JDBC driver: Difference between revisions
m clean up, typos fixed: e.g → e.g. using AWB |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
*Almost any database for which ODBC driver is installed, can be accessed. |
*Almost any database for which ODBC driver is installed, can be accessed. |
||
*A type 1 driver is easy to install. |
*A type 1 driver is easy to install. |
||
hj |
|||
====Disadvantages==== |
====Disadvantages==== |
||
Revision as of 11:38, 15 June 2009
This article possibly contains original research. (September 2007) |
A JDBC driver is a software component enabling a Java application to interact with a database.[1]
To connect with individual databases, JDBC (the Java Database Connectivity API) requires drivers for each database. The JDBC driver gives out the connection to the database and implements the protocol for transferring the query and result between client and database.
Type 1 Driver - JDBC-ODBC bridge
The JDBC type 1 driver, also known as the JDBC-ODBC bridge, is a database driver implementation that employs the ODBC driver to connect to the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into ODBC function calls.
The driver is platform-dependent as it makes use of ODBC which in turn depends on native libraries of the underlying operating system the JVM is running upon. Also, use of this driver leads to other installation dependencies; for example, ODBC must be installed on the computer having the driver and the database must support an ODBC driver. The use of this driver is discouraged if the alternative of a pure-Java driver is available. The other implication is that any application using a type 1 driver is non-portable given the binding between the driver and platform.
Functions
- Translates query obtained by JDBC into corresponding ODBC query, which is then handled by the ODBC driver.
- Sun provides a JDBC-ODBC Bridge driver. sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver. This driver is native code and not Java, and is closed source.
- Client -> JDBC Driver -> ODBC Driver -> Database
- There is some overhead associated with the translation work to go from JDBC to ODBC.
Advantages
- Almost any database for which ODBC driver is installed, can be accessed.
- A type 1 driver is easy to install.
hj
Disadvantages
- Performance overhead since the calls have to go through the JDBC overhead bridge to the ODBC driver, then to the native db connectivity interface.
- The ODBC driver needs to be installed on the client machine.
- Considering the client-side software needed, this might not be suitable for applets.
- Will not be suitable for internet applications.
Type 2 Driver - Native-API Driver specification

The JDBC type 2 driver, also known as the Native-API driver, is a database driver implementation that uses the client-side libraries of the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into native calls of the database API.
The type 2 driver is not written entirely in Java as it interfaces with non-Java code that makes the final database calls. The driver is compiled for use with the particular operating system. For platform interoperability, the Type 4 driver, being a full-Java implementation, is preferred over this driver.
However the type 2 driver provides more functionality and better performance than the type 1 driver as it does not have the overhead of the additional ODBC function calls.
Advantages
- Better performance than Type 1 Driver (JDBC-ODBC bridge).
Disadvantages
- The vendor client library needs to be installed on the client machine.
- Cannot be used in web-based application due the client side software needed.
- Not all databases have a client side library
Type 3 Driver - Network-Protocol Driver
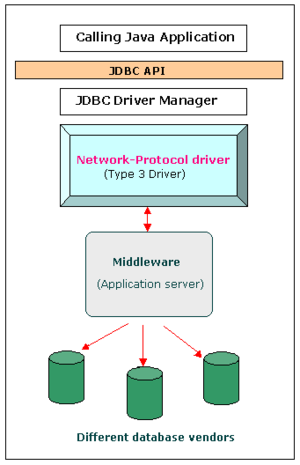
The JDBC type 3 driver, also known as the Pure Java Driver for Database Middleware, is a database driver implementation which makes use of a middle tier between the calling program and the database. The middle-tier (application server) converts JDBC calls directly or indirectly into the vendor-specific database protocol.
This differs from the type 4 driver in that the protocol conversion logic resides not at the client, but in the middle-tier. Like type 4 drivers, the type 3 driver is written entirely in Java. The same driver can be used for multiple databases. It depends on the number of databases the middleware has been configured to support. The type 3 driver is platform-independent as the platform-related differences are taken care by the middleware. Also, making use of the middleware provides additional advantages of security and firewall access.
Functions
- Follows a three tier communication approach.
- Can interface to multiple databases - Not vendor specific.
- The JDBC Client driver written in java, communicates with a middleware-net-server using a database independent protocol, and then this net server translates this request into database commands for that database.
- Thus the client driver to middleware communication is database independent.
- Client -> JDBC Driver -> Middleware-Net Server -> Any Database
Advantages
- Since the communication between client and the middleware server is database independent, there is no need for the vendor db library on the client machine. Also the client to middleware need not be changed for a new database.
- The Middleware Server (which can be a full fledged J2EE Application server) can provide typical middleware services like caching (connections, query results, and so on), load balancing, logging, auditing etc.
- Eg. for the above include jdbc driver features in Weblogic.
- Can be used in internet since there is no client side software needed.
- At client side a single driver can handle any database. (It works provided the middlware supports that database!)
Disadvantages
- Requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
- An extra layer added may result in a time-bottleneck. But typically this is overcome by providing efficient middleware services described above.
Type 4 Driver - Native-Protocol Driver

The JDBC type 4 driver, also known as the Direct to Database Pure Java Driver, is a database driver implementation that converts JDBC calls directly into the vendor-specific database protocol.
The type 4 driver is written completely in Java and is hence platform independent. It is installed inside the Java Virtual Machine of the client. It provides better performance over the type 1 and 2 drivers as it does not have the overhead of conversion of calls into ODBC or database API calls. Unlike the type 3 drivers, it does not need associated software to work.
As the database protocol is vendor-specific, separate drivers, usually vendor-supplied, need to be used to connect to the database.
Functions
- Type 4 drivers are entirely written in Java that communicate directly with a vendor's database, usually through socket connections. No translation or middleware layers are required, improving performance.
- The driver converts JDBC calls into the vendor-specific database protocol so that client applications can communicate directly with the database server.
- Completely implemented in Java to achieve platform independence.
- e.g. include the widely used Oracle thin driver - oracle.jdbc.driver. OracleDriver which connect to jdbc:oracle:thin URL format.
- Client Machine -> Native protocol JDBC Driver -> Database server
Advantages
- These drivers don't translate the requests into an intermediary format (such as ODBC), nor do they need a middleware layer to service requests. Thus the performance may be considerably improved.
- All aspects of the application to database connection can be managed within the JVM; this can facilitate easier debugging.
Disadvantage
- At client side, a separate driver is needed for each database.
