Invasion of Normandy by Philip II of France
| Invasion of Normandy by Philip II of France | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the First Hundred Years' War | |||||||||
 Phillip II's successful invasion of Normandy in 1204 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| Mercenary army | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | ||||||||
The Invasion of Normandy by Philip II of France were wars in Normandy from 1202 to 1204. The Angevin Empire fought the Kingdom of France as well as fighting off rebellions from nobles. Philip II of France conquered the Anglo-Angevin territories in Normandy, resulting in the Siege of Château Gaillard. The Normandy Campaigns ended in a victory for France when the Anglo-Angevin territory was greatly diminished.
Background
[edit]After Richard the Lionheart's death on 6 April 1199, there were two potential claimants to the Angevin throne: John, whose claim rested on being the sole surviving son of Henry II, and young Arthur of Brittany, who held a claim as the son of Geoffrey, and hence was Henry II's grandson.[2] Medieval law gave little guidance as to how the competing claims should be decided, with Norman law favouring John and Angevin law favouring Arthur; the matter rapidly became an open conflict.[3] John was supported by the bulk of the English and Norman nobility and was crowned king at Westminster, backed by his mother, Eleanor of Aquitaine. Arthur was supported by the majority of the Breton, Maine and Anjou nobles and received the support of Philip II, who remained committed to breaking up the Angevin territories on the continent.[4] With Arthur's army pressing up the Loire valley towards Angers and Philip's forces moving down the valley toward Tours, John's continental empire was in danger of being cut in two.[5]
Warfare in Normandy at the time was shaped by the defensive potential of castles and the increasing costs of conducting campaigns.[6] The Norman frontiers had limited natural defences but were heavily reinforced with castles, such as Château Gaillard, at strategic points, built and maintained at considerable expense.[7] It was difficult for a commander to advance far into fresh territory without having secured his lines of communication by capturing these fortifications, which slowed the progress of any attack.[8] Armies of the period could be formed from either feudal or mercenary forces.[9] Feudal levies could only be raised for a fixed length of time and proved an inflexible asset; mercenary forces, often called Brabançons after the Duchy of Brabant but actually recruited from across Northern Europe, could provide much greater military agility and operate all year long, but cost much more than equivalent feudal forces.[10]
Treaty of Le Goulet
[edit]
The new peace, the Treaty of Le Goulet, would only last for two years; war recommenced in the aftermath of John's decision in August 1200 to marry Isabella of Angoulême. To remarry, John first needed to abandon Isabel, Countess of Gloucester, his first wife; John accomplished this by arguing that he had failed to get the necessary papal permission to marry Isabel in the first place – as a cousin, John could not have legally wed her without this.[11] It remains unclear why John chose to marry Isabella of Angoulême. Contemporary chroniclers argued that John had fallen deeply in love with Isabella, and John may have been motivated by a sexual desire for an apparently beautiful, if rather young, girl.[11] On the other hand, the Angoumois lands that came with Isabella were strategically vital to John: by marrying Isabella, John was acquiring a key land route between Poitou and Gascony, which significantly strengthened his grip on Aquitaine.[12]
Unfortunately, Isabella had already been engaged to be married to Hugh IX of Lusignan, an important member of a key Poitou noble family and brother of Raoul, the count of Eu, who possessed lands along the sensitive eastern Normandy border.[11] Just as John stood to benefit strategically from marrying Isabella, so the marriage threatened the interests of the Lusignans, whose own lands currently provided the key route for royal goods and troops across Aquitaine.[13] Rather than negotiating some form of compensation, John treated Hugh "with contempt"; this resulted in a Lusignan uprising that was promptly crushed by John, who also intervened to suppress Raoul in Normandy.[12]
Although John was the count of Poitou and therefore the rightful feudal lord over the Lusignans, they could legitimately appeal to John's own feudal lord, Philip, in respect to decisions John took within his French lands.[12] Hugh did exactly this in 1201 and Philip summoned John to attend court in Paris in 1202, citing the Le Goulet treaty to strengthen his case.[12] John was unwilling to weaken his authority in western France in this way. He argued that he need not attend Philip's court because of his special status as the duke of Normandy, who was exempt by feudal tradition from being called to the French court.[12] Philip argued that he was summoning John not as the duke of Normandy, but as the count of Poitou, which carried no such special status.[12] When John still refused to come, Philip declared John in breach of his feudal responsibilities, reassigned all of John's lands that fell under the French crown to Arthur – with the exception of Normandy, which he took back for himself – and began a fresh war against John.[12]
