soldiers from the South involving mad honey intoxication.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
The chemical compound andromedotoxin ([[grayanotoxin I]]) was isolated from Trabzon honey by German scientist P.C. Plugge in 1891.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> The 1929 edition of the ''[[Encyclopædia Britannica]]'' dismissed the notion of poison honey as described in Greek and Roman texts, concluding that "in all likelihood the symptoms described by these old writers were due to overeating" or that the honey had been eaten on empty stomachs.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
<!--In 2022, Balkiz,<ref>{{cite news |last1=Paúl |first1=María Luisa |title=A bear cub got high on hallucinogenic ‘mad honey’ — and there’s video |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2022/08/15/bear-high-hallucinogenic-honey-turkey/ |work=Washington Post |date=15 August 2022}}</ref> a bear cub in a national park in Turkey's [[Düzce Province]] suffering from mad honey poisoning was rescued by park rangers and treated.<ref>{{cite news |title=High on ‘mad honey’: intoxicated brown bear cub rescued in Turkey |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/aug/11/high-on-mad-honey-intoxicated-brown-bear-cub-rescued-in-turkey |work=The Guardian |date=11 August 2022}}</ref> --> |
|||
==Prevalence and harvesting== |
|||
[[File:ApisLaboriosa1.jpg|thumb|Mad honey is Nepal is typically produced by ''[[Apis laboriosa]]'' bees]] |
|||
''[[Rhododendron]]'' species and other plants in the family [[Ericaceae]] produce [[grayanotoxin]]s. Honey made from the [[nectar]] contains [[pollen]] from these plants as well as the grayanotoxins.<ref name="Jansen-2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Jansen SA, Kleerekooper I, Hofman ZL, Kappen IF, Stary-Weinzinger A, van der Heyden MA | title = Grayanotoxin poisoning: 'mad honey disease' and beyond | journal = Cardiovascular Toxicology | volume = 12 | issue = 3 | pages = 208–15 | date = September 2012 | pmid = 22528814 | pmc = 3404272 | doi = 10.1007/s12012-012-9162-2 }}</ref><ref name="Assimon-2012"/> Mad honey is darker and redder than other honeys, and has a slightly bitter taste.<ref name="Big Think">{{cite web |last1=Johnson |first1=Stephen |title="Mad honey": The rare hallucinogen from the mountains of Nepal |url=https://bigthink.com/health/mad-honey/ |website=Big Think |date=26 December 2022}}</ref> Due to its reddish color, it is sometimes called '''rose of the forest honey'''.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Neumeier |first1=Elaine |title=Sweet Madness: One Honey of a Mysterious Tale |date=2016 |journal=The Witches' Almanac |issue=36 |isbn=978-1-881098-40-9 |pages=76–77 |url=https://www.google.com.ar/books/edition/The_Witches_Almanac_Issue_36_Spring_2017/Ts_kDAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1&dq=%22deli%20bal%22&pg=PA77&printsec=frontcover |language=en}}</ref> Mad honey is produced in specific world regions, notably the [[Black Sea Region]] of Turkey and [[Nepal]].<ref name="gunduz">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gunduz A, Şimşek P, Ayaz FA |title=Worldwide distribution and clinical characteristics of mad honey poisoning cases |journal=Central European Journal of Public Health |volume=31 |issue=1 |pages=69–73 |date=March 2023 |pmid=37086424 |doi=10.21101/cejph.a7501 |url=https://cejph.szu.cz/pdfs/cjp/2023/01/11.pdf}}</ref> |
|||
Small-scale producers of mad honey typically harvest honey from a small area or single [[Beehive|hive]], producing a honey containing a significant concentration of grayanotoxins. In contrast, large-scale honey production often mixes honey gathered from different locations, diluting the concentration of any contaminated honey.<ref name="Assimon-2012">{{Cite web|url=https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Food/FoodborneIllnessContaminants/UCM297627.pdf|title=Grayanotoxins. In: Bad Bug Book: Handbook of Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins|vauthors=Assimon SA|date=2012|publisher=US [[Food and Drug Administration]]|access-date=3 May 2018}}</ref> A [[Caucasus]] beekeeper noted in a 1929 article in ''Bee World'' that the potency of the honey could vary across a single honeycomb and that the most dangerous mad honey was produced at high elevations during dry spells.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
===In Turkey=== |
|||
