Giardia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Undid revision 276639828 by 71.191.66.21 (talk) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| name = ''Giardia'' |
| name = ''Giardia'' |
||
| image = Giardia lamblia SEM 8698 lores.jpg |
| image = Giardia lamblia SEM 8698 lores.jpg |
||
| image_width = |
| image_width =100 and i was so totally here.hehehe |
||
| image_caption = ''Giardia'' [[trophozoite]], [[Scanning electron microscope|SEM]] |
| image_caption = ''Giardia'' [[trophozoite]], [[Scanning electron microscope|SEM]] |
||
| domain = [[Eukaryota]] |
| domain = [[Eukaryota]] |
||
Revision as of 00:45, 12 March 2009
| Giardia | |
|---|---|
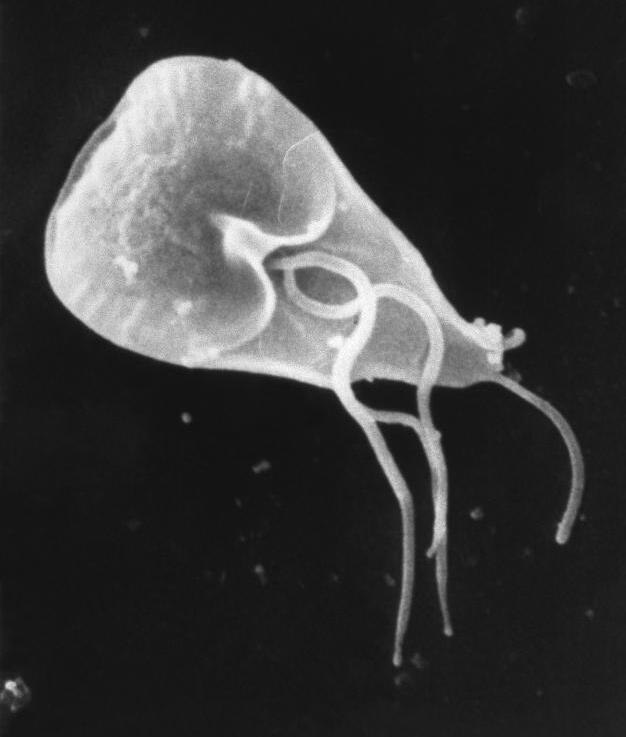
| |
| Giardia trophozoite, SEM | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Kunstler, 1882
|
| species | |
|
Giardia agilis | |
Giardia is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates between an actively swimming trophozoite and an infective, resistant cyst. The genus was named after French zoologist Alfred Mathieu Giard.
Characteristics
Like other diplomonads, Giardia have two nuclei, each with four associated flagella and lack both mitochondria and a Golgi apparatus. However they are now known to possess mitochondrial relics, called mitosomes. These are not used in ATP synthesis the way mitochondria are, but are involved in the maturation of iron-sulfur proteins.[1]. The synapomorphies of genus Giardia include cells with duplicate organelles, absence of cytostomes, and ventral adhesive disc[2]
Systematics
About 40 species have been described from different animals, but many of them are probably synonyms[3]. Currently, five to six morphologically distinct species are recognised[4]. Giardia lamblia (=G. intestinalis, =G. duodenalis) is a well-known human parasite, G. muris is found from other mammals, G. ardeae and G. psittaci from birds, G. agilis from amphibians and G. microti from voles[5]. Other described, (but not certainly valid) species include:
- Giardia beckeri
- Giardia beltrani
- Giardia botauri
- Giardia bovis
- Giardia bradypi
- Giardia canis
- Giardia caprae
- Giardia cati
- Giardia caviae
- Giardia chinchillae
- Giardia dasi
- Giardia equii
- Giardia floridae
- Giardia hegneri
- Giardia herodiadis
- Giarida hyderabadensis
- Giardia irarae
- Giardia marginalis
- Giardia melospizae
- Giardia nycticori
- Girdia ondatrae
- Giardia otomyis
- Giardia pitymysi
- Giardia pseudoardeae
- Giardia recurvirostrae
- Giardia sanguinis
- Giardia serpentis
- Giardia simoni
- Giardia sturnellae
- Giardia suricatae
- Giardia tucani
- Giardia varani
- Giardia viscaciae
- Giardia wenyoni
[6]. Genetic and biochemical studies have revealed the heterogenity of Giardia lamblia, which contains probably at least eight lineages or cryptic species[7].
See also
References
- ^ Tovar J, León-Avila G, Sánchez LB, et al Mitochondrial remnant organelles of Giardia function in iron-sulphur protein maturation Nature vol.426, 6963 2003
- ^ Cepicka, Ivan. 2008. Fornicata. Version 02 September 2008 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Fornicata/121182/2008.09.02 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/
- ^ Meyer,E.A., Radulescu,S. Giardia and Giardasis. In: Advances in Parasitology, vol.17, Academic Press, 1979
- ^ R.C.Brusca, G.J.Brusca. Invertebrates. Sinauer Associates, 2 ed.(2003)
- ^ Adam,R.D. Biology of Giardia. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, July 2001, p. 447–475
- ^ Tree of Life Web Project. 2008. Giardia Kunstler. Version 02 September 2008 (temporary). http://tolweb.org/Giardia/97370/2008.09.02 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/
- ^ R.C.A. Thompson and P.T. Monis, Variation in Giardia: implications for taxonomy and epidemiology. Advances in Parasitology 58, 69-137 (2004)
