Heat pump: Difference between revisions
Reify-tech (talk | contribs) Add abbreviations |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Heat pumps have the ability to move thermal energy against a thermal gradient at the expense of an external source of power, usually a mechanical compressor. |
Heat pumps have the ability to move thermal energy against a thermal gradient at the expense of an external source of power, usually a mechanical compressor. |
||
[[heat]] spontaneously flows in the direction of the gradient of temperature. A heat pump moves heat in the opposite direction. A heat pump absorbs heat from a colder space and releases it to a warmer one. "heat" is not conserved in this process and it is augmented by the high grade energy expended. |
|||
The name ''heat pump'' is by analogy with a conventional fluid pump that pumps a fluid against its natural flow from higher to lower elevation. |
The name ''heat pump'' is by analogy with a conventional fluid pump that pumps a fluid against its natural flow from higher to lower elevation. |
||
Heat pumps use a refrigerant as an intermediate fluid to absorb heat where it vaporizes, in the evaporator, and then to release heat where the refrigerant condenses, in the condenser. The refrigerant flows through insulated pipes between the evaporator and the condenser, allowing for efficient thermal |
Heat pumps use a refrigerant as an intermediate fluid to absorb heat where it vaporizes, in the evaporator, and then to release heat where the refrigerant condenses, in the condenser. The refrigerant flows through insulated pipes between the evaporator and the condenser, allowing for efficient thermal entergy transfer at relatively long distances. |
||
If the heat pump is reversible, then a [[reversing valve]] allows for the flow direction of the refrigerant to be changed. |
If the heat pump is reversible, then a [[reversing valve]] allows for the flow direction of the refrigerant to be changed. |
||
Revision as of 06:26, 3 June 2012

A heat pump is a device that transfers thermal energy from a source to a sink that is at a higher temperature than the source. Thus, heat pumps move thermal energy in a direction which is opposite to the direction of spontaneous heat flow. The heat pump uses some form of low entropy energy to accomplish the desired transfer of thermal energy from source to sink.
Compressor-driven air conditioners and freezers are examples of heat pumps. However, the term "heat pump" is more general and applies to devices which are used to heat a conditioned-space (i.e., a confined space such as a building), that must be warmer than a cold environment. A heat pump can provide either heating or cooling of a given conditioned-space, depending upon whether the surrounding environment is cooler or warmer than the conditioned-space. When a heat pump is used for heating, it uses the same basic refrigeration-type cycle employed by an air conditioner or a refrigerator, but releasing heat into the conditioned-space rather than into the surrounding environment. In this use, heat pumps generally draw heat from the cooler external air or from the ground.[1]
Heat pumps are used to provide heating because less high-grade (i.e., low-entropy) energy is required for their operation, than appears in the released heat. In general, most of the energy for heating in such systems comes from the external environment, and only a fraction comes from the high-grade energy source. For example, in an electrically powered heat pump, the heat power released to the conditioned environment can be typically two or three times larger than the electrical power consumed, making the system efficiency 200 or 300%, as opposed to the 100% efficiency of a conventional electrical heater, in which all heat is produced from input electrical energy.
Some heat pumps are able to accomplish either conditioned-space cooling or warming, depending on operational setting. Reversible-cycle heat pumps are devices designed to work in either thermal direction, in order to provide heating or cooling of the same conditioned environment. These devices operate by changing which coil is the condenser and which coil is the evaporator, rather than physically turn the device around. Such a function is achieved by a "reversing valve." In heating and air conditioning (HVAC) applications, the term heat pump usually refers to easily reversible vapor-compression refrigeration devices that are optimized for high efficiency in both directions of thermal energy transfer.
Overview
Heat pumps have the ability to move thermal energy against a thermal gradient at the expense of an external source of power, usually a mechanical compressor.
heat spontaneously flows in the direction of the gradient of temperature. A heat pump moves heat in the opposite direction. A heat pump absorbs heat from a colder space and releases it to a warmer one. "heat" is not conserved in this process and it is augmented by the high grade energy expended.
The name heat pump is by analogy with a conventional fluid pump that pumps a fluid against its natural flow from higher to lower elevation.
