Antonie van Leeuwenhoek: Difference between revisions
Flagged the second paragraph of the "Life" section for its informal tone and unverified statements |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
Van Leeuwenhoek was the son of the basket maker Philip Thonisz and Grietje Jacobs. At age 16, he secured an apprenticeship with a Scottish [[cloth merchant]] in Amsterdam. In 1653 Van Leeuwenhoek saw his first simple microscope, a [[magnifying glass]] mounted on a small stand used by textile merchants, capable of magnifying to a power of 3. He soon acquired one for his own use. In 1654, he left Amsterdam, moved back to Delft for the rest of his life and started his own lucrative [[drapery]] business there. On July 11, he married Barbara de Mey, the daughter of a cloth merchant and settled as a linen-draper. He was registered as Anthoni Leeuwenhouck. Four out of his five children died young. In 1660, he was appointed chamberlain of the [[schepen|Lord Regents of Delft]]. In 1666 his wife died and in 1671 he married Cornelia Swalmius, the daughter of a minister. Van Leeuwenhoek outlived his second wife, who died in 1694.<ref>Life and work of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek of Delft in Holland; 1632-1723 (1980) Published by the Municipal Archives Delft, p. 3.</ref> |
Van Leeuwenhoek was the son of the basket maker Philip Thonisz and Grietje Jacobs. At age 16, he secured an apprenticeship with a Scottish [[cloth merchant]] in Amsterdam. In 1653 Van Leeuwenhoek saw his first simple microscope, a [[magnifying glass]] mounted on a small stand used by textile merchants, capable of magnifying to a power of 3. He soon acquired one for his own use. In 1654, he left Amsterdam, moved back to Delft for the rest of his life and started his own lucrative [[drapery]] business there. On July 11, he married Barbara de Mey, the daughter of a cloth merchant and settled as a linen-draper. He was registered as Anthoni Leeuwenhouck. Four out of his five children died young. In 1660, he was appointed chamberlain of the [[schepen|Lord Regents of Delft]]. In 1666 his wife died and in 1671 he married Cornelia Swalmius, the daughter of a minister. Van Leeuwenhoek outlived his second wife, who died in 1694.<ref>Life and work of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek of Delft in Holland; 1632-1723 (1980) Published by the Municipal Archives Delft, p. 3.</ref> |
||
=={{story}} |
|||
Van Leeuwenhoek did not learn Latin, or attend university, but in 1669 he obtained a degree in [[surveying]]; it is possible he was involved in Subdivision Plans for the city of Delft. Demonstrable is his appointment in 1676 as a [[bailiff]]. In 1679 he got a post as a [[gauger]], an inspector of wine and beer at the local publicans, who were heavily taxed for the amount that was sold. Obviously the [[burgomaster]]s gave Van Leeuwenhoek cushy jobs, usually called [[sinecure]]s, as he was a reliable and very smart man. |
Van Leeuwenhoek did not learn Latin, or attend university, but in 1669 he obtained a degree in [[surveying]]; it is possible he was involved in Subdivision Plans for the city of Delft. Demonstrable is his appointment in 1676 as a [[bailiff]]. In 1679 he got a post as a [[gauger]], an inspector of wine and beer at the local publicans, who were heavily taxed for the amount that was sold. Obviously the [[burgomaster]]s gave Van Leeuwenhoek cushy jobs, usually called [[sinecure]]s, as he was a reliable and very smart man. |
||
Revision as of 20:14, 13 August 2009
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek | |
|---|---|
 Portrait of Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) by Jan Verkolje | |
| Born | October 24, 1632 |
| Died | August 30, 1723 (aged 90) |
| Nationality | Dutch |
| Known for | Discovery of protozoa First red blood cell description |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Microscopist |
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek (in Dutch also Anthonie, Antoni, or Theunis, in English, Antony or Anton) [1] (born on October 24, 1632 – baptized on November 4, and buried on August 30, 1723) was a Dutch tradesman and scientist from Delft, the Netherlands. He is commonly known as "the Father of Microbiology", and considered to be the first microbiologist. He is best known for his work on the improvement of the microscope and for his contributions towards the establishment of microbiology. Using his handcrafted microscopes he was the first to observe and describe single celled organisms, which he originally referred to as animalcules, and which we now refer to as microorganisms. He was also the first to record microscopic observations of muscle fibers, bacteria, spermatozoa and blood flow in capillaries (small blood vessels). Van Leeuwenhoek never wrote a book, just letters.