In Turkey, mad honey is known as '''''deli bal''''' and is used as a recreational drug and traditional medicine. It is most commonly made from the nectar of ''Rhododendron luteum'' and ''[[Rhododendron ponticum]]'' in the [[Caucasus]] region.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2014/oct/01/mad-honey-hot-honey-mead-buzz|title=The buzz about 'mad honey', hot honey and mead | first = Jamie | last = Waters | name-list-style = vanc |date=1 October 2014|work=The Guardian}}</ref> Beekeepers in the [[Kaçkar Mountains]] have produced mad honey for centuries.<ref name="McKernan2020"/> |
|||
===In the Hindu Kush Himalayan region=== |
|||
[[File:Apis laboriosa in Sikkim (cropped).jpg|thumb|A honeycomb colony of ''Apis laboriosa'' on a vertical rockface in the Himalayas]] |
|||
Mad honey is produced in the foothills of the Himalayas by [[Apis laboriosa|Himalayan giant honey bees]] (''Apis laboriosa'').<ref name="McKernan2020">{{cite news |last1=McKernan |first1=Bethan |title=Creating a buzz: Turkish beekeepers risk life and limb to make mad honey |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/jan/16/creating-a-buzz-turkish-beekeepers-risk-life-and-limb-to-make-mad-honey |work=The Guardian |date=16 January 2020}}</ref> In southern Asia, ''Apis laboriosa'' nests are found mostly in the [[Hindu Kush]] [[Himalayas|Himalayan]] region.<ref name="Gregory2021"/> The bees produce mad honey in the spring when plants from the [[Ericaceae]] family such as rhododendrons are in bloom.<ref name="Gregory2021"/> |
|||
''Apis laboriosa'' nests consist of single, open combs with large bases reaching {{cvt|1.5|m}}. The hives are built on tree limbs or steep, southeast or southwest-facing rocky cliffsides, at elevations of {{cvt|1200-4000|m}}, often situated underneath overhanging ledges where they are protected from the elements.<ref name="Third Pole"/><ref name="Gregory2021">{{cite journal |last1=Gregory |first1=Michelle |last2=Jack |first2=Cameron |title=Himalayan Giant Honey Bee, Cliff Honey Bee (suggested common names) Apis laboriosa Smith (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Apidae): EENY-777/IN1348, 8/2021 |journal=EDIS |date=1 August 2021 |volume=2022 |issue=1 |doi=10.32473/edis-IN1348-2021 |url=https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/IN1348}}</ref> |
|||
====Honey gathering==== |
|||
In central Nepal and northern India, the [[Gurung people]] have traditionally [[Honey hunting|gathered the honey]] for centuries, scaling cliffsides to reach the hives. Residents collect the honey twice a year, once in late spring and once in the late fall.<ref>{{cite news |last=Caprara |first=David |title=Hunting for Hallucinogenic Honey in Nepal |url=https://www.vice.com/en/article/wdbz55/hunting-for-hallucinogenic-honey-in-nepal-v23n6 |work=Vice |date=14 September 2016 |language=en}}</ref> The honey hunters use rope ladders with wooden rungs to access the nests and set fires underneath to smoke out the bees.<ref name="Gregory2021"/> |
|||
''Apis laboriosa'' populations in Nepal have experienced dramatic declines due to [[overharvesting]], hydroelectric dam and road construction, and the loss of water sources.<ref name="Third Pole"/> Population decline is also attributed to [[deforestation]] and [[landslide]]s.<ref name="Gregory2021"/> In Nepal, there has been an annual 70% decline in honeybee populations in Himalayan cliffs.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Thapa |first1=Ratna |last2=Aryal |first2=Sunil |last3=Jung |first3=Chuleui |title=Beekeeping and Honey Hunting in Nepal: Current Status and Future Perspectives |journal=Asian Beekeeping in the 21st Century |date=2018 |pages=111–127 |doi=10.1007/978-981-10-8222-1_5 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325491378_Beekeeping_and_Honey_Hunting_in_Nepal_Current_Status_and_Future_Perspectives}}</ref> A specialist with the [[International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development]] reported in 2022 that there had been a decrease both in the number of cliffs that host bees and in the number of colonies each cliff supports. Recommendations for sustainable honey harvesting include leaving half of the newly formed combs undisturbed and only harvesting portions of the combs.<ref name="Third Pole">{{cite news |last1=Baral |first1=Nabin |title=Nepal’s honey hunters cling to traditions as bee numbers fall |url=https://www.thethirdpole.net/en/culture/nepal-honey-hunters-cling-to-traditions-as-bee-numbers-fall/ |work=The Third Pole |date=22 July 2022}}</ref> |
