3-Deoxyanthocyanidin
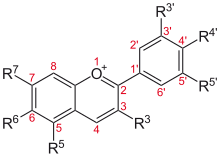

The 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins and their glycosides (3-deoxyanthocyanins or 3-DA) are molecules with an anthocyanidins backbone lacking an hydroxyl group at position 3 on the C-ring. This nomenclature is the inverse of that which is commonly used in flavonoids, where the hydroxy-group is assumed absent if it is not specified, e. g. flavan-3-ol, flavan-4-ol, flavan-3,4-ol and flavonol.
3-Deoxyanthocyanidins are yellow anthocyanidins that can be found primarily in ferns and mosses (Timberlake and Bridle, 1975, 1980),[1] in Sorghum bicolor[1][2] and in purple corn (Nakatani et al., 1979)[1] (maíz morado).
3-Deoxyanthocyanidins are reported to be stable to color loss due to change in pH.[3] Synthetic 3-deoxyanthocyanidins with a carboxylate group at carbon 4 show unusually stable colorant properties at pH 7.[1]
In Sorghum, the SbF3'H2 gene, encoding a flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase, seems to be expressed in pathogen-specific 3-deoxyanthocyanidin phytoalexins synthesis,[4] for example in Sorghum-Colletotrichum interactions.[5]
This category include:
References
- ^ a b c d Sweeny, James G.; Iacobucci, Guillermo A. (May 1, 1983). "Effect of substitution on the stability of 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in aqueous solutions". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 31 (3): 531–533. doi:10.1021/jf00117a017.
- ^ "Inclusions of flavonoid 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in Sorghum bicolor self-organize into spherical structures". Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology. 65 (4). Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved June 25, 2017.
- ^ Awika, Joseph M. (January 1, 2008). "Behavior of 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in the presence of phenolic copigments". Food Research International. 41 (5): 532–538. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2008.03.002.
- ^ Shih, Chun-Hat; Chu, Ivan K.; Yip, Wing Kin; Lo, Clive (October 1, 2006). "Differential Expression of Two Flavonoid 3′-Hydroxylase cDNAs Involved in Biosynthesis of Anthocyanin Pigments and 3-Deoxyanthocyanidin Phytoalexins in Sorghum". Plant and Cell Physiology. 47 (10): 1412–1419. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcl003. PMID 16943219.
- ^ "Biosynthesis and regulation of 3-deoxyanthocyanidin phytoalexins induced during Sorghum-Colletotrichum interaction: Heterologous expression in maize. Chopra, Surinder Gaffoor, Iffa Ibraheem, Farag". aspb.org. Archived from the original on July 25, 2011. Retrieved June 25, 2017.
