User talk:Ffran005
Welcome![edit]
Hello, Ffran005, and welcome to Wikipedia! My name is Ian and I work with the Wiki Education Foundation; I help support students who are editing as part of a class assignment.
I hope you enjoy editing here. If you haven't already done so, please check out the student training library, which introduces you to editing and Wikipedia's core principles. You may also want to check out the Teahouse, a community of Wikipedia editors dedicated to helping new users. Below are some resources to help you get started editing.
Handouts
|
|---|
Additional Resources
|
|
If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to contact me on my talk page. Ian (Wiki Ed) (talk) 12:44, 6 October 2016 (UTC)
Article I want to critique[edit]
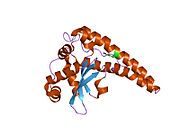
An Error has occurred retrieving Wikidata item for infobox Superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial (SOD2), also known as manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the SOD2 gene on chromosome 6.[1][2]
Structure[edit]
The SOD2 gene contains five exons interrupted by four introns, an uncharacteristic 5′-proximal promoter that possesses a GC-rich region in place of the TATA or CAAT, and an enhancer in the second intron. The proximal promoter region contains multiple binding sites for transcription factors, including specific-1 (Sp1), activator protein 2 (AP-2), and early growth response 1 (Egr-1).[2] This gene is a mitochondrial member of the iron/manganese superoxide dismutase family.[1][3] It encodes a mitochondrial matrix protein that forms a homotetramer and binds one manganese ion per subunit.[1][2] The manganese site forms a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with four ligands from the protein and a fifth solvent ligand. This solvent ligand is a hydroxide believed to serve as the electron acceptor of the enzyme. The active site cavity consists of a network of side chains of several residues associated by hydrogen bonding, extending from the aqueous ligand of the metal. Of note, the highly conserved residue Tyr34 plays a key role in the hydrogen-bonding network, as nitration of this residue inhibits the protein's catalytic ability.[4] This protein also possesses an N-terminal mitochondrial leader sequence which targets it to the mitochondrial matrix, where it converts mitochondrial-generated reactive oxygen species from the respiratory chain to H2.[2] Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized.[1]
Function[edit]
As a member of the iron/manganese superoxide dismutase family, this protein transforms toxic superoxide, a byproduct of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, into hydrogen peroxide and diatomic oxygen.[1] This function allows SOD2 to clear mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and, as a result, confer protection against cell death.[3] As a result, this protein plays an antiapoptotic role against oxidative stress, ionizing radiation, and inflammatory cytokines.[2]
Clinical significance[edit]
The SOD2 enzyme is an important constituent in apoptotic signaling and oxidative stress, most notably as part of the mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis signaling.[5] Programmed cell death is a distinct genetic and biochemical pathway essential to metazoans. An intact death pathway is required for successful embryonic development and the maintenance of normal tissue homeostasis. Apoptosis has proven to be tightly interwoven with other essential cell pathways. The identification of critical control points in the cell death pathway has yielded fundamental insights for basic biology, as well as provided rational targets for new therapeutics a normal embryologic processes, or during cell injury (such as ischemia-reperfusion injury during heart attacks and strokes) or during developments and processes in cancer, an apoptotic cell undergoes structural changes including cell shrinkage, plasma membrane blebbing, nuclear condensation, and fragmentation of the DNA and nucleus. This is followed by fragmentation into apoptotic bodies that are quickly removed by phagocytes, thereby preventing an inflammatory response.[6] It is a mode of cell death defined by characteristic morphological, biochemical and molecular changes. It was first described as a "shrinkage necrosis", and then this term was replaced by apoptosis to emphasize its role opposite mitosis in tissue kinetics. In later stages of apoptosis the entire cell becomes fragmented, forming a number of plasma membrane-bounded apoptotic bodies which contain nuclear and or cytoplasmic elements. The ultrastructural appearance of necrosis is quite different, the main features being mitochondrial swelling, plasma membrane breakdown and cellular disintegration. Apoptosis occurs in many physiological and pathological processes. It plays an important role during embryonal development as programmed cell death and accompanies a variety of normal involutional processes in which it serves as a mechanism to remove "unwanted" cells.