|||
===In other regions=== |
|||
Aside from Turkey and the Himalayas, mad honey is produced rarely in the United States. According to [[Texas A&M University|Texas A&M]] professor Vaughn Bryant, an expert on honey, mad honey is produced in the [[Appalachian Mountains]] in the Eastern U.S. when a late cold snap kills most flowers but not rhododendrons. Honeys produced from [[Kalmia latifolia|mountain laurel]] (''Kalmia latifolia'') and [[Kalmia angustifolia|sheep laurel]] (''Kalmia angustifolia'') also contain grayanotoxins and are potentially deadly if large quantities are eaten.<ref name="Texas">{{cite news |last1=Henton |first1=Lesley |title=Expert Gives The Buzz On Mad Honey |url=https://today.tamu.edu/2014/10/15/expert-gives-the-buzz-on-mad-honey/ |work=Texas A&M Today |date=15 October 2014}}</ref> |
|||
==Physiological effects== |
|||
[[File:Grayanotoxin I.svg|thumb|The chemical structure of grayanotoxin I]] |
|||
Consumption of mad honey can cause a poisonous reaction called grayanotoxin poisoning, mad honey disease, honey intoxication, or rhododendron poisoning.<ref name="Jansen-2012" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Demircan A, Keleş A, Bildik F, Aygencel G, Doğan NO, Gómez HF | title = Mad honey sex: therapeutic misadventures from an ancient biological weapon | journal = Annals of Emergency Medicine | volume = 54 | issue = 6 | pages = 824–9 | date = December 2009 | pmid = 19683834 | doi = 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2009.06.010 }}</ref> The honey is the most common cause of grayanotoxin poisoning.<ref name="Assimon-2012"/> |
|||
In humans and some other animals, grayanotoxins act on the central nervous system, binding to [[sodium ion channel]]s and preventing them from closing.<ref name="Silici2015"/> This results in low blood pressure ([[hypotension]]) and reduced heart rates ([[bradycardia]]). Corresponding effects include [[lightheadedness]], blurred vision, dizziness, and respiratory difficulty. In some cases, blood pressure may be reduced to potentially dangerous levels, causing nausea, fainting, seizures, [[arrhythmia]], [[atrioventricular block]]s, muscle paralysis, and unconsciousness.<ref name="McKernan2020"/><ref name="Silici2015"/><ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
The degree of mad honey intoxication depends on the quantity consumed as well as the concentration of grayanotoxins. It may act as a hypnotic, with milder symptoms including tingling sensations, numbness, dizziness, swooning, and giddiness. With stronger doses, the effects may include [[delirium]], [[vertigo]], nausea, psychedelic optical effects such as [[tunnel vision]] and whirling lights, hallucinations, and impaired speech where syllables and words are spoken out of sequence. The recovery time ranges from hours to days, but most symptoms typically subside after 12 hours.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
A 2015 systematic review of 1199 cases of mad honey intoxication found no reported deaths.<ref name="Silici2015">{{cite journal |last1=Silici |first1=Sibel |last2=Atayoglu |first2=A. Timucin |title=Mad honey intoxication: A systematic review on the 1199 cases |journal=Food and Chemical Toxicology |date=2015 |volume=86 |pages=282–290 |doi=10.1016/j.fct.2015.10.018 |url=https://www.academia.edu/download/103913748/j.fct.2015.10.01820230630-1-4l2ygu.pdf}}</ref> Treatments for mad honey poisoning include [[atropine]],<ref name="Silici2015"/> [[adrenaline]], and saline infusions.<ref name="McKernan2020"/> |
|||
Bees are not affected by grayanotoxins.<ref name="Texas"/> |
|||
==Use in traditional medicine== |
|||
Mad honey is most frequently produced and consumed in regions of [[Turkey]] and [[Nepal]] as a [[traditional medicine]] or [[recreational drug]].<ref name="gunduz">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gunduz A, Şimşek P, Ayaz FA |title=Worldwide distribution and clinical characteristics of mad honey poisoning cases |journal=Central European Journal of Public Health |volume=31 |issue=1 |pages=69–73 |date=March 2023 |pmid=37086424 |doi=10.21101/cejph.a7501 |url=https://cejph.szu.cz/pdfs/cjp/2023/01/11.pdf}}</ref><ref name="Sahin-2015">{{Cite journal|last=Sahin|first=Huseyin | name-list-style = vanc |date=18 April 2015|title=Grayanotoxin-III Detection and Antioxidant Activity of Mad Honey|journal=International Journal of Food Properties|volume=18|issue=12 |pages=2665–2674|doi=10.1080/10942912.2014.999866|s2cid=97859238 |doi-access=free}}</ref> It is used as a traditional medicine to treat sore throat, [[arthritis]], [[diabetes]], and [[hypertension]].<ref name="Big Think"/> In the Turkish Black Sea Region it is used to treat indigestion, abdominal pain, [[gastritis]], [[peptic ulcer]]s, and the flu.<ref name="Silici2015"/> |