Campaign
[edit]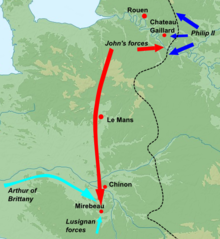
John initially adopted a defensive posture similar to that of 1199: avoiding open battle and carefully defending his key castles.[14] John's operations became more chaotic as the campaign progressed, and Philip began to make steady progress in the east.[14] John became aware in July that Arthur's forces were threatening his mother, Eleanor, at Mirebeau Castle. Accompanied by William de Roches, his seneschal in Anjou, he swung his mercenary army rapidly south to protect her.[14] His turn of speed caught Arthur by surprise and the entire rebel leadership were taken prisoner at the Battle of Mirebeau.[14] With his southern flank weakening, Philip was forced to withdraw in the east and turn south himself to contain John's army.[14]
John's position in France was considerably strengthened by the victory at Mirebeau. The king's treatment of his ally, William de Roches, and his new prisoners quickly undermined these gains. Despite de Roches being a powerful Anjou noble, John largely ignored him, causing considerable offence, whilst the king kept the rebel leaders in such bad conditions that twenty-two of them died.[15] At this time most of the regional nobility were closely linked through kinship, and this behaviour towards their relatives was regarded as unacceptable.[16] In the aftermath of these incidents, William de Roches and other of John's regional allies in Anjou and Brittany deserted him in favour of Philip, and Brittany rose in fresh revolt.[16] John's financial situation was tenuous: once factors such as the comparative military costs of materiel and soldiers were taken into account, Philip enjoyed a considerable, although not overwhelming, advantage of resources over John.[17][nb 1] In 1202–1203 Philip II maintained an army of 3,307 men on the Norman border. It was composed of 257 knights, 267 mounted sergeants, 80 mounted crossbowmen, 133 foot crossbowmen, 2,000 foot sergeants and 300 mercenaries under Cadoc. This army defended the border and was disbanded after Normandy had been conquered.[19]
Further desertions of John's local allies at the beginning of 1203 steadily reduced John's freedom to manoeuvre in the region.[16] He attempted to convince Pope Innocent III to intervene in the conflict, but the Pope's legate was unsuccessful.[16] As the situation became worse for John, he may have decided to have Arthur killed (though proof is lacking), to remove his potential rival and of undermining the rebel movement in Brittany.[16] Arthur had initially been imprisoned at Falaise and was then moved to Rouen. After this, Arthur's fate remains uncertain, but modern historians believe he was murdered by John.[16] The annals of Margam Abbey suggest that "John had captured Arthur and kept him alive in prison for some time in the castle of Rouen... when John was drunk he slew Arthur with his own hand and tying a heavy stone to the body cast it into the Seine."[20][nb 2] Rumours of Arthur's death further reduced support for John across the region.[21] Arthur's sister, Eleanor, who had also been captured at Mirebeau, was kept imprisoned by John for many years, albeit in relatively good conditions.[21]

In late 1203, John attempted to relieve Château Gaillard, although besieged by Philip was still guarding the eastern flank of Normandy.[22] John attempted a synchronised operation involving land-based and water-borne forces, considered by most historians today to have been imaginative in conception, but overly complex for forces of the period to have carried out successfully.[22] John's relief operation was blocked by Philip's forces, and John turned back to Brittany in an attempt to draw Philip away from eastern Normandy.[22] John successfully devastated much of Brittany, but did not deflect Philip's main thrust into the east of Normandy.[22] Opinions vary amongst historians as to the military skill shown by John during this campaign, with most recent historians arguing that his performance was passable, although not impressive.[11][nb 3] John's situation began to deteriorate rapidly. The eastern border region of Normandy had been extensively cultivated by Philip and his predecessors for several years, whilst Angevin authority in the south had been undermined by Richard's giving away of various key castles some years before.[24] His use of routier mercenaries in the central regions had rapidly eaten away his remaining support in this area too, which set the stage for a sudden collapse of Angevin power.[25][nb 4] John retreated across the Channel in December, sending orders for the establishment of a fresh defensive line to the west of Chateau Gaillard.[22] In March 1204, Gaillard fell. John's mother Eleanor died the following month.[22] This was not just a personal blow for John, but threatened to unravel the widespread Angevin alliances across the far south of France.[22] Philip moved south around the new defensive line and struck upwards at the heart of the Duchy, now facing little resistance.[22] By August, Philip had taken Normandy and advanced south to occupy Anjou and Poitou as well.[27] John's only remaining possession on the Continent was now the Duchy of Aquitaine.[28] Philip requested John to release Eleanor of Brittany, claiming that she was to be his daughter-in-law, but to no avail.