Role in oxidative stress[edit]
Most notably, SOD2 is pivotal in reactive oxygen species (ROS) release during oxidative stress by ischemia-reperfusion injury, specifically in the myocardium as part of a heart attack (also known as ischemic heart disease). Ischemic heart disease, which results from an occlusion of one of the major coronary arteries, is currently still the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in western society.[7][8] During ischemia reperfusion, ROS release substantially contribute to the cell damage and death via a direct effect on the cell as well as via apoptotic signals. SOD2 is known to have a capacity to limit the detrimental effects of ROS. As such, SOD2 is important for its cardioprotective effects.[9] In addition, SOD2 has been implicated in cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury, such as during ischemic preconditioning of the heart.[10] Although a large burst of ROS is known to lead to cell damage, a moderate release of ROS from the mitochondria, which occurs during nonlethal short episodes of ischemia, can play a significant triggering role in the signal transduction pathways of ischemic preconditioning leading to reduction of cell damage. It has even observed that during this release of ROS, SOD2 plays an important role hereby regulating apoptotic signaling and cell death.
Due to its cytoprotective effects, overexpression of SOD2 has been linked to increased invasiveness of tumor metastasis.[3] Its role in controlling ROS levels also involves it in ageing, cancer, and neurodegenerative disease.[4] Mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic cardiomyopathy (IDC), sporadic motor neuron disease, and cancer. A common polymorphism associated with greater susceptibility to various pathologies is found in the mitochondrial leader targeting sequence (Val9Ala).[11] Mice lacking Sod2 die shortly after birth, indicating that unchecked levels of superoxide are incompatible with mammalian life.[12] However, mice 50% deficient in Sod2 have a normal lifespan and minimal phenotypic defects but do suffer increased DNA damage and increased incidence of cancer.[13] In Drosophila melanogaster, over-expression of Sod2 has been show to increase lifespan by 20%[14]
Exercise-induced cardioprotection[edit]
When animals are exercised at a relatively high work rate, many exercise training studies report that exercise training promotes an increase in myocardial MnSOD activity. This is significant because two recent studies reveal that increased MnSOD activity is essential to achieve optimal training-induced protection against both ischemia/reperfusion(IR)-induced cardiac arrhythmias and infarction. Specifically, using an antisense oligonucleotide against MnSOD to prevent ExTr-induced increases in myocardial MnSOD activity, Yamashita et al. demonstrated that an increase in myocardial MnSOD activity is required to provide training-induced protection against IR-induced myocardial infarction. Similarly, Hamilton et al. [10], using a MnSOD gene silencing approach, reported that prevention of the ExTr-induced increase in myocardial MnSOD resulted in a loss of training-induced protection against IR-mediated arrhythmias. In contrast to these findings, training-induced increases in cardiac MnSOD are not required to achieve training-induced cardioprotection against myocardial stunning. (Power et al. 2007)
Interactions[edit]
The SOD2 gene has been shown to bind:
The SOD2 protein has been shown to interact with HIV-1 Tat and HIV-1 Vif.[15]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e "Entrez Gene: SOD2 superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial".
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Becuwe P, Ennen M, Klotz R, Barbieux C, Grandemange S (Dec 2014). "Manganese superoxide dismutase in breast cancer: from molecular mechanisms of gene regulation to biological and clinical significance". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 77: 139/51. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.08.026. PMID 25224035.
- ^ a b c Pias EK, Ekshyyan OY, Rhoads CA, Fuseler J, Harrison L, Aw TY (Apr 2003). "Differential effects of superoxide dismutase isoform expression on hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis in PC-12 cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (15): 13294–301. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208670200. PMID 12551919.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Perry JJ, Hearn AS, Cabelli DE, Nick HS, Tainer JA, Silverman DN (Apr 2009). "Contribution of human manganese superoxide dismutase tyrosine 34 to structure and catalysis". Biochemistry. 48 (15): 3417–24. doi:10.1021/bi8023288. PMID 19265433.
- ^ Danial, NN; Korsmeyer, SJ (23 January 2004). "Cell death: critical control points". Cell. 116 (2): 205–19. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00046-7. PMID 14744432.
- ^ Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (Aug 1972). "Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics". British Journal of Cancer. 26 (4): 239–57. doi:10.1038/bjc.1972.33. PMC 2008650. PMID 4561027.
- ^ Murray CJ, Lopez AD (May 1997). "Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990-2020: Global Burden of Disease Study". Lancet. 349 (9064): 1498–504. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(96)07492-2. PMID 9167458.
- ^ Braunwald E, Kloner RA (Nov 1985). "Myocardial reperfusion: a double-edged sword?". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 76 (5): 1713–9. doi:10.1172/JCI112160. PMC 424191. PMID 4056048.