Heat pumps use a refrigerant as an intermediate fluid to absorb heat where it vaporizes, in the evaporator, and then to release heat where the refrigerant condenses, in the condenser. The refrigerant flows through insulated pipes between the evaporator and the condenser, allowing for efficient thermal entergy transfer at relatively long distances.
If the heat pump is reversible, then a reversing valve allows for the flow direction of the refrigerant to be changed.
- In heating mode, the outdoor coil is an evaporator, while the indoor is a condenser. The refrigerant flowing from the evaporator (outdoor coil) carries the thermal energy from outside air (or ground) indoors, after the fluid's temperature has been augmented by compressing it. The indoor coil then transfers thermal energy (including energy from the compression) to the indoor air, which is then moved around the inside of the building by an air handler. The refrigerant is then allowed to expand, cool, and absorb heat to reheat to the outdoor temperature in the outside evaporator, and the cycle repeats. This is a standard refrigeration cycle, save that the "cold" side of the refrigerator (the evaporator coil) is positioned so it is outdoors where the environment is colder.
- In cooling mode the cycle is similar, but the outdoor coil is now the condenser and the indoor coil (which reaches a lower temperature) is the evaporator. This is the familiar mode in which air conditioners operate.
Operating principles
Mechanical heat pumps exploit the physical properties of a volatile evaporating and condensing fluid known as a refrigerant. The heat pump does work on the refrigerant to make it hotter on the side to be warmed, than at the cold side where heat is absorbed.
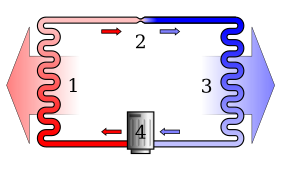
The working fluid, in its gaseous state, is pressurized and circulated through the system by a compressor. On the discharge side of the compressor, the now hot and highly pressurized vapor is cooled in a heat exchanger, called a condenser, until it condenses into a high pressure, moderate temperature liquid. The condensed refrigerant then passes through a pressure-lowering device also called a metering device. This may be an expansion valve, capillary tube, or possibly a work-extracting device such as a turbine. The low pressure liquid refrigerant then enters another heat exchanger, the evaporator, in which the fluid absorbs heat and boils. The refrigerant then returns to the compressor and the cycle is repeated.[citation needed]
In such a system, it is essential that the refrigerant reaches a sufficiently high temperature, when compressed, to release heat through the "hot" heat exchanger (the condensor). Similarly, the fluid must reach a sufficiently low temperature when allowed to expand, or else heat cannot flow from the ambient cold region into the fluid in the cold heat exchanger (the evaporator). In particular, the pressure difference must be great enough for the fluid to condense at the hot side and still evaporate in the lower pressure region at the cold side. The greater the temperature difference, the greater the required pressure difference, and consequently the more energy needed to compress the fluid. Thus, as with all heat pumps, the Coefficient of Performance (amount of thermal energy moved per unit of input work required) decreases with increasing temperature difference.
Insulation is used to reduce the work and energy required to achieve a low enough temperature in the space to be cooled.
To operate in different temperature conditions, different refrigerants are available. Refrigerators, air conditioners, and some heating systems are common applications that use this technology.[citation needed]
Heat transport
Heat is typically transported through engineered heating or cooling systems by using a flowing gas or liquid. Air is sometimes used, but quickly becomes impractical under many circumstances because it requires large ducts to transfer relatively small amounts of heat. In systems using refrigerant, this working fluid can also be used to transport heat a considerable distance, though this can become impractical because of increased risk of expensive refrigerant leakage. When large amounts of heat are to be transported, water is typically used, often supplemented with antifreeze, corrosion inhibitors, and other additives.
Heat sources/sinks
A common source or sink for heat in smaller installations is the outside air, in a so-called "air-sourced" heat pump setup. A fan is usually used to improve heat exchange efficiency.
Larger installations handling more heat, or in tight physical spaces, often use "water-sourced" heat pumps. The heat is sourced or rejected in water flow, which can carry much larger amounts of heat through a given pipe or duct cross-section than air flow can carry. The water may be heated at a remote location by boilers, solar energy, or other means. Alternatively when needed, the water may be cooled by using a cooling tower, or discharged into a large body of water, such as a lake or stream.