|||
In the Caucasus, small amounts of Pontic azalea honey have been added to alcoholic drinks to amplify the intoxicating effect for centuries.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> In Turkey, a spoonful of mad honey is traditionally added to milk as a tonic.<ref name="Mayor1995"/> |
|||
Mad honey is also thought to help with [[erectile dysfunction]]<ref name="Big Think"/> and increase sexual performance.<ref name="Silici2015"/> Most cases of mad honey poisoning are experienced by middle-aged men.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Norton |first1=Amy |title="Mad" honey sends virility-seeking men to the ER |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE5BG49N/ |work=Reuters |date=17 December 2009}}</ref> |
|||
==Legality== |
|||
Mad honey was [[Drug policy of South Korea|banned in South Korea]] in 2005.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Ullah |first1=Sana |last2=Khan |first2=Shahid Ullah |last3=Saleh |first3=Tawfik A. |last4=Fahad |first4=Shah |title=Mad honey: uses, intoxicating/poisoning effects, diagnosis, and treatment |journal=RSC Advances |date=2018 |volume=8 |issue=33 |pages=18635–18646 |doi=10.1039/C8RA01924J}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
*[[Bees and toxic chemicals]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
*[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y_b2i_FvYPw Hallucinogen Honey Hunters - Hunting Mad Honey], documentary on YouTube |
|||
[[Category:Honey]] |
|||
[[Category:Deliriants]] |
|||
[[Category:Psychoactive drugs]] |
|||
[[Category:Foodborne illnesses]] |
|||
[[Category:Biological weapons]] |
|||
Revision as of 14:18, 7 April 2024

Mad honey is a type of honey that contains grayanotoxins. The dark, reddish honey is produced from the nectar and pollen of Rhododendron species and has intoxicating effects.
Mad honey is produced principally in Turkey and Nepal, where it is used as a traditional medicine and recreational drug. In the Hindu Kush Himalayan range, it is produced by Himalayan giant honey bees (Apis laboriosa). Honey hunting in Nepal has been traditionally performed by the Gurung people. The honey can also be found rarely in the eastern United States.
Historical accounts of mad honey are found in Ancient Greek texts. The Greek military leader Xenophon wrote in his Anabasis about the effects of mad honey on soldiers in 401 BCE. In 65 BCE, during the Third Mithridatic War, King Mithridates used mad honey as a biological weapon against Roman soldiers under General Pompey. During the 18th century, mad honey was imported to Europe where it was added to alcoholic beverages.
Historical accounts
Historical accounts of mad honey stretch back over two millennia. Early accounts by Ancient Greek historians noted the properties of the honey and its floral origins. There are a few accounts of its use as a biological weapon, usually as experienced by foraging soldiers.[1]

The 6th-century BCE Homeric Hymn to Hermes, part of the Homeric Hymns, may have indirectly alluded to the use of mad honey. The text refers to the melissai (bee-oracles) of Delphi's Mount Parnassus who could prophesy only after ingesting meli chloron (green honey), and may have been referring to Pythia, the Oracle of Delphi.[2]
The Greek military leader and historian Xenophon wrote an account of a 401 BCE incident involving mad honey in his work Anabasis about the expedition of the Ten Thousand. In his account, he describes how Greek soldiers traveling near Trabzon (now part of Turkey) near the Black Sea, ate mad honey and then became disoriented, suffering vomiting and diarrhea, and no longer able to stand. The soldiers recovered the following day.[3]
The number of bee-hives was extraordinary, and all the soldiers that ate of the combs, lost their senses, vomited, and were affected with purging, and none of them were able to stand upright; such as had eaten only a little were like men greatly intoxicated, and such as had eaten much were like mad-men, and some like persons at the point of death.
