Probing Lensing Anomalies Network
The Probing Lensing Anomalies NETwork (PLANET) collaboration coordinates a network of telescopes to rapidly sample photometric measurements of the magnification of stars in the galactic bulge undergoing gravitational microlensing by intervening foreground stars (or other compact massive objects). This network consists of five 1m-class optical telescopes distributed in longitude around the southern hemisphere in order to perform quasi-continuous round-the-clock precision monitoring. On a target-of-opportunity basis, less frequent spectroscopic measurements complement the rapid photometry for selected prime targets. Since 2005, PLANET performs a common microlensing campaign with RoboNet-1.0, a network of UK-operated 2.0m robotic telescopes.
In January 2009, PLANET has merged with the MicroFUN collaboration.[1]
Telescopes
[edit]
For the 2006 observing season, the telescopes involved were (apart from the RoboNet telescopes):
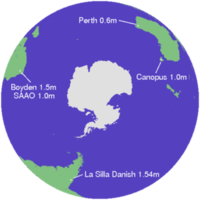
- Danish 1.54m telescope at ESO, La Silla, Chile [1]
- 1.0 meter telescope at Canopus Observatory of the University of Tasmania, Australia [2]
- 0.6 meter telescope at the Perth Observatory
- South African Astronomical Observatory 1.0 meter telescope at Sutherland, South Africa [3]
- Rockefeller 1.52 meter telescope at Boyden Observatory (Bloemfontein), South Africa [4]
Members
[edit]As of late 2006, PLANET had 31 members from 11 countries: France, United Kingdom, Germany, Denmark, Austria, Chile, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa and the United States.
References
[edit]External links
[edit]