- ^ Maslov LN, Naryzhnaia NV, Podoksenov IuK, Prokudina ES, Gorbunov AS, Zhang I, Peĭ ZhM (Jan 2015). "[Reactive oxygen species are triggers and mediators of an increase in cardiac tolerance to impact of ischemia-reperfusion]". Rossiĭskii Fiziologicheskiĭ Zhurnal Imeni I.M. Sechenova / Rossiĭskaia Akademiia Nauk. 101 (1): 3–24. PMID 25868322.
- ^ Liem DA, Honda HM, Zhang J, Woo D, Ping P (Dec 2007). "Past and present course of cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury". Journal of Applied Physiology. 103 (6): 2129–36. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00383.2007. PMID 17673563.
- ^ Muller FL, Lustgarten MS, Jang Y, Richardson A, Van Remmen H (Aug 2007). "Trends in oxidative aging theories". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 43 (4): 477–503. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.034. PMID 17640558.
- ^ Li Y, Huang TT, Carlson EJ, Melov S, Ursell PC, Olson JL, Noble LJ, Yoshimura MP, Berger C, Chan PH, Wallace DC, Epstein CJ (Dec 1995). "Dilated cardiomyopathy and neonatal lethality in mutant mice lacking manganese superoxide dismutase". Nature Genetics. 11 (4): 376–81. doi:10.1038/ng1295-376. PMID 7493016.
- ^ Van Remmen H, Ikeno Y, Hamilton M, Pahlavani M, Wolf N, Thorpe SR, Alderson NL, Baynes JW, Epstein CJ, Huang TT, Nelson J, Strong R, Richardson A (Dec 2003). "Life-long reduction in MnSOD activity results in increased DNA damage and higher incidence of cancer but does not accelerate aging". Physiological Genomics. 16 (1): 29–37. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00122.2003. PMID 14679299.
- ^ Curtis C, Landis GN, Folk D, Wehr NB, Hoe N, Waskar M, Abdueva D, Skvortsov D, Ford D, Luu A, Badrinath A, Levine RL, Bradley TJ, Tavaré S, Tower J (2007). "Transcriptional profiling of MnSOD-mediated lifespan extension in Drosophila reveals a species-general network of aging and metabolic genes". Genome Biology. 8 (12): R262. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-12-r262. PMC 2246264. PMID 18067683.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Woollard SM, Bhargavan B, Yu F, Kanmogne GD (Jun 2014). "Differential effects of Tat proteins derived from HIV-1 subtypes B and recombinant CRF02_AG on human brain microvascular endothelial cells: implications for blood-brain barrier dysfunction". Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 34 (6): 1047–59. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2014.54. PMC 4050250. PMID 24667918.
Further reading[edit]
- Zelko IN, Mariani TJ, Folz RJ (Aug 2002). "Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 33 (3): 337–49. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00905-X. PMID 12126755.
- Faraci FM, Didion SP (Aug 2004). "Vascular protection: superoxide dismutase isoforms in the vessel wall". Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 24 (8): 1367–73. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000133604.20182.cf. PMID 15166009.
Critique[edit]
This is well written and nicely put together. There some additional changes I would like to add to it. For example, I will add a brief section pertaining to the history of SOD2. After the section on structure I will add a section on SOD2's location with in the mitochondria and elaborate how it varies from its counterparts (SOD1 & SOD3). I will also add the step by step process of how SOD2 works within the mitochondria to eradicate ROS to end up with the final products and pair it with an image.
http://www.omim.org/entry/147460Cite error: There are <ref> tags on this page without content in them (see the help page).
[1]
http://www.nature.com/nri/journal/v11/n6/images/nri2975-i1.jpgCite error: There are <ref> tags on this page without content in them (see the help page).
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0968000416300202Cite error: There are <ref> tags on this page without content in them (see the help page).
Feedback request[edit]
I got your request for feedback and took a quick look at your sandbox. It looks to me like you copied content from an existing article into your sandbox. However, it appears that you didn't click the Edit button in the original article before copying it over. As a result, the formatting is messed up. You should re-do that copy and paste before you make changes to the content.
(When replying to this message, please include {{ping|Ian (Wiki Ed)}} in your response, to ensure that I see your reply.)
Ian (Wiki Ed) (talk) 19:49, 24 October 2016 (UTC)