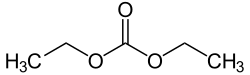
Diethyl carbonate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diethyl carbonate | |
| Other names
Carbonic ether; Ethyl carbonate, di-; Eufin[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.011 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2366 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 118.132 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.975 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −43[2] °C (−45 °F; 230 K) |
| Boiling point | 126 to 128 °C (259 to 262 °F; 399 to 401 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H226, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 33 °C (91 °F; 306 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Diethyl carbonate (sometimes abbreviated DEC) is an ester of carbonic acid and ethanol with the formula OC(OCH2CH3)2. At room temperature (25 °C) diethyl carbonate is a colorless liquid with a low flash point.
Diethyl carbonate is used as a solvent such as in erythromycin intramuscular injections.[3][4][5] It can be used as a component of electrolytes in lithium batteries. It has been proposed as a fuel additive to support cleaner diesel fuel combustion because its high boiling point might reduce blended fuels' volatility, minimizing vapor buildup in warm weather that can block fuel lines.[6] As a fuel additive, it can also reduce emissions CO2 and other particulates.[7]
Production
It can be made by reacting phosgene with ethanol, producing hydrogen chloride as a byproduct. Because chloroform can react with oxygen to form phosgene, chloroform can be stabilized for storage by adding 1 part (by mass) of ethanol to 100 parts (by mass) of chloroform, so that any phosgene that forms is converted into diethyl carbonate.
It can also be made by the alcoholysis of urea with ethanol. This reaction requires a heterogeneous catalysis that can act both as a Lewis acid and a base, such as various metal oxides. The reaction proceeds via the formation of the intermediary ethyl carbamate.[7]
It can also be synthesized directly from carbon dioxide and ethanol using various methods, and via oxidative carbonylation with carbon monoxide. Another method is transesterification from dimethyl carbonate. Yet another method is from the reaction of ethyl nitrite and carbon monoxide, where the ethyl nitrite can be made from nitric oxide and ethanol. This method requires a catalyst such as palladium.[7]
See also
References
- ^ "DIETHYL CARBONATE". Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ^ Ding, Michael (2001). "Liquid/Solid Phase Diagrams of Binary Carbonates for Lithium Batteries". Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 148: A299–A304. doi:10.1149/1.1353568.
- ^ Anderson, Robert C.; Harris, Paul N.; Chen, K. K. (1955). "Further toxicological studies with ilotycin® (Erythromycin, Lilly)". Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association. 44 (4): 199–204. doi:10.1002/jps.3030440404. ISSN 1930-2304. PMID 14367139.
- ^ US 4382086, Sciavolino, Frank C. & Hauske, James R., "9-Dihydro-11,12-ketal derivatives of erythromycin A and epi-erythromycin A", published 1983-05-03, issued 1982-03-01, assigned to Pfizer Inc.
- ^ US 4363803, Hauske, James R., "3",4"-Oxyallylene erythromycin and oleandomycin, composition and method of use", published 1982-12-14, issued 1982-03-01, assigned to Pfizer Inc.
- ^ Walter, K. Scientists Discover Method for Cleaner Fossil Fuel. MR&D Magazine. 09/18/2017 - 3:16pm
- ^ a b c Shukla, Kartikeya; Srivastava, Vimal Chandra (2016). "Diethyl carbonate: critical review of synthesis routes, catalysts used and engineering aspects". RSC Advances. 6 (39): 32624–32645. Bibcode:2016RSCAd...632624S. doi:10.1039/c6ra02518h. Retrieved Aug 3, 2021.
