Gastropod shell: Difference between revisions
links and add caption item for # 2 |
GrahamBould (talk | contribs) m Link |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[Image:Czescimuszli shells.jpg|left|thumb|300px|The shell with the part broken out.</br> |
[[Image:Czescimuszli shells.jpg|left|thumb|300px|The shell with the part broken out.</br> |
||
1 - [[Umbilicus (mollusk)|umbilicus]]</br> |
1 - [[Umbilicus (mollusk)|umbilicus]]</br> |
||
2 - Parietal callus</br> |
2 - [[Parietal callus]]</br> |
||
3 - [[Aperture (mollusc)|aperture]]</br> |
3 - [[Aperture (mollusc)|aperture]]</br> |
||
4 - [[columella]]</br> |
4 - [[columella]]</br> |
||
Revision as of 08:50, 28 September 2007
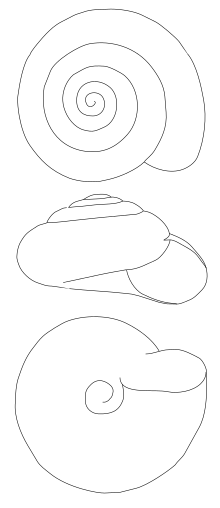
Upper image: Dorsal view, showing whorls and apex
Central image: Lateral view showing the profile of the shell
Lower image: Basal view showing umbilicus in the centre
The gastropod shell is an animal shell which is part of the body of a gastropod or snail. It is an external skeleton or exoskeleton, which serves not only for muscle attachment, but also for protection from predators and from mechanical damage. In land snails the shell is an essential protection against the sun, and against drying out.
The gastropod shell has several layers, and is typically made of calcium carbonate precipitated out into an organic matrix. It is secreted by a part of the molluscan body known as the mantle.
Not all gastropods have a shell, but the majority do. The shell is in one piece, and is typically spirally coiled, although some groups, such as the various families of limpets, have simple cone-shaped shells as adults.

1 - umbilicus
2 - Parietal callus
3 - aperture
4 - columella
5 - suture
6 - whorl
7 - apex
Parts of the gastropod shell may include:
- periostracum: a thin layer of organic "skin" which forms the outer layer of the shell of many species
- protoconch: the larval shell, often remains in postion even on an adult shell
- apex: the smallest few whorls of the shell
- spire: the part of the shell that protrudes above the body whorl
- whorl: each one of the complete rotations of the shell spiral
- body whorl: the largest whorl in which the main part of the viseral mass of the mollusk is found
- aperture: the opening of the shell
- peristome: the part of the shell that is right around the aperture
- columella: the "little column" at the axis of revolution of the shell
- umbilicus: in shells where the whorls move apart as they grow, on the underside of the shell there is a deep depression reaching up towards the spire; this is the umbilicus
- lira: one kind of shell sculpture
- plait: another kind of shell sculpture
- varix: on some mollusk shells, spaced raised and thickened vertical ribs mark the end of a period of rapid growth; these are varices
- operculum: the "trapdoor" of the shell
- Siphonal canal: an extension of the aperture in certain gastropods
- Parietal callus: a ridge on the inner lip of the aperture in certain gastropods
Various types of shells
-
Planispiral shell of freshwater pulmonate snail - Marisa cornuarietis
-
Shell and live animal of edible land pulmonate snail - Helix pomatia -
Shell of marine cowry snail - Cypraea nebrites
-
Shell of marine Turban snail showing operculum - Turbo chinensis -
Many-whorled shell of tower snail, Turritellidae -
Shell of marine limpet, probably a Patella species
See also
External links
- Gastropods by J. H. Leal - guide to shell morphology, terminology and sea species of Central America