Geothermal heat pumps or "ground-sourced" heat pumps use shallow underground heat exchangers as a heat source or sink, and water as the heat transport medium. This is possible because not too far below ground level, the temperature is seasonally constant "shirt-sleeve temperature", and the earth can source or sink a large amount of heat. These systems work in the same manner as an air-sourced heat pump, but the outdoors heat exchanger transfers heat using water pumped through pipes in the ground. These systems usually have higher complexity and initial cost that may be compensated in the long run by more efficient operation.
Many heat pump installations may optionally use an auxiliary conventional heat source. Electrical resistance heaters, and oil or gas combustion are the most common sources. The auxiliary source is installed so that if the heat pump fails or can't provide enough heat, the auxiliary heat will kick in to make up for the difference.
Applications
In HVAC applications, a heat pump is typically a vapor-compression refrigeration device that includes a reversing valve and optimized heat exchangers so that the direction of heat flow (thermal energy movement) may be reversed. The reversing valve switches the direction of refrigerant through the cycle and therefore the heat pump may deliver either heating or cooling to a building. In cooler climates, the default setting of the reversing valve is heating. The default setting in warmer climates is cooling. Because the two heat exchangers, the condenser and evaporator, must swap functions, they are optimized to perform adequately in both modes. As such, the efficiency of a reversible heat pump is typically slightly less than two separately optimized machines.
In plumbing applications, a heat pump is sometimes used to heat or preheat water for swimming pools or domestic water heaters.
In rare cases both the heating and cooling of a single heat pump can be exploited simultaneously resulting in very effective use of the input energy. For example a heat pump water heater could cool the interior of a home, reducing or eliminating the need for air conditioning. [citation needed]
Refrigerants
Until the 1990s, the refrigerants were often chlorofluorocarbons such as R-12 (dichlorodifluoromethane), one in a class of several refrigerants using the brand name Freon, a trademark of DuPont. Its manufacture was discontinued in 1995 because of the damage that CFCs cause to the ozone layer[citation needed] if released into the atmosphere.
One widely adopted replacement refrigerant is the hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) known as R-134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane). R-134a is not as efficient as the R-12 it replaced (in automotive applications) and therefore, more energy is required to operate systems utilizing R-134a than those using R-12. Other substances such as liquid R-717 ammonia are widely used in large-scale systems, or occasionally the less corrosive but more flammable propane or butane, can also be used.
Since 2001, carbon dioxide, R-744, has increasingly been used, utilizing the transcritical cycle. In residential and commercial applications, the hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC) R-22 is still widely used, however, HFC R-410A does not deplete the ozone layer and is being used more frequently. Hydrogen, helium, nitrogen, or plain air is used in the Stirling cycle, providing the maximum number of options in environmentally friendly gases.
More recent refrigerators use R600A which is isobutane, and does not deplete the ozone and is friendly to the environment.[citation needed]
Dimethyl ether (DME) is also gaining popularity as a refrigerant.[2]
Efficiency
When comparing the performance of heat pumps, it is best to avoid the word "efficiency" which has a very specific thermodynamic definition. The term coefficient of performance (COP) is used to describe the ratio of useful heat movement per work input. Most vapor-compression heat pumps use electrically powered motors for their work input. However, in many vehicle applications, mechanical energy from an internal combustion engine provides the needed work.
When used for heating a building on a mild day, for example 10 °C, a typical air-source heat pump (ASHP) has a COP of 3 to 4, whereas a typical electrical resistance heater has a COP of 1.0. That is, one joule of electrical energy will cause a resistance heater to produce only one joule of useful heat, while under ideal conditions, one joule of electrical energy can cause a heat pump to move much more than one joule of heat from a cooler place to a warmer place. Note that the heat pump is more efficient on average in hotter climates than cooler ones, so when the weather is much warmer the unit will perform better than average COP. Conversely in cold weather the COP approaches 1. Thus when there is a wide temperature differential between the hot and cold reservoirs, the COP is lower (worse).
When there is a high temperature differential on a cold day, (e.g., when an air-source heat pump is used to heat a house on a very cold winter day of 0 °C), it takes more work to move the same amount of heat to indoors than on a mild day. Ultimately, due to Carnot efficiency limits, the heat pump's performance will approach 1.0 as the outdoor-to-indoor temperature difference increases for colder climates (outside temperature gets colder). This typically occurs around −18 °C (0 °F) outdoor temperature for air source heat pumps.
