Ilha Grande
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2011) |
 View of Ilha Grande from the mainland | |
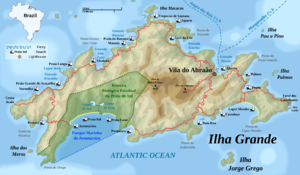 English topographic map of Ilha Grande | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Atlantic Ocean |
| Coordinates | 23°09′S 44°14′W / 23.150°S 44.233°W |
| Area | 193 km2 (75 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,031 m (3383 ft) |
| Highest point | Pico da Pedra D'Água |
| Administration | |
| Municipality | Angra dos Reis |
| State | Rio de Janeiro |
| Demographics | |
| Population | ~5000 (2014) |
| Official name | Paraty and Ilha Grande – Culture and Biodiversity |
| Criteria | Cultural and Natural: (v), (x) |
| Designated | 2019 (43rd session) |
| Reference no. | 1308 |
| Region | Latin America and the Caribbean |
Ilha Grande (Portuguese pronunciation: [ˈiʎɐ ˈɡɾɐ̃dʒi] "Big Island") is an island located off the coast of Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. The island, which is part of the municipality of Angra dos Reis, remains largely undeveloped. For almost a century it was closed by the Brazilian government to free movement or settlement because it first housed a leper colony and later a top-security prison (Colônia Penal de Dois Rios, later known as Instituto Penal Cândido Mendes). The Cândido Mendes prison, which housed some of the most dangerous prisoners within the Brazilian penal system, was finally closed in 1994. The largest village on the island is called Vila do Abraão with approximately 1900 inhabitants.
The island, which is 193 km2 (75 sq mi) in area, is now a popular tourist destination that is noted for its scenic beauty, unspoiled tropical beaches, luxuriant vegetation and rugged landscape. The highest point is the 1,031 m (3,383 ft) Pico da Pedra D'Água. Most of its territory is within the Ilha Grande State Park. The remainder of the island is subject to stringent development restrictions.
On 5 July 2019, Ilha Grande and Paraty were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[1]
Flora & fauna
The Ilha Grande is one of the most pristine remnants of Brazil's Atlantic rainforest making it one of the richest ecosystems in the world. As a hotspot for biodiversity and conservation, it holds some of the largest remaining populations of many endangered species, including the red-ruffed fruitcrow, the brown howler monkey, the maned sloth, the red-browed amazon parrot, and the broad-snouted caiman. The seas around the island, which are also protected, feature a unique convergence of tropical, subtropical, and temperate-zone marine life, where it is possible to see corals and tropical fish including sharks, sea turtles, Magellanic penguins and cetaceans such as the southern right whale,[2] humpback whale, Bryde's whale,[3] orca,[4] and dolphins.[5]
The islands are contained within the 12,400 hectares (31,000 acres) Tamoios Environmental Protection Area (APA), created in 1982.[6] The island (and APA) contains the Aventureiro Sustainable Development Reserve, created in 2014 from the former Aventureiro Marine State Park, which was integrated with the Praia do Sul Biological Reserve.[7] 62.5% of the island is covered by the Ilha Grande State Park, making a total of 87% of the island protected.[8]
Tourism industry
Most of the visitor facilities, lodging and the park headquarters are located at Vila do Abraão. The village may be reached from the mainland by local ferries. The island is a popular ecotourism destination. Although it has no roads and motorised vehicles are banned, the island has more than 150 km (93 mi) of hiking trails connecting the coastal villages and hamlets. A popular activity for visitors is to trek to Lopes Mendes beach, about a two-hour hike from Vila do Abraão. Travel companies offer trips to see the island's various beaches, mountains trails and waterfalls.
On January 1, 2010, devastating mudslides killed at least 19 people on the island.[9]
Gallery
-
Chouette on the island
-
Dolphin nearby the island
-
Sea turtle swims in the ocean
References
- ^ "Five sites inscribed on UNESCO's World Heritage List". UNESOC. 2019-07-05. Retrieved 2019-07-05.
- ^ Ilha Grande. Org. 2016. Baleias Jubartes na Ilha Grande - RJ. Retrieved on September 18, 2017
- ^ Lodi L.. 2016. Baleia-de-bryde: Navegando com as gigantes. Blog ECONSERV – Ecologia, Conservação e Serviços. Retrieved on September 18, 2017
- ^ Cruzeiro do Su (pt). 2015. Grupo de sete orcas é avistado em praia de Ubatuba. Retrieved on September 18, 2017
- ^ Ilha Grande. Com. Ilustres visitantes. Retrieved on September 18, 2017
- ^ APA de Tamoios (in Portuguese), INEA: Instituto Estadual do Ambiente, retrieved 2016-09-26
- ^ PES Marinho do Aventureiro (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-09-23
- ^ "Parque Estadual da Ilha Grande - Angra dos Reis - RJ", Ilhagrande.org (in Portuguese), retrieved 2016-09-23
- ^ "Mudslide in Brazil resort kills at least 19 people". BBC News. 2 January 2010.
External links
- Prefeitura de Angra dos Reis (in Portuguese)
- Portal Turístico da Ilha Grande (in Portuguese)
- O Caldeirão do Diabo
- Ilha Grande Travel Guide in English





