Electronic oscillator: Difference between revisions
→Types of electronic oscillator: Added link |
|||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
* [http://www.torex-usa.com/knowledgeBase.do?vo.productCategoryId=10&target=categoryQuestions Oscillators Knowledge Base] |
|||
* [http://www.howstuffworks.com/oscillator.htm Howstuffworks: oscillator]. |
* [http://www.howstuffworks.com/oscillator.htm Howstuffworks: oscillator]. |
||
* [http://www.ieee.li/pdf/viewgraphs_oscillator_oddities.pdf Oscillator Oddities]. |
* [http://www.ieee.li/pdf/viewgraphs_oscillator_oddities.pdf Oscillator Oddities]. |
||
Revision as of 12:36, 8 October 2008
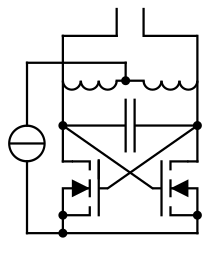
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a repetitive electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave.
A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an electronic oscillator that generates an AC waveform between 0.1 Hz and 10 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesizers, to distinguish it from an audio frequency oscillator.
Oscillators designed to produce a high-power AC output from a DC supply are usually called inverters.
Types of electronic oscillator
There are two main types of electronic oscillator: the harmonic oscillator and the relaxation oscillator.
Harmonic oscillator
The harmonic oscillator produces a sinusoidal output. The basic form of a harmonic oscillator is an electronic amplifier with the output attached to a narrow-band electronic filter, and the output of the filter attached to the input of the amplifier. When the power supply to the amplifier is first switched on, the amplifier's output consists only of noise. The noise travels around the loop, being filtered and re-amplified until it increasingly resembles the desired signal.
A piezoelectric crystal (commonly quartz) may be coupled to the filter to stabilise the frequency of oscillation, resulting in a crystal oscillator.
There are many ways to implement harmonic oscillators, because there are different ways to amplify and filter. For example:
- Armstrong oscillator
- Hartley oscillator
- Colpitts oscillator
- Clapp oscillator
- Delay line oscillator
- Pierce oscillator (crystal)
- Phase-shift oscillator
- RC oscillator (Wien Bridge and "Twin-T")
- cross-coupled LC oscillator
- Vačkář oscillator
- Opto-Electronic Oscillator
Relaxation oscillator
The relaxation oscillator is often used to produce a non-sinusoidal output, such as a square wave or sawtooth. The oscillator contains a nonlinear component such as a transistor that periodically discharges the energy stored in a capacitor or inductor, causing abrupt changes in the output waveform.
Square-wave relaxation oscillators can be used to provide the clock signal for sequential logic circuits such as timers and counters, although crystal oscillators are often preferred for their greater stability.
Triangle-wave or sawtooth oscillators are used in the timebase circuits that generate the horizontal deflection signals for cathode ray tubes in analogue oscilloscopes and television sets. In function generators, this triangle wave may then be further shaped into a close approximation of a sine wave.
Other types of relaxation oscillators include the multivibrator and the rotary traveling wave oscillator.
See also
- Crystal oscillator
- Electronic circuit
- RLC circuit
- Voltage-controlled oscillator
- Injection locked oscillator
- Ring oscillator
- Opto-Electronic Oscillator