Also, as the heat pump takes heat out of the air, some moisture in the outdoor air may condense and possibly freeze on the outdoor heat exchanger. The system must periodically melt this ice. When it is extremely cold outside, it is simpler, and wears the machine less, to heat using an electric-resistance heater rather than to overload an air-source heat pump.
On the other hand, ground-source heat pumps (GSHP) are dependent upon the temperature underground, which is "mild" (typically 10 °C at a depth of more than 1.5m for the UK) all year round. Their year-round COP is therefore normally in the range of 4.0 to 5.0.
The design of the evaporator and condenser heat exchangers is also very important to the overall efficiency of the heat pump. The heat exchange surface areas and the corresponding temperature differential (between the refrigerant and the air stream) directly affect the operating pressures and hence the work the compressor has to do in order to provide the same heating or cooling effect. Generally, the larger the heat exchanger the lower the temperature differential and the more efficient the system becomes.
Heat exchangers are expensive, requiring drilling for some heat-pump types or large spaces to be efficient, and the heat pump industry generally competes on price rather than efficiency. Heat pumps are already at a price disadvantage when it comes to initial investment (not long-term savings) compared to conventional heating solutions like boilers, so the drive towards more efficient heat pumps and air conditioners is often led by legislative measures on minimum efficiency standards.[3]
In cooling mode, a heat pump's operating performance is described in the US as its energy efficiency ratio (EER) or seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER), and both measures have units of BTU/(h·W) (1 BTU/(h·W) = 0.293 W/W). A larger EER number indicates better performance. The manufacturer's literature should provide both a COP to describe performance in heating mode, and an EER or SEER to describe performance in cooling mode. Actual performance varies, however, and depends on many factors such as installation, temperature differences, site elevation, and maintenance.
Heat pumps are more effective for heating than for cooling an interior space if the temperature differential is held equal. This is because the compressor's input energy is also converted to useful heat when in heating mode, and is discharged along with the transported heat via the condenser to the interior space. But for cooling, the condenser is normally outdoors, and the compressor's dissipated work (waste heat) must also be transported to outdoors using more input energy, rather than being put to a useful purpose. For the same reason, opening a food refrigerator or freezer actually heats up the room rather than cooling it because its refrigeration cycle rejects heat to the indoor air. This heat includes the compressor's dissipated work as well as the heat removed from the inside of the appliance.
The COP for a heat pump in a heating or cooling application, with steady-state operation, is:
where
- is the amount of heat extracted from a cold reservoir at temperature ,
- is the amount of heat delivered to a hot reservoir at temperature ,
- is the compressor's dissipated work.
- All temperatures are absolute temperatures usually measured in kelvins (K).
Coefficient of performance (COP) and lift
The COP increases as the temperature difference, or "lift", decreases between heat source and destination. The COP can be maximized at design time by choosing a heating system requiring only a low final water temperature (e.g. underfloor heating), and by choosing a heat source with a high average temperature (e.g. the ground). Domestic hot water (DHW) and conventional heating radiators require high water temperatures, reducing the COP that can be attained, and affecting the choice of heat pump technology.[citation needed]
| Pump type and source | Typical use | COP variation with output temperature | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35 °C (e.g. heated screed floor) |
45 °C (e.g. heated screed floor) |
55 °C (e.g. heated timber floor) |
65 °C (e.g. radiator or DHW) |
75 °C (e.g. radiator and DHW) |
85 °C (e.g. radiator and DHW) | ||
| High-efficiency air source heat pump (ASHP), air at −20 °C[4] | 2.2 | 2.0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Two-stage ASHP, air at −20 °C[5] | Low source temperature | 2.4 | 2.2 | 1.9 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| High efficiency ASHP, air at 0 °C[4] | Low output temperature | 3.8 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 2.0 | ‐ | ‐ |
| Prototype transcritical CO 2 (R744) heat pump with tripartite gas cooler, source at 0 °C[6] |
High output temperature | 3.3 | ‐ | ‐ | 4.2 | ‐ | 3.0 |
| Ground source heat pump (GSHP), water at 0 °C[4] | 5.0 | 3.7 | 2.9 | 2.4 | ‐ | ‐ | |
| GSHP, ground at 10 °C[4] | Low output temperature | 7.2 | 5.0 | 3.7 | 2.9 | 2.4 | ‐ |