Life

Van Leeuwenhoek was the son of the basket maker Philip Thonisz and Grietje Jacobs. At age 16, he secured an apprenticeship with a Scottish cloth merchant in Amsterdam. In 1653 Van Leeuwenhoek saw his first simple microscope, a magnifying glass mounted on a small stand used by textile merchants, capable of magnifying to a power of 3. He soon acquired one for his own use. In 1654, he left Amsterdam, moved back to Delft for the rest of his life and started his own lucrative drapery business there. On July 11, he married Barbara de Mey, the daughter of a cloth merchant and settled as a linen-draper. He was registered as Anthoni Leeuwenhouck. Four out of his five children died young. In 1660, he was appointed chamberlain of the Lord Regents of Delft. In 1666 his wife died and in 1671 he married Cornelia Swalmius, the daughter of a minister. Van Leeuwenhoek outlived his second wife, who died in 1694.[2]
==
This article is written like a story. |
Van Leeuwenhoek did not learn Latin, or attend university, but in 1669 he obtained a degree in surveying; it is possible he was involved in Subdivision Plans for the city of Delft. Demonstrable is his appointment in 1676 as a bailiff. In 1679 he got a post as a gauger, an inspector of wine and beer at the local publicans, who were heavily taxed for the amount that was sold. Obviously the burgomasters gave Van Leeuwenhoek cushy jobs, usually called sinecures, as he was a reliable and very smart man.
Early involvement with the microscope


Van Leeuwenhoek's interest in microscopes and a familiarity with glass processing led to one of the most significant, and simultaneously well-hidden, technical insights in the history of science. By placing the middle of a small rod of soda lime glass in a hot flame, Van Leeuwenhoek could pull the hot section apart like taffy to create two long whiskers of glass. By then reinserting the end of one whisker into the flame, he could create a very small, high-quality glass sphere. These spheres became the lenses of his microscopes, with the smallest spheres providing the highest magnifications. An experienced businessman, Leeuwenhoek realized that if his simple method for creating the critically important lens was revealed, the scientific community of his time would likely disregard or even forget his role in microscopy. He therefore allowed others to believe that he was laboriously spending most of his nights and free time grinding increasingly tiny lenses to use in microscopes, even though this belief conflicted both with his construction of hundreds of microscopes and his habit of building a new microscope whenever he chanced upon an interesting specimen that he wanted to preserve.
Van Leeuwenhoek used samples and measurements to estimate numbers of microorganisms in units of water.[3][4] Van Leeuwenhoek made good use of the huge lead provided by his method. He studied a broad range of microscopic phenomena, and shared the resulting observations freely with groups such as the English Royal Society.[5] Such work firmly established his place in history as one of the first and most important explorers of the microscopic world.
Eventual recognition by the English Royal Society
After developing his method for creating powerful lenses and applying them to a thorough study of the microscopic world, Van Leeuwenhoek was introduced via correspondence to the English Royal Society by the famous Dutch Physician Reinier de Graaf. He soon began to send copies of his recorded microscopic observations to the Royal Society. In 1673 his earliest observations were published by the Royal Society in its journal: Philosophical Transactions. Amongst these published observations were Van Leeuwenhoek's accounts of bee mouthparts and stings.
Despite the initial success of Van Leeuwenhoek's relationship with the Royal Society, this relationship was soon severely strained. In 1676 his credibility was questioned when he sent the Royal Society a copy of his first observations of microscopic single-celled organisms. Previously, the existence of single-celled organisms was entirely unknown. Thus, even with his established reputation with the Royal Society as a reliable observer, his observations of microscopic life were initially met with skepticism. Eventually, in the face of Van Leeuwenhoek's insistence, the Royal Society arranged to send an English vicar, as well as a team of respected jurists and doctors, to Delft, to determine whether it was in fact Van Leeuwenhoek's ability to observe and reason clearly, or perhaps the Royal Society's theories of life itself that might require reform. Finally in 1680, Van Leeuwenhoek's observations were fully vindicated by the Society.