They lay upon the ground, in consequence, in great numbers, as if there had been a defeat; and there was general dejection. The next day no one of them was found dead; and they recovered their senses about the same hour that they had lost them on the preceding day; and on the third and fourth days they got up as if after having taken physic.[4]

Roman and Greek authorities believed mad honey could cure insanity.[1] Aristotle noted that "at Trapezus honey from boxwood has a heavy scent, and they say that healthy men go mad, but that epileptics are cured by immediately".[5] Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder referred to mad honey as meli mænomenon and was among the first to recognize that the toxicity was linked to oleander, azalea, and Rhododendron species.[1]
Historians also noted that mad honey's potency or intoxicating effects varied seasonally or cyclically. Pliny noted that the honey was most hazardous after wet springs, while Greek physician Pedanius Dioscorides noted that the honey was only dangerous in certain seasons.[1]
Mad honey was used as an early biological weapon in the Black Sea region. In 65 BCE, during the Third Mithridatic War,[6][3] King Mithridates staged a strategic withdrawal from Roman soldiers under General Pompey. Possibly under the counsel of Greek botanist Kateuas, Mithridates had the withdrawing soldiers place combs of mad honey on their path. The Roman soldiers who ate the honey succumbed to mad honey intoxication and were slain.[7] The Greek geographer Strabo described the incident as having wiped out three maniples of Romans, which could mean anywhere from 480 to 1,800 soldiers.[1][6]
Other incidents of honey poisonings may have been caused by mad honey. In 946, allies of Queen Olga of Kyiv sent several tons of fermented honey to her Russian foes. 5,000 Russians were massacred as they lay in a stupor.[1][8] Later in 1489, in the same region, Tatars consumed casks of mead that had been left in an abandoned camp. 10,000 of the Tatars were slaughtered by Russians.[1]
During the 18th century, around 25 tons of mad honey were exported from the Black Sea Region to Europe every year.[1] It was known then in France as miel fou (crazy honey) and was added to beer and other alcoholic drinks to give them extra potency.[9][10][1] American botanist Benjamin Smith Barton observed that beekeepers in Pennsylvania became intoxicated by mad honey. They added the honey to liquor and sold the concoction in New Jersey as an elixir they named 'metheglin'. Barton noted that the inebriation began pleasantly, but could suddenly turn "ferocious".[1] Former Confederate surgeon J. Grammer described in 1875 in Gleanings in Bee Culture that there were several incidents with soldiers from the South involving mad honey intoxication.[1]
The chemical compound andromedotoxin (grayanotoxin I) was isolated from Trabzon honey by German scientist P.C. Plugge in 1891.[1] The 1929 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica dismissed the notion of poison honey as described in Greek and Roman texts, concluding that "in all likelihood the symptoms described by these old writers were due to overeating" or that the honey had been eaten on empty stomachs.[1]
Prevalence and harvesting

Rhododendron species and other plants in the family Ericaceae produce grayanotoxins. Honey made from the nectar contains pollen from these plants as well as the grayanotoxins.[11][10] Mad honey is darker and redder than other honeys, and has a slightly bitter taste.[4] Due to its reddish color, it is sometimes called rose of the forest honey.[12] Mad honey is produced in specific world regions, notably the Black Sea Region of Turkey and Nepal.[13]
Small-scale producers of mad honey typically harvest honey from a small area or single hive, producing a honey containing a significant concentration of grayanotoxins. In contrast, large-scale honey production often mixes honey gathered from different locations, diluting the concentration of any contaminated honey.[10] A Caucasus beekeeper noted in a 1929 article in Bee World that the potency of the honey could vary across a single honeycomb and that the most dangerous mad honey was produced at high elevations during dry spells.[1]
In Turkey
In Turkey, mad honey is known as deli bal and is used as a recreational drug and traditional medicine. It is most commonly made from the nectar of Rhododendron luteum and Rhododendron ponticum in the Caucasus region.[14] Beekeepers in the Kaçkar Mountains have produced mad honey for centuries.[9]
In the Hindu Kush Himalayan region

Mad honey is produced in the foothills of the Himalayas by Himalayan giant honey bees (Apis laboriosa).[9] In southern Asia, Apis laboriosa nests are found mostly in the Hindu Kush Himalayan region.[15] The bees produce mad honey in the spring when plants from the Ericaceae family such as rhododendrons are in bloom.[15]
