Endosteum: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
Reverting edit(s) by Samia9910 (talk) to rev. 1020187184 by Serols: Unexplained content removal (RW 16.1) |
Aura Mind33 (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The '''endosteum''' (plural endostea) is a thin vascular membrane of [[connective tissue]] that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that forms the [[medullary cavity]] of long [[bone]]s.<ref>[[Frank H. Netter|Netter, Frank H.]] (1987). ''Musculoskeletal system: anatomy, physiology, and metabolic disorders''. Summit, New Jersey: Ciba-Geigy Corporation {{ISBN|0-914168-88-6}}, p.171</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Definition of ENDOSTEUM|url=https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/endosteum|website=www.merriam-webster.com|language=en}}</ref> |
The '''endosteum''' (plural endostea) is a thin vascular membrane of [[connective tissue]] that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that forms the [[medullary cavity]] of long [[bone]]s.<ref>[[Frank H. Netter|Netter, Frank H.]] (1987). ''Musculoskeletal system: anatomy, physiology, and metabolic disorders''. Summit, New Jersey: Ciba-Geigy Corporation {{ISBN|0-914168-88-6}}, p.171</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Definition of ENDOSTEUM|url=https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/endosteum|website=www.merriam-webster.com|language=en}}</ref> |
||
This endosteal surface is usually resorbed during long periods of [[malnutrition]], resulting in less [[cortical bone|cortical]] thickness. |
This endosteal surface is usually resorbed during long periods of [[malnutrition]], resulting in less [[cortical bone|cortical]] thickness.{{Citation needed|date=December 2021}} |
||
The outer surface of a bone is lined by a thin layer of connective tissue that is very similar in [[morphology (biology)|morphology]] and function to endosteum. It is called the [[periosteum]], or the periosteal surface. During [[bone growth]], the width of the bone increases as [[osteoblasts]] lay new bone tissue at the periosteum. To prevent the bone from becoming unnecessarily thick, [[osteoclasts]] resorb the bone from the endosteal side. |
The outer surface of a bone is lined by a thin layer of connective tissue that is very similar in [[morphology (biology)|morphology]] and function to endosteum. It is called the [[periosteum]], or the periosteal surface. During [[bone growth]], the width of the bone increases as [[osteoblasts]] lay new bone tissue at the periosteum. To prevent the bone from becoming unnecessarily thick, [[osteoclasts]] resorb the bone from the endosteal side. |
||
Revision as of 09:30, 31 December 2021
| Endosteum | |
|---|---|
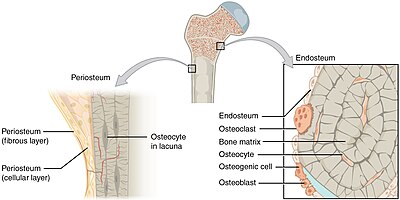 Endosteum covers the inside of bones, and surrounds the medullary cavity. | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA98 | A02.0.00.038 |
| TA2 | 387 |
| TH | H2.00.03.7.00022 |
| FMA | 32692 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The endosteum (plural endostea) is a thin vascular membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that forms the medullary cavity of long bones.[1][2]
This endosteal surface is usually resorbed during long periods of malnutrition, resulting in less cortical thickness.[citation needed]
The outer surface of a bone is lined by a thin layer of connective tissue that is very similar in morphology and function to endosteum. It is called the periosteum, or the periosteal surface. During bone growth, the width of the bone increases as osteoblasts lay new bone tissue at the periosteum. To prevent the bone from becoming unnecessarily thick, osteoclasts resorb the bone from the endosteal side.
Additional images
-
Long bone
References
- ^ Netter, Frank H. (1987). Musculoskeletal system: anatomy, physiology, and metabolic disorders. Summit, New Jersey: Ciba-Geigy Corporation ISBN 0-914168-88-6, p.171
- ^ "Definition of ENDOSTEUM". www.merriam-webster.com.
External links
- Anatomy photo: Musculoskeletal/bone/structure1/structure2 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Bone, structure (LM, High)"
- Image at dal.ca