Van Leeuwenhoek's vindication resulted in his appointment as a Fellow of the Royal Society in that year. After his appointment to the Society, he wrote approximately 560 letters to the Society and other scientific institutions over a period of 50 years. These letters dealt with the subjects he had investigated. Even when dying, Van Leeuwenhoek kept sending letters full of observations to London. The last few also contained a precise description of his own illness. He suffered from a rare disease, an uncontrolled movement of the midriff, which is now named Van Leeuwenhoek's disease.[6] He died at the age of 90, on August 26, 1723 and was buried four days later in the Oude Kerk (Delft).
In 1981 the British microscopist Brian J. Ford found that Van Leeuwenhoek's original specimens had survived in the collections of the Royal Society of London.[7] They were found to be of high quality, and were all well preserved. Ford carried out observations with a range of microscopes, adding to our knowledge of Van Leeuwenhoek's work.
Discoveries
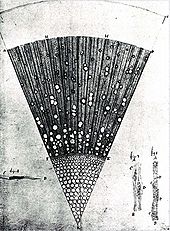
During his lifetime Van Leeuwenhoek ground over 500 optical lenses. He also created over 400 different types of microscopes, only nine of which still exist today. His microscopes were made of silver or copper metal frames holding hand-ground lenses. Those that have survived the years are able to magnify up to 275 times. It is suspected, though, that Van Leeuwenhoek possessed some microscopes that could magnify up to 500 times. Although he has been widely regarded as a dilettante or amateur, his scientific research was of remarkably high quality.[8]
Van Leeuwenhoek's main discoveries are:
- the infusoria (protists in modern zoological classification), in 1674
- the bacteria, (e.g. large Selenomonads from the human mouth), in 1676
- the spermatozoa in 1677. Van Leeuwenhoek had troubles with Dutch theologists about his practice.
- the banded pattern of muscular fibers, in 1682.[9]
He was visited by Leibniz, William III of Orange and his wife, the Amsterdam burgomaster Johan Huydecoper, the latter very interested in collecting and growing plants for the Hortus Botanicus Amsterdam and all gazed at the tiny creatures. Nicolaes Witsen sent him a map of Tartaria and a mineral found near the origin of the river Amur.[10] In 1698 Van Leeuwenhoek was invited in the boat of tsar Peter the Great, who went off to Delft, curiously. On the occasion Van Leeuwenhoek presented the tsar an "eel-viewer", so Peter could study the blood circulation, whenever he wanted.
Lenses secret
With skills, however, Van Leeuwenhoek maintained throughout his life that there were aspects of their construction "which I only keep for myself", including in particular his most critical secret of how he created lenses. For a long time nobody could reconstruct Van Leeuwenhoek's know-how. But in the 1950s, C.L. Stong used thin glass thread fusing instead of polishing, and successfully created some working samples of a Leeuwenhoek design microscope.[11] Such a method was also discovered independently by A.Mosolov and A.Belkin in the Novosibirsk State Medical Institute.[12]
Religious interpretations of Van Leeuwenhoek's discoveries
Van Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch Reformed Calvinist.[13] He often referred with reverence to the wonders God designed in making creatures great and small. He believed that his amazing discoveries were merely further proof of the great wonder of God's creation.[14][15]
Van Leeuwenhoek's discoveries of how smaller organisms procreate just as larger organisms do, did eventually overturn the traditional belief of the time in the spontaneous generation of such organisms. This belief was generally held by the 17th century scientific community, and was also tacitly endorsed by the 17th century Church. Still, the Church's position on the exact nature of the spontaneous generation of smaller organisms was ambivalent.[16] Possibly because Van Leeuwenhoek's discoveries of microscopic life appeared at the time to pose no direct challenge to any Church doctrines such as the doctrine of creationism, the Church made no effort to challenge or question any of Van Leeuwenhoek's discoveries in any way.
