2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran: Difference between revisions
m →Preparation: Typo |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== Preparation == |
== Preparation == |
||
The synthesis of 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran via [[Gamma-Butyrolactone|γ-butyrolactone]] and the [[Meerwein salt]] (triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate) in [[diethyl ether]] was first described by [[Hans Meerwein]] and co-workers.<ref name="Meerwein">{{citation |author=H. Meerwein |author2=P. Borner |author3=O. Fuchs |author4=H.J. Sasse |author5=H. Schrodt |author6=J. Spille |periodical=Chem. Ber.|title=Reaktionen mit Alkylkationen|volume=89|issue=9|pages=2060–2079|date= 1956|language=German|doi=10.1002/cber.19560890907 |
The synthesis of 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran via [[Gamma-Butyrolactone|γ-butyrolactone]] and the [[Meerwein salt]] (triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate) in [[diethyl ether]] was first described by [[Hans Meerwein]] and co-workers.<ref name="Meerwein">{{citation |author=H. Meerwein |author2=P. Borner |author3=O. Fuchs |author4=H.J. Sasse |author5=H. Schrodt |author6=J. Spille |periodical=Chem. Ber.|title=Reaktionen mit Alkylkationen|volume=89|issue=9|pages=2060–2079|date= 1956|language=German|doi=10.1002/cber.19560890907 |
||
}}</ref> In the reaction the electrophilic ethyl cation |
}}</ref> In the reaction the electrophilic ethyl cation attacks the [[Carbonyl group|carbonyl oxygen]] and forms the stable but extraordinarily hygroscopic ''O''-ethyl-γ-butyrolactonium tetrafluoroborate ([[melting point]] 42 °C). The compound dissolves in [[dichloromethane]], [[chloroform]] and [[1,2-Dichloroethane|1,2-dichloroethane]] but is insoluble in diethyl ether, benzene and [[tetrachloromethane]]. The [[onium salt]] reacts practically quantitatively with an ethanolate anion from sodium ethoxide in [[ethanol]] forming 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran. |
||
:[[File:2,2-DETHF Meerwein.svg|500px|Synthese von 2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran nach Meerwein]] |
:[[File:2,2-DETHF Meerwein.svg|500px|Synthese von 2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran nach Meerwein]] |
||
Latest revision as of 07:42, 18 June 2024

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Diethoxyoxolane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.161.490 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H16O3 | |
| Molar mass | 160.213 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a cyclic orthoester which can be reacted with diols to biodegradable polyorthoesters.
Preparation
[edit]The synthesis of 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran via γ-butyrolactone and the Meerwein salt (triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate) in diethyl ether was first described by Hans Meerwein and co-workers.[1] In the reaction the electrophilic ethyl cation attacks the carbonyl oxygen and forms the stable but extraordinarily hygroscopic O-ethyl-γ-butyrolactonium tetrafluoroborate (melting point 42 °C). The compound dissolves in dichloromethane, chloroform and 1,2-dichloroethane but is insoluble in diethyl ether, benzene and tetrachloromethane. The onium salt reacts practically quantitatively with an ethanolate anion from sodium ethoxide in ethanol forming 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran.
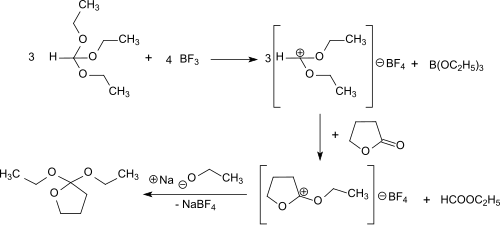
2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran can also be produced in a solvent-free one-pot reaction using γ-butyrolactone, orthoformic triethyl ester and gaseous boron trifluoride. This route avoids the use of diethyl ether and its side-products and sensible intermediates.[2]
First diethoxymethylium tetrafluoroborate is formed from the triethyl orthoformate and boron trifluoride at -30 °C. This electrophilically attacks the carbonyl group of the γ-butyrolactone and the O-ethyl-γ-butyrolactonium tetrafluoroborate. The addition of sodium ethoxide leads to the final product, which is obtained after distillation in 69% overall yield.
The reaction proceeds under gentle conditions (<0 °C) and the almost quantitative addition of ethanolate to O-ethyl-γ-butyrolactonium tetrafluoroborate can also be catalyzed by bases such as ammonia and triethylamine.
Properties
[edit]2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a clear liquid which boils at 10 mm Hg vacuum at 60 - 61.5 °C according to the original literature.[1]
Application
[edit]The cyclic orthoester 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a reactive bifunctional monomer which forms biodegradable polyorthoesters of the type POE-I by transesterification with α, ω-diols.
Polyorthoesters are used as embedding media for pharmaceuticals in depot drug dosage forms for controlled drug release by surface erosion under physiological conditions.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ a b H. Meerwein; P. Borner; O. Fuchs; H.J. Sasse; H. Schrodt; J. Spille (1956), "Reaktionen mit Alkylkationen", Chem. Ber. (in German), vol. 89, no. 9, pp. 2060–2079, doi:10.1002/cber.19560890907
- ^ US 4990631, K. Alster, "Reacting trialkyl orthoformate with boron trifluoride and lactone, then with alkoxide or alkanol and base", published 1991-02-05, assigned to Alza Corp.
- ^ Jorge Heller (1997), A.J. Domb; J. Kost; D.M. Wiseman (eds.), "6. Poly (Ortho Esters)", Handbook of Biodegradable Polymers, Harwood Academic Press, pp. 99–118, ISBN 90-5702-153-6