Communicating vessels

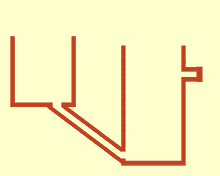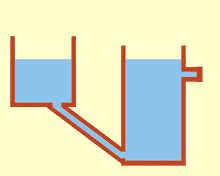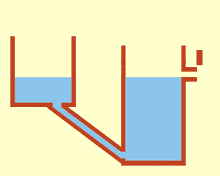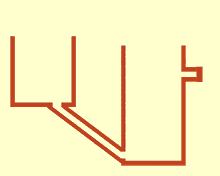
Communicating vessels or communicating vases[1] are a set of containers containing a homogeneous fluid and connected sufficiently far below the top of the liquid: when the liquid settles, it balances out to the same level in all of the containers regardless of the shape and volume of the containers. If additional liquid is added to one vessel, the liquid will again find a new equal level in all the connected vessels. This was discovered by Simon Stevin as a consequence of Stevin's Law.[2] It occurs because gravity and pressure are constant in each vessel (hydrostatic pressure).[3]
Blaise Pascal proved in the seventeenth century that the pressure exerted on a molecule of a liquid is transmitted in full and with the same intensity in all directions.
Applications
[edit]Since the days of ancient Rome, the concept of communicating vessels has been used for indoor plumbing, via aquifers and lead pipes. Water will reach the same level in all parts of the system, which acts as communicating vessels, regardless of what the lowest point is of the pipes – although in practical terms the lowest point of the system depends on the ability of the plumbing to withstand the pressure of the liquid.

In cities, water towers are frequently used so that city plumbing will function as communicating vessels, distributing water to higher floors of buildings with sufficient pressure.
Hydraulic presses, using systems of communicating vessels, are widely used in various applications of industrial processes.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Mario Bunge, Philosophy of Science: From Explanation to Justification, 1998, ISBN 1412830834, p. 369
- ^ Spellman, Frank R.; Whiting, Nancy E. (2005). Environmental engineer's mathematics handbook. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-56670-681-0.
- ^ Fontana, Fabrizio; DiCapua Roberto (August 2005). "Role of hydrostatic paradoxes towards the formation of the scientific thought of students at academic level". European Journal of Physics. 26 (6): 1017–1030. Bibcode:2005EJPh...26.1017F. doi:10.1088/0143-0807/26/6/009. S2CID 120595888.