| Theoretical Carnot cycle limit, source −20 °C | 5.6 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.4 | |
| Theoretical Carnot cycle limit, source 0 °C | 8.8 | 7.1 | 6.0 | 5.2 | 4.6 | 4.2 | |
| Theoretical Lorentzen cycle limit (CO 2 pump), return fluid 25 °C, source 0 °C[6] |
10.1 | 8.8 | 7.9 | 7.1 | 6.5 | 6.1 | |
| Theoretical Carnot cycle limit, source 10 °C | 12.3 | 9.1 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 5.4 | 4.8 | |
One observation is that while current "best practice" heat pumps (ground source system, operating between 0° and 35° Celsius) have a typical COP around 4, no better than 5, the maximum achievable is 12 because of fundamental Carnot cycle limits. This means that in the coming decades, the energy efficiency of top-end heat pumps could at least double. Cranking up efficiency requires the development of a better gas compressor, fitting HVAC machines with larger heat exchangers with slower gas flows, and solving internal lubrication problems resulting from slower gas flow.
Compression vs. absorption types
The two main types of heat pumps are compression heat pumps and absorption heat pumps. Compression heat pumps always operate on mechanical energy (typically driven by electricity), while absorption heat pumps may also run on heat as an energy source (from electricity or burnable fuels).[7] An absorption heat pump may be fueled by natural gas or LP gas, for example. While the Gas Utilization Efficiency in such a device, which is the ratio of the energy supplied to the energy consumed, may average only 1.5; that is better than a natural gas or LP gas furnace, which can only approach 1.
Although an absorption heat pump may not be as efficient as an electric compression heat pump, an absorption heat pump fueled by natural gas may be advantageous in locations where electricity is relatively expensive and natural gas is relatively inexpensive. A natural gas-fired absorption heat pump might also avoid the cost of an electrical service upgrade which is sometimes necessary for an electric heat pump installation. In the case of air-to-air heat pumps, an absorption heat pump might also have an advantage in colder regions, due to a lower minimum operating temperature.[8]
Heat sources and sinks
By definition, all heat sources for a heat pump must be colder in temperature than the space to be heated. Most commonly, heat pumps draw heat from the air (outside or inside air) or from the ground (groundwater or soil).[9]
The heat drawn from ground-sourced systems is in most cases stored solar heat, and it should not be confused with direct geothermal heating, though the latter will contribute in some small measure to all heat in the ground. True geothermal heat, when used for heating, requires a circulation pump but no heat pump, since for this technology the ground temperature is higher than that of the space that is to be heated, so the technology relies only upon simple heat convection.
Other heat sources for heat pumps include water; nearby streams and other natural water bodies have been used, and sometimes domestic waste water (via drain water heat recovery) which is often warmer than cold winter ambient temperatures (though still of lower temperature than the space to be heated).
A number of sources have been used for the heat source for heating private and communal buildings.[10]
- air source heat pump (extracts heat from outside air)
- air–air heat pump (transfers heat to inside air)
- air–water heat pump (transfers heat to a heating circuit and a tank of domestic hot water)
- exhaust air heat pump (extracts heat from the exhaust air of a building, requires mechanical ventilation)
- exhaust air - water heat pump (transfers heat to a heating circuit and a tank of domestic hot water)
- geothermal heat pump (extracts heat from the ground or similar sources)
- geothermal–air heat pump (transfers heat to inside air)
- ground–air heat pump (ground as a source of heat)
- rock–air heat pump (rock as a source of heat)
- water–air heat pump (body of water as a source of heat)
- geothermal–water heat pump (transfers heat to a heating circuit and a tank of domestic hot water)
- ground–water heat pump (ground as a source of heat)
- rock–water heat pump (rock as a source of heat)
- water–water heat pump (body of water as a source of heat)
- hybrid (or twin source) heat pumps: when outdoor air is above 4 to 8 Celsius, (40-50 Fahrenheit, depending on ground water temperature) they use air, when air is colder, they use the ground source. These twin source systems can also store summer heat, by running ground source water through the air exchanger or through the building heater-exchanger, even when the heat pump itself is not running. This has dual advantage: it functions as a low running cost for air cooling, and (if ground water is relatively stagnant) it cranks up the temperature of the ground source, which improves the energy efficiency of the heat pump system by roughly 4 percent for each degree in temperature rise of the ground source.
