Bluntnose sixgill shark: Difference between revisions
GrahamBould (talk | contribs) Many improvements |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Sharksportal}} |
{{Sharksportal}} |
||
The '''bluntnose sixgill shark''', |
The '''bluntnose sixgill shark''', ''Hexanchus griseus'', often simply called the '''cow shark''', is the largest [[hexanchoid]] [[shark]], growing to more than 4.8 [[metre|m]] (15.5 [[foot (measurement)|ft]]) in length. |
||
==Taxonomy== |
|||
| ⚫ | The bluntnose sixgill shark is a member of the [[Hexanchidae]] [[family (biology)|family]]. Many of its relatives are [[extinct]]. The living species that are closest genetically include the [[dogfish]], the [[Greenland shark]], as well as other six- and sevengilled sharks. There are more closely related relatives in the fossil record than living species. Some of the shark's relatives date back to 200 million years ago. This shark is a very interesting species due to it's both primitive and current physical characteristics. |
||
==Description== |
|||
| ⚫ | Skin color ranges from tan to brown, or as dark as black. It has a light colored [[lateral line]] down the sides and on the fins' edges. There are darker colored spots on the sides. The general body shape is a heavy, powerful body with a broad head with small eyes. The pupils are black and the eye color is a [[fluorescent]] blue green. As an adult the bluntnose sixgill shark can grow to a massive size. True body length is determined by the gender of the individual. Males generally average between 309 and 330 cm. Females tend to be larger, averaging between 350 and 420 cm. This shark can attain a length of up to 550 cm. |
||
[[Image:Hexanchus griseus (Bluntnose sixgill shark) teeth.gif|thumb|left|200px|Teeth of the bluntnose sixgill shark.]] |
[[Image:Hexanchus griseus (Bluntnose sixgill shark) teeth.gif|thumb|left|200px|Teeth of the bluntnose sixgill shark.]] |
||
| ⚫ | The bluntnose sixgill shark resembles many of the fossil sharks from the [[Triassic]] period. This could be due to the fact that there are a greater number of ''Hexicanus'' relatives in the fossil record than there are left alive today. They have one [[dorsal fin]] located near the [[caudal fin]]. The [[pectoral fin]]s are broad with rounded edges. There are six gill slits which gives the shark its name. Most common sharks today have only 5 gill slits. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==Habitat== |
|||
| ⚫ | The bluntnose sixgill shark can be seen at depths of |
||
| ⚫ | This species typically inhabits depths greater than 90 m (300 ft), and has been recorded as deep as 1,875 m (6,150 ft). Like many deep-sea creatures, the bluntnose sixgill shark is known to undertake [[diel vertical migration|nightly vertical migrations]] (travelling surfaceward at night, returning to the depths before dawn). |
||
| ⚫ | The bluntnose sixgill shark can be seen at depths of 30 m (100 ft) during parts of the year in some specific places e.g. Flora Islet, near [[Hornby Island]] in [[British Columbia]], [[Monterey Canyon]] in [[San Francisco Bay]] and in [[fjord]]s in [[Norway]]. It is unknown why the shark come to these shallow depths and what they do, but they have been observed for over 20 years doing this. |
||
==Family History== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The |
||
==Characteristics== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Biology== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Feeding patterns== |
==Feeding patterns== |
||
Although sluggish in nature, the |
Although sluggish in nature, the bluntnose sixgill shark is capable of attaining high speeds for chasing and catching its prey. Because of the bluntnose sixgill shark's large and diverse range they have a wide variety of prey items. Their diet consists of a variety of [[mollusks]], [[crustaceans]], [[Agnatha]]ns (which is a family consisting of [[hagfish]]), and sea [[lamprey]]s. They also dine on Cape anchovies, [[Pacific salmon]], various species of [[hake]]. There are also many more species that are eaten depending upon the shark's home range. |
||
==Reproduction== |
==Reproduction== |
||
Very little is known about the reproductive process of |
Very little is known about the reproductive process of bluntnose sixgill sharks. What little is known is actually scientific speculation. Many biologists believe that the male bluntnose sixgill shark's teeth are specially adapted to the courtship ritual. The male will nip at the female's gill slits using its longer-cusped teeth. This action is thought to entice the female into mating. Evidence of this theory is that female bluntnose sixgill sharks show up with seasonal scars around their gill slits, which apparently is from breeding with males. The female bluntnose sixgill shark reaches sexual maturity between the ages of 18 and 35. Males usually reach sexual maturity much younger, between the ages of 11 and 14 years old. Scientists are unsure of how the bluntnose sixgill shark reproduces but it is thought that males and females meet seasonally between the months of May and November. The gestation period is unknown but scientists believe that it is longer than 2 years. The bluntnose sixgill shark is [[ovoviviparity|ovoviviparous]], which means that the young are carried within the mother's body until the eggs hatch. They develop without a [[placenta]] to provide nourishment. The pups are born at a fairly large and developed stage at 65 to 74 cm. New pups are also born with a lighter belly than adults. This is a form of [[cryptic coloration]] or [[camouflage]] that is used to disguise the pup's appearance. The litter size ranges from 22 to 108 pups. When such a large litter hatches it is a sign that there is a high mortality rate of the young pups. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 12:05, 20 November 2007
| Bluntnose sixgill shark | |
|---|---|
| |
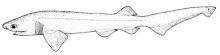
| Drawing by Dr Tony Ayling | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | H. griseus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hexanchus griseus (Bonnaterre, 1788)
| |
| |
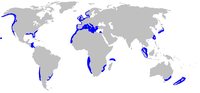
| Range of bluntnose sixgill shark (in blue) | |
Template:Sharksportal The bluntnose sixgill shark, Hexanchus griseus, often simply called the cow shark, is the largest hexanchoid shark, growing to more than 4.8 m (15.5 ft) in length.