Aftermath
[edit]The struggle for Normandy was renewed a decade later. In 1214, when Pope Innocent III assembled an alliance of states against France, John registered in. In the Battle of Bouvines, the allied forces met those of Philip II. The French used couched lances to slay the Anglo-Flemish-German army's troops down to a formation of mercenary units.[citation needed]
Following this decisive defeat, John faced unrest in his kingdom, and was forced to sign Magna Carta to appease the English nobility.[citation needed]
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ This interpretation has been challenged by John Gillingham, whose minority view is that Richard, unlike John, successfully defended Normandy with a similar level of military resources.[18]
- ^ Although all modern biographers of John believe that he had his rival, Arthur, killed, the details of the Margam Abbey account can be questioned; as Frank McLynn points out, the Welsh monks appear "curiously well-informed" about the details of the incident in France.[20]
- ^ For positive interpretations of John's military skills in the campaign see Kate Norgate, who argues that John's attempt to relieve Château Gaillard was a "masterpiece of ingenuity"; Ralph Turner terms his performance as a general "capable"; Lewis Warren places the blame on John's inability to inspire loyalty amongst the local nobles, rather than a simple lack of military skill. Frank McLynn is more damning, describing the military aspects of the campaign as a "disastrous failure".[23]
- ^ David Carpenter provides an accessible summary of Power's argument on the collapse of Normandy.[26]
Notes
[edit]- ^ de l'histoire du moyen age, depuis la chute de l'empire romain d ... "Philippe-Auguste s'empara bientôt de tout le territoire anglais au nord de la Loire et Jean ne conserva qu'une partie de la Guienne et de la Gascogne."
- ^ Carpenter (2004), p.264.
- ^ Barlow, p.305.
- ^ Warren, p.53.
- ^ Warren, p.51.
- ^ Barrett, p.91.
- ^ Warren, pp.57–8; Barlow, p.280.
- ^ Warren, p.57.
- ^ Warren, p.59.
- ^ Huscroft, pp.169–70.
- ^ a b c d Turner, p.98.
- ^ a b c d e f g Turner, p.99.
- ^ Turner, pp.98–9.
- ^ a b c d e Turner, p.100.
- ^ Turner, pp.100–1.
- ^ a b c d e f Turner, p.101.
- ^ Holt (1984), p.94; Turner, p.94; Bradbury (1998), p.159; Moss, p.119.
- ^ Gillingham (1994), p.76.
- ^ Verbruggen 1997, p. 165.
- ^ a b McLynn, p.306.
- ^ a b Warren, p.83.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Turner, p.102.
- ^ Norgate (1902), p.96; Turner, p.98; Warren, p.88; McLynn, p.473.
- ^ Power, pp.135–6.
- ^ Power, p.135.
- ^ Carpenter (2004), pp.264–5.
- ^ Turner, pp.102–3.
- ^ Turner, p.103.
References
[edit]- Kohn, George Childs (31 October 2013). Dictionary of Wars. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-95494-9.
- F.M. Powicke, The Loss of Normandy (1189-1204)
- Verbruggen, J.F. (1997) [1954]. De Krijgskunst in West-Europa in de Middeleeuwen, IXe tot begin XIVe eeuw [The Art of Warfare in Western Europe During the Middle Ages: From the Eighth Century to 1340]. Translated by Willard, S. (2nd ed.). Suffolk: Boydell Press. ISBN 0-85115-630-4.
- Conflicts in 1202
- Conflicts in 1203
- Conflicts in 1204
- Anglo-French wars
- 1200s in Europe
- Military history of Normandy
- 1200s in France
- 13th-century military history of the Kingdom of England
- Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Europe
- Philip II of France
- John, King of England
- Annexations by France
