Interatrial septum
| Interatrial septum | |
|---|---|
 Interior of right side of heart. (labeled at left of image, as 'atrial septum') | |
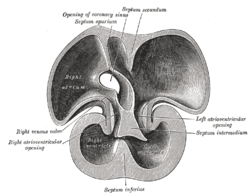 Interior of dorsal half of heart of human embryo of about thirty-five days. | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D054087 |
| TA98 | A12.1.00.019 |
| TA2 | 3964 |
| FMA | 7108 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart.
Structure
Development
The interatrial septum forms during the first and second months of fetal development. Formation of the septum occurs in several stages. The first is the development of the septum primum, a crescent-shaped piece of tissue forming the initial divider between the right and left atria. Because of its crescent shape, the septum primum does not fully occlude the space between left and right atria; the opening that remains is called the ostium primum. During fetal development, this opening allows blood to be shunted from the right atrium to the left.
As the septum primum grows, the ostium primum progressively narrows. Before the ostium primum is completely occluded, a second opening called the ostium secundum begins to form in the septum primum. The ostium secundum allows continued shunting of blood from the right atrium to the left.
To the right of the septum primum, the septum secundum begins to form. This thick, muscular structure initially takes on the same crescent shape as the septum primum, except that it originates anteriorly, whereas the septum primum originates posteriorly. As the septum secundum grows, it leaves a small opening called the foramen ovale. The foramen ovale is continuous with the ostium secundum, again providing for continued shunting of blood.
The ostium secundum progressively enlarges and the size of the septum primum diminishes. Eventually, the septum primum is nothing more than a small flap that covers the foramen ovale on its left side. This flap of tissue is called the valve of the foramen ovale. It opens and closes in response to pressure gradients between the left and right atria. When the pressure is greater in the right atrium, the valve opens; when the pressure is greater in the left atrium, the valve closes. Because the lungs are nonfunctional in fetal life, pressure in the pulmonary circulation is greater than that of the systemic circulation. Consequently, the right atrium is generally under higher pressures than the left atrium, and the valve of the foramen ovale is normally open.
At birth, there is a reversal in the pressure gradient between the atria, resulting in functional closure of the valve of the foramen ovale. Permanent anatomical closure of the foramen ovale occurs with time in normal infants. Inappropriate closure of the foramen ovale results in patent foramen ovale.
Clinical significance
- Atrial septal defect is a relatively common heart malformation that occurs when the interatrial septum fails to develop properly.
References
- Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 39th ed. (2005). ISBN 0-443-07168-3
- "Septum, interatrial." Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed. (2000). ISBN 0-683-40007-X
