Interior (topology)

In mathematics, specifically in topology, the interior of a subset S of a topological space X is the union of all subsets of S that are open in X. A point that is in the interior of S is an interior point of S.
The interior of S is the complement of the closure of the complement of S. In this sense interior and closure are dual notions.
The exterior of a set S is the complement of the closure of S; it consists of the points that are in neither the set nor its boundary. The interior, boundary, and exterior of a subset together partition the whole space into three blocks (or fewer when one or more of these is empty).
Definitions
Interior point
If S is a subset of a Euclidean space, then x is an interior point of S if there exists an open ball centered at x which is completely contained in S. (This is illustrated in the introductory section to this article.)
This definition generalizes to any subset S of a metric space X with metric d: x is an interior point of S if there exists r > 0, such that y is in S whenever the distance d(x, y) < r.
This definition generalises to topological spaces by replacing "open ball" with "open set". Let S be a subset of a topological space X. Then x is an interior point of S if x is contained in an open subset of X which is completely contained in S. (Equivalently, x is an interior point of S if S is a neighbourhood of x.)
Interior of a set
The interior of a subset S of a topological space X, denoted by Int S or S°, can be defined in any of the following equivalent ways:
- Int S is the largest open subset of X contained (as a subset) in S
- Int S is the union of all open sets of X contained in S
- Int S is the set of all interior points of S
Examples
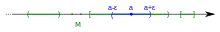
- In any space, the interior of the empty set is the empty set.
- In any space X, if S ⊆ X, then int S ⊆ S.
- If X is the real line (with the standard topology), then int([0, 1]) = (0, 1).
- If X is the real line , then the interior of the set of rational numbers is empty.
- If X is the complex plane , then
- In any Euclidean space, the interior of any finite set is the empty set.
On the set of real numbers, one can put other topologies rather than the standard one:
- If X is the real numbers with the lower limit topology, then int([0, 1]) = [0, 1).
- If one considers on the topology in which every set is open, then int([0, 1]) = [0, 1].
- If one considers on the topology in which the only open sets are the empty set and itself, then int([0, 1]) is the empty set.
These examples show that the interior of a set depends upon the topology of the underlying space. The last two examples are special cases of the following.
- In any discrete space, since every set is open, every set is equal to its interior.
- In any indiscrete space X, since the only open sets are the empty set and X itself, we have X = int X and for every proper subset S of X, int S is the empty set.
Properties
Let X be a topological space and let S and T be subsets of X.
- Int S is open in X.
- If T is open in X then T ⊆ S if and only if T ⊆ Int S.
- Int S is an open subset of S when S is given the subspace topology.
- S is an open subset of X if and only if S = int S.
- Intensive: Int S ⊆ S.
- Idempotence: Int(Int S) = Int S.
- Preserves/distributes over binary intersection: Int (S ∩ T) = (Int S) ∩ (Int T).
- Monotone/nondecreasing with respect to ⊆: If S ⊆ T then Int S ⊆ Int T.
The above statements will remain true if all instances of the symbols/words
- "interior", "Int", "open", "subset", and "largest"
are respectively replaced by
- "closure", "Cl", "closed", "superset", and "smallest"
and the following symbols are swapped:
- "⊆" swapped with "⊇"
- "∪" swapped with "∩"
For more details on this matter, see interior operator below or the article Kuratowski closure axioms.
Other properties include:
- If S is closed in X and Int T = ∅ then Int (S ∪ T) = Int S.
Interior operator
The interior operator is dual to the closure operator, which is denoted by or by an overline —, in the sense that and also where is the topological space containing and the backslash denotes set-theoretic difference. Therefore, the abstract theory of closure operators and the Kuratowski closure axioms can be readily translated into the language of interior operators, by replacing sets with their complements in
In general, the interior operator does not commute with unions. However, in a complete metric space the following result does hold:
Theorem[1] (C. Ursescu) — Let be a sequence of subsets of a complete metric space
- If each is closed in then
- If each is open in then
The result above implies that every complete metric space is a Baire space.
Exterior of a set
The exterior of a subset of a topological space denoted by or simply is the largest open set disjoint from namely, it is the union of all open sets in that are disjoint from The exterior is the interior of the complement, which is the same as the complement of the closure; in formulas,
Similarly, the interior is the exterior of the complement:
The interior, boundary, and exterior of a set together partition the whole space into three blocks (or fewer when one or more of these is empty): where denotes the boundary of The interior and exterior are always open, while the boundary is closed.
Some of the properties of the exterior operator are unlike those of the interior operator:
- The exterior operator reverses inclusions; if then
- The exterior operator is not idempotent. It does have the property that
Interior-disjoint shapes

Two shapes a and b are called interior-disjoint if the intersection of their interiors is empty. Interior-disjoint shapes may or may not intersect in their boundary.
See also
- Algebraic interior – Generalization of topological interior
- DE-9IM – Topological model
- Interior algebra – Algebraic structure
- Jordan curve theorem – A closed curve divides the plane into two regions
- Quasi-relative interior – Generalization of algebraic interior
- Relative interior – Generalization of topological interior
References
- ^ Zalinescu, C (2002). Convex analysis in general vector spaces. River Edge, N.J. London: World Scientific. p. 33. ISBN 981-238-067-1. OCLC 285163112.
Bibliography
- Bourbaki, Nicolas (1989) [1966]. General Topology: Chapters 1–4 [Topologie Générale]. Éléments de mathématique. Berlin New York: Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-540-64241-1. OCLC 18588129.
- Dixmier, Jacques (1984). General Topology. Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics. Translated by Berberian, S. K. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-90972-1. OCLC 10277303.
- Császár, Ákos (1978). General topology. Translated by Császár, Klára. Bristol England: Adam Hilger Ltd. ISBN 0-85274-275-4. OCLC 4146011.
- Dugundji, James (1966). Topology. Boston: Allyn and Bacon. ISBN 978-0-697-06889-7. OCLC 395340485.
- Joshi, K. D. (1983). Introduction to General Topology. New York: John Wiley and Sons Ltd. ISBN 978-0-85226-444-7. OCLC 9218750.
- Kelley, John L. (1975). General Topology. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 27. New York: Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-0-387-90125-1. OCLC 338047.
- Munkres, James R. (2000). Topology (Second ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, Inc. ISBN 978-0-13-181629-9. OCLC 42683260.
- Schubert, Horst (1968). Topology. London: Macdonald & Co. ISBN 978-0-356-02077-8. OCLC 463753.
- Wilansky, Albert (17 October 2008) [1970]. Topology for Analysis. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 978-0-486-46903-4. OCLC 227923899.
- Willard, Stephen (2004) [1970]. General Topology. Mineola, N.Y.: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-43479-7. OCLC 115240.
External links
- Interior at PlanetMath.





























