Quassin: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation ( |
reference did not indicate compound was bitterest, changed to reflect reference |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Quassin''' is a white bitter, crystalline substance extracted from the [[quassia]] tree. It is the |
'''Quassin''' is a white bitter, crystalline substance extracted from the [[quassia]] tree. It is one of the most bitter substances found in nature with a bitter threshold of 0.08 ppm and it is 50 times more bitter than [[quinine]].<ref name=ooscf-2002>Scientific Committee on Food [http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/sc/scf/out134_en.pdf Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on quassin (expressed on 2 July 2002).] SCF/CS/FLAV/FLAVOUR/29 Final </ref> |
||
Quassin is used as a [[medicine]] in [[traditional Chinese medicine]]. |
Quassin is used as a [[medicine]] in [[traditional Chinese medicine]]. |
||
Revision as of 00:28, 4 April 2011
Template:Chembox Identifiers2
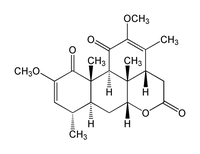
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,12-dimethoxypicrasa-2,12-diene-1,11,16-trione
| |
| Other names
(3aS,6aR,7aS,8S,11aS,11bS,11cS) -1,3a,4,5,6a,7,7a,8,11,11a,11b,11c-dodecahydro-2,10-dimethoxy-3,8,11a,11c- tetramethyldibenzo[de,g]chromene-1,5,11-trione
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H28O6 | |
| Molar mass | 388.460 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline substance |
| Melting point | 200-222 °C |
| Boiling point | 586 °C |
| Insoluble | |
| Vapor pressure | 13 mmHg (@25 °C) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Quassin is a white bitter, crystalline substance extracted from the quassia tree. It is one of the most bitter substances found in nature with a bitter threshold of 0.08 ppm and it is 50 times more bitter than quinine.[1]
Quassin is used as a medicine in traditional Chinese medicine.
Extracts of the Bitter tree (or bitter wood) (Quassia amara L. or Picrasma excelsa) are also used as additives in soft drinks.[1]
Although its skeleton possesses 20 carbon atoms, quassin is not a diterpene but rather a triterpene lactone, which derives from euphol by loss of 10 carbon atoms including C4.
References
- ^ a b Scientific Committee on Food Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on quassin (expressed on 2 July 2002). SCF/CS/FLAV/FLAVOUR/29 Final
