Wheatstone bridge: Difference between revisions
m →External links: Cat. |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A '''Wheatstone bridge''' is a [[measuring instrument]] invented by [[Samuel Hunter Christie]] in [[1833]] and improved and popularized by Sir [[Charles Wheatstone]] in [[1843]]. It is used to measure an unknown [[electrical resistance]] by balancing two legs of a [[bridge circuit]], one leg of which includes the unknown component. Its operation is similar to the ''original'' [[potentiometer]] except that in potentiometer circuits the meter used is a sensitive galvanometer. |
A '''Wheatstone bridge''' is a [[measuring instrument]] invented by [[Samuel Hunter Christie]] in [[1833]] and improved and popularized by Sir [[Charles Wheatstone]] in [[1843]]. It is used to measure an unknown [[electrical resistance]] by balancing two legs of a [[bridge circuit]], one leg of which includes the unknown component. Its operation is similar to the ''original'' [[potentiometer]] except that in potentiometer circuits the meter used is a sensitive galvanometer. |
||
[[image: |
[[image:Wheatstone_Bridge.svg|left|300px]] |
||
| ⚫ | In the circuit to the left, <math>R_x</math> is the unknown resistance to be measured; <math>R_1</math>, <math>R_2</math> and <math>R_3</math> are resistors of known resistance and the resistance of <math>R_2</math> is adjustable. If the ratio of the two resistances in the known leg <math>(R_2 / R_1)</math> is equal to the ratio of the two in the unknown leg <math>(R_x / R_3)</math>, then the [[voltage]] between the two midpoints will be zero and no [[Current (electricity)|current]] will flow between the midpoints. <math>R_2</math> is varied until this condition is reached. The current direction indicates if <math>R_2</math> is too high or too low. |
||
---- |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Detecting zero current can be done to extremely high accuracy (see [[Galvanometer]]). Therefore, if <math>R_1</math>, <math>R_2</math> and <math>R_3</math> are known to high precision, then <math>R_x</math> can be measured to high precision. Very small changes in <math>R_x</math> disrupt the balance and are readily detected. |
Detecting zero current can be done to extremely high accuracy (see [[Galvanometer]]). Therefore, if <math>R_1</math>, <math>R_2</math> and <math>R_3</math> are known to high precision, then <math>R_x</math> can be measured to high precision. Very small changes in <math>R_x</math> disrupt the balance and are readily detected. |
||
Revision as of 15:28, 22 May 2006
A Wheatstone bridge is a measuring instrument invented by Samuel Hunter Christie in 1833 and improved and popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone in 1843. It is used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. Its operation is similar to the original potentiometer except that in potentiometer circuits the meter used is a sensitive galvanometer.
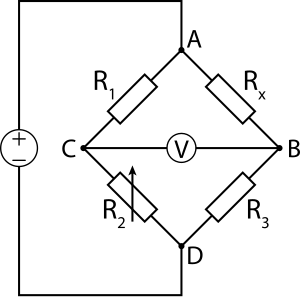
In the circuit to the left, is the unknown resistance to be measured; , and are resistors of known resistance and the resistance of is adjustable. If the ratio of the two resistances in the known leg is equal to the ratio of the two in the unknown leg , then the voltage between the two midpoints will be zero and no current will flow between the midpoints. is varied until this condition is reached. The current direction indicates if is too high or too low.
Detecting zero current can be done to extremely high accuracy (see Galvanometer). Therefore, if , and are known to high precision, then can be measured to high precision. Very small changes in disrupt the balance and are readily detected.
If the bridge is balanced, which means that the current through the galvanometer is equal to zero, the equivalent resistance of the circuit between the source voltage terminals is:
in parallel with
Alternatively, if , , and are known, but is not adjustable, the voltage or current flow through the meter can be used to calculate the value of , using Kirchhoff's circuit laws (also known as Kirchhoff's rules). This setup is frequently used in strain gauge and Resistance Temperature Detector measurements, as it is usually faster to read a voltage level off a meter than to adjust a resistance to zero the voltage.
First, we can use the first Kirchhoff rule to find the currents in junctions B and D:
Then, we use Kirchoff's second rule to find the voltage in the loops ABD and BCD:
The bridge is balanced and , so we can rewrite the second set of equations:
Then, we divide the equations and rearrange them, giving:
From the first rule, we know that and . The desired value of is now known to be given as:
If all four resistor values and the supply voltage () are known, the voltage across the bridge () can be found by working out the voltage from each potential divider and subtracting one from the other. The equation for this is:
This can be simplified to:
The Wheatstone bridge illustrates the concept of a difference measurement, which can be extremely accurate. Variations on the Wheatstone bridge can be used to measure capacitance, inductance, impedance and other quantities, such as the amount of combustible gases in a sample, with an explosimeter. The Kelvin bridge was one specially adapted for measuring very low resistances. This was invented in 1861 by William Thomson, Lord Kelvin.
The concept was extended to alternating current measurements by James Clerk Maxwell in 1865, and further improved by Alan Blumlein in about 1926.

