Possible Vermeer connection

Van Leeuwenhoek was a contemporary of another famous Delft citizen, painter Johannes Vermeer, who was baptized just four days earlier. It has been suggested that he is the man portrayed in two of Vermeer's paintings of the late 1660s, The astronomer and The Geographer. However, others argue that there appears to be little physical similarity. Because they were both relatively important men in a city with only 24,000 inhabitants, it is likely that they were at least acquaintances. Also, it is known that Van Leeuwenhoek acted as the executor when the painter died in 1675. [17]
In A Short History of Nearly Everything (p. 236) Bill Bryson alludes to rumors that Vermeer's mastery of light and perspective came from use of a camera obscura produced by Van Leeuwenhoek. This is one of the examples of the controversial Hockney–Falco thesis, which claims that some of the Old Masters used optical aids to produce their masterpieces.
Footnotes
- ^ Leeuwenhoek was christened as Thonis and always signed his name Antonij, which corresponds with Antony in modern English. His given name can also be found written as Anton, Anthon, Anthony, Antonie, Antony, Anthonie, Antoni, Antonio and Anthoni. Leeuwenhoek, believing that he was by then an established figure, added a 'van' to his name in 1686. See http://www.archief.delft.nl/
- ^ Life and work of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek of Delft in Holland; 1632-1723 (1980) Published by the Municipal Archives Delft, p. 3.
- ^ Egerton, F. N. 1967. Van Leeuwenhoek as a founder of animal demography. Journal of the History of Biology 1:1–22.
- ^ Frank N. Egerton (2006) A History of the Ecological Sciences, Part 19: Leeuwenhoek's Microscopic Natural History. Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America: Vol. 87, No. 1, pp. 47-58. doi:10.1890/0012-9623(2006)87[47:AHOTES]2.0.CO;2
- ^ UCMP Hooke bio
- ^ Life and work of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek of Delft in Holland; 1632-1723 (1980) Published by the Municipal Archives Delft, p. 9
- ^ The discovery by Brian J Ford of Leeuwenhoek's original specimens, from the dawn of microscopy in the 16th century
- ^ Ford, Brian J. (1992), From Dilettante to Diligent Experimenter: a Reappraisal of Leeuwenhoek as microscopist and investigator, Biology History, 5 (3), available at http://www.brianjford.com/a-avl01.htm
- ^ A disease in the city of Kampen (1736, The Netherlands) which originated (caused) by "little animals". These 'bloedloze dieren' (bloodless animals, the Invertebrata) are - most likely - the little animals described in the work of Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (Evert Valk, a physician about an epidemic in the city of Kampen {The Netherlands} during the year 1736)
- ^ Driessen, J. (1996) Tsaar Peter de Grote en zijn Amsterdamse vrienden, p. 35, 95, 96.
- ^ A glass-sphere microscope
- ^ A.Mosolov (1980). "Secret of Antony van Leeuwenhoek?". Nauka i Zhizn (Science and Life). 09–1980: 80–2.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ The religious affiliation of Biologist A. van Leeuwenhoek
- ^ "The Religion of Antony van Leeuwenhoek". 2006. Retrieved 2006-04-23.
- ^ A. Schierbeek, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of the Collected Letters of A. v. Leeuwenhoek, Formerly Lecturer in the History of Biology in the University of Leyden, Measuring the Invisible World: The Life and Works of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek F R S, Abelard-Schuman (London and New York, 1959), QH 31 L55 S3, LC 59-13233. This book (223 pp.) contains excerpts of Leeuwenhoek’s letters and focuses on his priority in several new branches of science, but makes several important references to his spiritual life and motivation.
- ^ "Catholic Apologetics International/ Robert Sungenis". 2006. Retrieved 2006-04-23.
- ^ Van Berkel, K. (February 24 1996). Vermeer, Van Leeuwenhoek en De Astronoom. Vrij Nederland (Dutch magazine), p. 62–67.
See also
External links
- Dutch online biography of Van Leeuwenhoek
- Vermeer connection website
- University of California, Berkeley article on Van Leeuwenhoek
- Works by Antoni van Leeuwenhoek at Project Gutenberg
- Retrospective paper on the Leeuwenhoek research by Brian J. Ford.
- Images seen through a van Leeuwenhoek microscope by Brian J. Ford.
- Instructions on making a Van Leeuwenhoek Microscope Replica by Alan Shinn
