Juglandaceae
| Juglandaceae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Juglans regia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Juglandaceae DC. ex Perleb[1] |
| Type genus | |
| Juglans L. | |
| Subfamilies | |
|
See text | |

| |
| The range of subfamily Engelhardioideae. | |
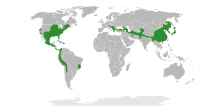
| |
| The range of subfamily Juglandoideae. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Platycaryaceae Nakai ex Doweld Pterocaryaceae Nakai, nom. inval. Rhoipteleaceae Hand.-Mazz., nom. cons.[2] | |
The Juglandaceae are a family, known as the walnut family, of trees, or sometimes shrubs, in the order Fagales. Various members of this family are native to the Americas, Eurasia, and Southeast Asia. Members of the walnut family have large, aromatic leaves that are usually alternate, but opposite in Alfaroa and Oreomunnea. The leaves are pinnately compound or ternate, and usually 20–100 cm long.
The trees are wind-pollinated, and the flowers are usually arranged in catkins.
The nine or ten genera in the family have a total of ca 50 species,[3] and include the commercially important nut-producing trees walnut (Juglans), pecan (Carya illinoinensis), and hickory (Carya). The Persian walnut, Juglans regia, is one of the major nut crops of the world. Walnut, hickory, and gaulin are also valuable timber trees.
Systematics
The known living genera are grouped into subfamilies, tribes, and subtribes as follows:[4]
- Subfamily Engelhardioideae
- Alfaroa Standl. – gaulin
- Engelhardia Lesch. ex Blume – cheo
- Oreomunnea Oerst.
- Subfamily Juglandoideae
- Tribe Platycaryeae
- Platycarya Siebold & Zucc.
- Tribe Juglandeae
- Subtribe Caryinae
- Carya Nutt. – hickory and pecan
- Annamocarya A.Chev.
- Subtribe Juglandinae
- Cyclocarya Iljinsk – wheel wingnut
- Juglans L. – walnut
- Pterocarya Kunth – wingnut
- Subtribe Caryinae
- Tribe Platycaryeae
- Incertae sedis
- Rhoiptelea Diels & Hand.-Mazz.[5]


The only member of the genus Alfaropsis I.A.Iljinsk., Alfaropsis roxburghiana (Wall.) I.A.Iljinsk. is a synonym for Engelhardia roxburghiana Wall. (or perhaps vice versa).
The only member of the genus Annamocarya A.Chev., Annamocarya sinensis (Dode) J.-F.Leroy, may actually be a member of Carya.
Fruits
Some fruits are borderline and difficult to categorize. Hickory nuts (Carya) and walnuts (Juglans) grow within an outer husk; these fruits are sometimes considered to be drupes or drupaceous nuts, rather than true botanical nuts. "Tryma" is a specialized term for such nut-like drupes.[6][7]
The fruits of the Juglandaceae are often confused with drupes but are actually accessory fruit because the outer covering of the fruit is technically an involucre and thus not morphologically part of the carpel; this means it can not be a drupe but is instead a drupe-like nut. These odd nuts fall into two different types: in the walnut genus (Juglans), it is a pseudodrupe and in the hickory genus (Carya), it is a tryma.[8]
References
- ^ Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (2009). "An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III" (PDF). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 161 (2): 105–121. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2009.00996.x. Retrieved 2013-07-06.
- ^ "Family: Juglandaceae DC. ex Perleb, nom. cons". Germplasm Resources Information Network. United States Department of Agriculture. 2003-01-17. Retrieved 2011-11-17.
- ^ Christenhusz, M. J. M., and Byng, J. W. (2016). "The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase". Phytotaxa. 261 (3). Magnolia Press: 201–217. doi:10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Manos, P. S.; D. E. Stone (2001). "Evolution, phylogeny and systematics of the Juglandaceae". Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden. 88: 231–269. doi:10.2307/2666226.
- ^ "GRIN Genera of Juglandaceae". Germplasm Resources Information Network. United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 2011-11-17.
- ^ Armstrong, W.P. "Identification Of Major Fruit Types". Wayne's World. Retrieved 2011-11-17.
- ^ Armstrong, W.P. (2009-03-15). "Fruits Called Nuts". Wayne's World. Retrieved 2011-11-17.
- ^ John Derek Bewley, Michael Black, Peter Halmer (2006) The Encyclopedia of Seeds: Science, Technology And Uses