Apis laboriosa nests consist of single, open combs with large bases reaching 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in). The hives are built on tree limbs or steep, southeast or southwest-facing rocky cliffsides, at elevations of 1,200–4,000 m (3,900–13,100 ft), often situated underneath overhanging ledges where they are protected from the elements.[16][15]
Honey gathering
In central Nepal and northern India, the Gurung people have traditionally gathered the honey for centuries, scaling cliffsides to reach the hives. Residents collect the honey twice a year, once in late spring and once in the late fall.[17] The honey hunters use rope ladders with wooden rungs to access the nests and set fires underneath to smoke out the bees.[15]
Apis laboriosa populations in Nepal have experienced dramatic declines due to overharvesting, hydroelectric dam and road construction, and the loss of water sources.[16] Population decline is also attributed to deforestation and landslides.[15] In Nepal, there has been an annual 70% decline in honeybee populations in Himalayan cliffs.[18] A specialist with the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development reported in 2022 that there had been a decrease both in the number of cliffs that host bees and in the number of colonies each cliff supports. Recommendations for sustainable honey harvesting include leaving half of the newly formed combs undisturbed and only harvesting portions of the combs.[16]
In other regions
Aside from Turkey and the Himalayas, mad honey is produced rarely in the United States. According to Texas A&M professor Vaughn Bryant, an expert on honey, mad honey is produced in the Appalachian Mountains in the Eastern U.S. when a late cold snap kills most flowers but not rhododendrons. Honeys produced from mountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia) and sheep laurel (Kalmia angustifolia) also contain grayanotoxins and are potentially deadly if large quantities are eaten.[19]
Physiological effects
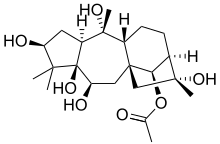
Consumption of mad honey can cause a poisonous reaction called grayanotoxin poisoning, mad honey disease, honey intoxication, or rhododendron poisoning.[11][20] The honey is the most common cause of grayanotoxin poisoning.[10]
In humans and some other animals, grayanotoxins act on the central nervous system, binding to sodium ion channels and preventing them from closing.[5] This results in low blood pressure (hypotension) and reduced heart rates (bradycardia). Corresponding effects include lightheadedness, blurred vision, dizziness, and respiratory difficulty. In some cases, blood pressure may be reduced to potentially dangerous levels, causing nausea, fainting, seizures, arrhythmia, atrioventricular blocks, muscle paralysis, and unconsciousness.[9][5][1]
The degree of mad honey intoxication depends on the quantity consumed as well as the concentration of grayanotoxins. It may act as a hypnotic, with milder symptoms including tingling sensations, numbness, dizziness, swooning, and giddiness. With stronger doses, the effects may include delirium, vertigo, nausea, psychedelic optical effects such as tunnel vision and whirling lights, hallucinations, and impaired speech where syllables and words are spoken out of sequence. The recovery time ranges from hours to days, but most symptoms typically subside after 12 hours.[1]
A 2015 systematic review of 1199 cases of mad honey intoxication found no reported deaths.[5] Treatments for mad honey poisoning include atropine,[5] adrenaline, and saline infusions.[9]
Bees are not affected by grayanotoxins.[19]
Use in traditional medicine
Mad honey is most frequently produced and consumed in regions of Turkey and Nepal as a traditional medicine or recreational drug.[13][21] It is used as a traditional medicine to treat sore throat, arthritis, diabetes, and hypertension.[4] In the Turkish Black Sea Region it is used to treat indigestion, abdominal pain, gastritis, peptic ulcers, and the flu.[5]
In the Caucasus, small amounts of Pontic azalea honey have been added to alcoholic drinks to amplify the intoxicating effect for centuries.[1] In Turkey, a spoonful of mad honey is traditionally added to milk as a tonic.[1]
Mad honey is also thought to help with erectile dysfunction[4] and increase sexual performance.[5] Most cases of mad honey poisoning are experienced by middle-aged men.[22]
Legality
Mad honey was banned in South Korea in 2005.[23]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Mayor, Adrienne (1995). "Mad Honey!". Archaeology. 48 (6): 32–40. ISSN 0003-8113.
- ^ Ott, Jonathan (1998). "The Delphic Bee: Bees and Toxic Honeys as Pointers to Psychoactive and Other Medicinal Plants". Economic Botany. 52 (3): 260–266. ISSN 0013-0001.