Taxonomy
The bluntnose sixgill shark is a member of the Hexanchidae family. Many of its relatives are extinct. The living species that are closest genetically include the dogfish, the Greenland shark, as well as other six- and sevengilled sharks. There are more closely related relatives in the fossil record than living species. Some of the shark's relatives date back to 200 million years ago. This shark is a very interesting species due to it's both primitive and current physical characteristics.
Description
Skin color ranges from tan to brown, or as dark as black. It has a light colored lateral line down the sides and on the fins' edges. There are darker colored spots on the sides. The general body shape is a heavy, powerful body with a broad head with small eyes. The pupils are black and the eye color is a fluorescent blue green. As an adult the bluntnose sixgill shark can grow to a massive size. True body length is determined by the gender of the individual. Males generally average between 309 and 330 cm. Females tend to be larger, averaging between 350 and 420 cm. This shark can attain a length of up to 550 cm.

The bluntnose sixgill shark resembles many of the fossil sharks from the Triassic period. This could be due to the fact that there are a greater number of Hexicanus relatives in the fossil record than there are left alive today. They have one dorsal fin located near the caudal fin. The pectoral fins are broad with rounded edges. There are six gill slits which gives the shark its name. Most common sharks today have only 5 gill slits.
Habitat
This species typically inhabits depths greater than 90 m (300 ft), and has been recorded as deep as 1,875 m (6,150 ft). Like many deep-sea creatures, the bluntnose sixgill shark is known to undertake nightly vertical migrations (travelling surfaceward at night, returning to the depths before dawn).
The bluntnose sixgill shark can be seen at depths of 30 m (100 ft) during parts of the year in some specific places e.g. Flora Islet, near Hornby Island in British Columbia, Monterey Canyon in San Francisco Bay and in fjords in Norway. It is unknown why the shark come to these shallow depths and what they do, but they have been observed for over 20 years doing this.
Feeding patterns
Although sluggish in nature, the bluntnose sixgill shark is capable of attaining high speeds for chasing and catching its prey. Because of the bluntnose sixgill shark's large and diverse range they have a wide variety of prey items. Their diet consists of a variety of mollusks, crustaceans, Agnathans (which is a family consisting of hagfish), and sea lampreys. They also dine on Cape anchovies, Pacific salmon, various species of hake. There are also many more species that are eaten depending upon the shark's home range.
Reproduction
Very little is known about the reproductive process of bluntnose sixgill sharks. What little is known is actually scientific speculation. Many biologists believe that the male bluntnose sixgill shark's teeth are specially adapted to the courtship ritual. The male will nip at the female's gill slits using its longer-cusped teeth. This action is thought to entice the female into mating. Evidence of this theory is that female bluntnose sixgill sharks show up with seasonal scars around their gill slits, which apparently is from breeding with males. The female bluntnose sixgill shark reaches sexual maturity between the ages of 18 and 35. Males usually reach sexual maturity much younger, between the ages of 11 and 14 years old. Scientists are unsure of how the bluntnose sixgill shark reproduces but it is thought that males and females meet seasonally between the months of May and November. The gestation period is unknown but scientists believe that it is longer than 2 years. The bluntnose sixgill shark is ovoviviparous, which means that the young are carried within the mother's body until the eggs hatch. They develop without a placenta to provide nourishment. The pups are born at a fairly large and developed stage at 65 to 74 cm. New pups are also born with a lighter belly than adults. This is a form of cryptic coloration or camouflage that is used to disguise the pup's appearance. The litter size ranges from 22 to 108 pups. When such a large litter hatches it is a sign that there is a high mortality rate of the young pups.
References
- Template:IUCN2006 Database entry includes justification for why this species is near threatened
- "Hexanchus griseus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. 23 January.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2005). "Hexanchus griseus" in FishBase. 09 2005 version.
External links
- Information on H. griseus from ReefQuest Center for Shark Research