White seabass: Difference between revisions
refine cat, Replaced: [[Category:Native fauna of California → [[Category:Fauna of Western United States using AWB |
GrahamBould (talk | contribs) m Layout |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = ([[William Orville Ayres|Ayres]], 1860) |
| binomial_authority = ([[William Orville Ayres|Ayres]], 1860) |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''White seabass''' or '''white weakfish''' |
'''White seabass''' or '''white weakfish''', ''Atractoscion nobilis'', is a species of [[croaker]] occurring from [[Magdalena Bay]], [[Baja California]], to [[Juneau]], [[Alaska]]. They usually travel in [[swarm|school]]s over deep rocky bottoms (0-122 m) and in and out of [[kelp]] beds. |
||
==Description== |
==Description== |
||
[[Image:Atractoscion nobilis mspc097.gif| |
[[Image:Atractoscion nobilis mspc097.gif|300px|left|thumb]] |
||
The body of the white seabass is elongate, and somewhat compressed. The head is pointed and slightly compressed. The mouth is large, with a row of small teeth in the roof; the lower jaw slightly projects. The color is bluish to gray above, with dark speckling, becoming silver below. The young have several dark vertical bars. The white seabass is closely related to the [[California corbina]], but is the only California member of the croaker family to exceed 20 pounds in weight. The largest recorded specimen was 5 feet, 83 pounds. They are most easily separated from other croakers by the presence of a ridge running the length of the belly. |
The body of the white seabass is elongate, and somewhat compressed. The head is pointed and slightly compressed. The mouth is large, with a row of small teeth in the roof; the lower jaw slightly projects. The color is bluish to gray above, with dark speckling, becoming silver below. The young have several dark vertical bars. The white seabass is closely related to the [[California corbina]], but is the only California member of the croaker family to exceed 20 pounds in weight. The largest recorded specimen was 5 feet, 83 pounds. They are most easily separated from other croakers by the presence of a ridge running the length of the belly. |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
*Much of this article is copied from [http://www.dfg.ca.gov/mrd/mspcont3.html#seabass California Marine Sportfish] by the California Department of Fish and Game, Marine Region; a public domain resource.[http://www.dfg.ca.gov/html/conditions.html#ownership] |
* Much of this article is copied from [http://www.dfg.ca.gov/mrd/mspcont3.html#seabass California Marine Sportfish] by the California Department of Fish and Game, Marine Region; a public domain resource.[http://www.dfg.ca.gov/html/conditions.html#ownership] |
||
*{{FishBase species|genus=Atractoscion|species=nobilis|year=2006|month=5}} |
* {{FishBase species|genus=Atractoscion|species=nobilis|year=2006|month=5}} |
||
[[Category:Sciaenidae]] |
[[Category:Sciaenidae]] |
||
Revision as of 19:30, 19 November 2006
| White seabass | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | A. nobilis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Atractoscion nobilis (Ayres, 1860)
| |
White seabass or white weakfish, Atractoscion nobilis, is a species of croaker occurring from Magdalena Bay, Baja California, to Juneau, Alaska. They usually travel in schools over deep rocky bottoms (0-122 m) and in and out of kelp beds.
Description
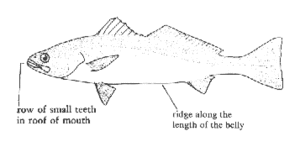
The body of the white seabass is elongate, and somewhat compressed. The head is pointed and slightly compressed. The mouth is large, with a row of small teeth in the roof; the lower jaw slightly projects. The color is bluish to gray above, with dark speckling, becoming silver below. The young have several dark vertical bars. The white seabass is closely related to the California corbina, but is the only California member of the croaker family to exceed 20 pounds in weight. The largest recorded specimen was 5 feet, 83 pounds. They are most easily separated from other croakers by the presence of a ridge running the length of the belly.
The diet of white seabass includes fishes, especially anchovies and sardines, and squid. At times, large fish are found which have eaten only Pacific mackerel. At the minimum legal length of 28 inches, the average white seabass is about 5 years of age, weighs about 7.5 pounds and has been sexually mature for at least one spawning season.
Fishing information
White seabass are fished primarily with live bait in relatively shallow water, but they will also take a fast-trolled spoon, artificial squid or bone jig. Live squid appear to be the best bait for a white seabass, but large anchovies and medium-size sardines are also good. At times, large white seabass will bite only on fairly large, live Pacific mackerel. The young of this species are exceptionally vulnerable to sport anglers for two reasons. The first is that as juveniles they inhabit shallow nearshore areas, bays, and estuaries, and the second is that they are not easily recognized as white seabass by the average angler. Commonly, these young fish are mistakenly called "sea trout" because of their sleek profile and vertical bars or "parr marks". To add to the confusion, these bars fade as the fish grows.
In California, there is a 28 inch size limit and current fishing regulations should be checked concerning bag limits.
References
- Much of this article is copied from California Marine Sportfish by the California Department of Fish and Game, Marine Region; a public domain resource.[1]
- Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Atractoscion nobilis". FishBase. May 2006 version.