- ^ a b Gunduz, Abdülkadir; Ayaz, Faik Ahmet (2013). "Mad Honey: The Reality". Honey in Traditional and Modern Medicine. CRC Press. pp. 360–376. ISBN 978-1-4398-4016-0.
- ^ a b c d Johnson, Stephen (26 December 2022). ""Mad honey": The rare hallucinogen from the mountains of Nepal". Big Think.
- ^ a b c d e f g Silici, Sibel; Atayoglu, A. Timucin (2015). "Mad honey intoxication: A systematic review on the 1199 cases" (PDF). Food and Chemical Toxicology. 86: 282–290. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2015.10.018.
- ^ a b Turner, Matthew D (29 April 2023). "Mad Honey and the Poisoner King: A Case of Mass Grayanotoxin Poisoning in the Roman Military". Cureus. doi:10.7759/cureus.38289.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bryce, Emma (4 September 2014). "The Strange History of 'Mad Honey'". Modern Farmer.
- ^ "Ridiculous History: Ancient Armies Waged War With Hallucinogenic Honey". HowStuffWorks. 27 February 2017.
- ^ a b c d e McKernan, Bethan (16 January 2020). "Creating a buzz: Turkish beekeepers risk life and limb to make mad honey". The Guardian.
- ^ a b c d Assimon SA (2012). "Grayanotoxins. In: Bad Bug Book: Handbook of Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins" (PDF). US Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- ^ a b Jansen SA, Kleerekooper I, Hofman ZL, Kappen IF, Stary-Weinzinger A, van der Heyden MA (September 2012). "Grayanotoxin poisoning: 'mad honey disease' and beyond". Cardiovascular Toxicology. 12 (3): 208–15. doi:10.1007/s12012-012-9162-2. PMC 3404272. PMID 22528814.
- ^ Neumeier, Elaine (2016). "Sweet Madness: One Honey of a Mysterious Tale". The Witches' Almanac (36): 76–77. ISBN 978-1-881098-40-9.
- ^ a b Gunduz A, Şimşek P, Ayaz FA (March 2023). "Worldwide distribution and clinical characteristics of mad honey poisoning cases" (PDF). Central European Journal of Public Health. 31 (1): 69–73. doi:10.21101/cejph.a7501. PMID 37086424.
- ^ Waters J (1 October 2014). "The buzz about 'mad honey', hot honey and mead". The Guardian.
- ^ a b c d e Gregory, Michelle; Jack, Cameron (1 August 2021). "Himalayan Giant Honey Bee, Cliff Honey Bee (suggested common names) Apis laboriosa Smith (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Apidae): EENY-777/IN1348, 8/2021". EDIS. 2022 (1). doi:10.32473/edis-IN1348-2021.
- ^ a b c Baral, Nabin (22 July 2022). "Nepal's honey hunters cling to traditions as bee numbers fall". The Third Pole.
- ^ Caprara, David (14 September 2016). "Hunting for Hallucinogenic Honey in Nepal". Vice.
- ^ Thapa, Ratna; Aryal, Sunil; Jung, Chuleui (2018). "Beekeeping and Honey Hunting in Nepal: Current Status and Future Perspectives". Asian Beekeeping in the 21st Century: 111–127. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-8222-1_5.
- ^ a b Henton, Lesley (15 October 2014). "Expert Gives The Buzz On Mad Honey". Texas A&M Today.
- ^ Demircan A, Keleş A, Bildik F, Aygencel G, Doğan NO, Gómez HF (December 2009). "Mad honey sex: therapeutic misadventures from an ancient biological weapon". Annals of Emergency Medicine. 54 (6): 824–9. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2009.06.010. PMID 19683834.
- ^ Sahin H (18 April 2015). "Grayanotoxin-III Detection and Antioxidant Activity of Mad Honey". International Journal of Food Properties. 18 (12): 2665–2674. doi:10.1080/10942912.2014.999866. S2CID 97859238.
- ^ Norton, Amy (17 December 2009). ""Mad" honey sends virility-seeking men to the ER". Reuters.
- ^ Ullah, Sana; Khan, Shahid Ullah; Saleh, Tawfik A.; Fahad, Shah (2018). "Mad honey: uses, intoxicating/poisoning effects, diagnosis, and treatment". RSC Advances. 8 (33): 18635–18646. doi:10.1039/C8RA01924J.
External links
- Hallucinogen Honey Hunters - Hunting Mad Honey, documentary on YouTube
