Carbon–nitrogen bond
A carbon–nitrogen bond is a covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen and is one of the most abundant bonds in organic chemistry and biochemistry.[1]
Nitrogen has five valence electrons and in simple amines it is trivalent, with the two remaining electrons forming a lone pair. Through that pair, nitrogen can form an additional bond to hydrogen making it tetravalent and with a positive charge in ammonium salts. Many nitrogen compounds can thus be potentially basic but its degree depends on the configuration: the nitrogen atom in amides is not basic due to delocalization of the lone pair into a double bond and in pyrrole the lone pair is part of an aromatic sextet.
Similar to carbon–carbon bonds, these bonds can form stable double bonds, as in imines, and triple bonds such as nitriles. Bond lengths range from 147.9 pm for simple amines to 147.5 pm for C-N= compounds such as nitromethane to 135.2 pm for partial double bonds in pyridine to 115.8 pm for triple bonds as in nitriles.[2]
A CN bond is strongly polarized towards nitrogen (electronegativity for C and N is 2.55 and 3.04, respectively) and subsequently molecular dipole moments can be high: cyanamide 4.27 D, diazomethane 1.5 D, methyl azide 2.17, pyridine 2.19. For this reason many compounds containing CN bonds are water-soluble.
Nitrogen functional groups
| Chemical class | Bond order | Formula | Structural Formula | Example | Avg. C–N bond length (Å)[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amines | 1 | R2C-NH2 | 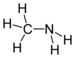 Methylamine |
1.469 (neutral amine) 1.499 (ammonium salt) | |
| Aziridines | 1 | CH2NHCH2 | 
|
 Mitomycin |
1.472 |
| Azides | 1 | R2C-N3 |  phenyl azide |
||
| Anilines | 1 | Ph-NH2 | 
|
 Anisidine |
1.355 (sp2 N) 1.395 (sp3 N) 1.465 (ammonium salt) |
| Pyrroles | 1 | 
|
 Porphyrin |
1.372 | |
| Amides | 1.2 | R-CO-NR2 | 
|
 Acetamide |
1.325 (primary) 1.334 (secondary) 1.346 (tertiary) |
| Pyridines | 1.5 | pyr | 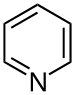
|
 Nicotinamide |
1.337 |
| Imines | 2 | R2C=NR | imine |  DBN |
1.279 (C=N bond) 1.465 (C–N bond) |
| Nitriles | 3 | R-CN |  Benzonitrile |
1.136 | |
| Isonitriles | 3 | R-NC | TOSMIC |
See also
- Cyanide
- Other carbon bonds with group 15 elements: carbon–nitrogen bonds, carbon–phosphorus bonds
- Other carbon bonds with period 2 elements: carbon–lithium bonds, carbon–beryllium bonds, carbon–boron bonds, carbon–carbon bonds, carbon–nitrogen bonds, carbon–oxygen bonds, carbon–fluorine bonds
References
- ^ Organic Chemistry John McMurry 2nd Ed.
- ^ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 65Th Ed.
- ^ F. H. Allen, O. Kennard, D. G. Watson, L. Brammer, A. G. Orpen. Tables of bond Lengths determined by X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction. Part 1. Bond Lengths in Organic Compounds. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. II 1987, S1-S19.