- geothermal–air heat pump (transfers heat to inside air)
Air-source heat pumps (ASHP)
Air source heat pumps are relatively easy (and inexpensive) to install and have therefore historically been the most widely used heat pump type. However, they suffer limitations due to their use of the outside air as a heat source. The higher temperature differential during periods of extreme cold or heat leads to declining efficiency, as explained above. In mild weather, COP may be around 4.0, while at temperatures below around −8 °C (17 °F) an air-source heat pump can achieve a COP of 2.5 or better, which is considerably more than the energy efficiency that may be achieved by a 1980's heating systems, and very similar to state of the art oil or gas heaters.[11] The average COP over seasonal variation is typically 2.5-2.8, with exceptional models able to exceed 6.0 in very mild climate, but not in freezing climates.[12]
Air source heat pumps for cold climates
At least two manufacturers are selling heat pumps that maintain better heating output at lower outside temperatures than conventional air source heat pumps. These low temperature optimized models make air source heat pumps more practical for cold climates because they don't freeze and shut down as readily. Some models however, defrost their outdoor unit using electrical resistance heating at regular intervals, which increases electricity consumption dramatically during the coldest periods. In areas where only one fossil fuel is currently available (e.g. heating oil only; no natural gas pipes available) these heat pumps could be used as an alternative, supplemental heat source to reduce a building's direct dependence on fossil fuel. Depending on fuel and electricity prices, using the heat pump for heating may be less expensive than fossil fuel. A backup, fossil-fuel heat source may still be required for the coldest days.[citation needed]
The heating output of low temperature optimized heat pumps (and hence their energy efficiency) still declines dramatically as the temperature drops, but the threshold at which the decline starts is lower than conventional pumps, as shown in the following table (temperatures are approximate and may vary by manufacturer and model):
| Air Source Heat Pump Type | Full heat output at or above this temperature | Heat output down to 60% of maximum at |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 47 °F (8.3 °C) | 17 °F (-8.3 °C) |
| Low Temp Optimized | 14 °F (-10 °C) | -13 °F (-25 °C) |
Ground source heat pumps (GSHP)
Ground-source heat pumps, which are also referred to as geothermal heat pumps, typically have higher efficiencies than air-source heat pumps. This is because they draw heat from the ground or groundwater which is at a relatively constant temperature all year round below a depth of about 30 feet (9 m).[13] This means that the temperature differential is lower, leading to higher efficiency. Ground-source heat pumps typically have COPs of 3.5-4.0 at the beginning of the heating season, with lower COPs as heat is drawn from the ground. The tradeoff for this improved performance is that a ground-source heat pump is more expensive to install, due to the need for the drilling of wells or digging of trenches in which to place the pipes that carry the heat exchange fluid.
When compared, groundwater heat pumps are generally more efficient than heat pumps using heat from the soil. Ground sources tend to accumulate cold, which is a significant problem if ground water is stagnant, and the overall system has been designed to be just big enough to handle a "typical worst case" cold spell. One way to fix cold accumulation, is to use ground water to cool the floors on hot days.[further explanation needed] Another way is to make large solar collectors, for instance by putting plastic pipes just under the roof, or by putting coils of black polyethylene pipes under glass on the roof, or by piping the tarmac of the parking lot. The most cost effective way is to put a large air-to-water heat exchanger on the rooftop.[citation needed]
Heat distribution
Heat pumps are only highly efficient when they distribute produced heat at a low temperature differential, ideally around or below 32 °C (90 °F). Normal steel plate radiators are not practical, because they would need to have four to six times their current size. Underfloor heating is one ideal solution. When wooden floors or carpets would spoil efficiency, wall heaters (plastic pipes covered with a thick layer of chalk) and piped ceilings can be used. These systems have the disadvantage that they are slow starters, and that they would require extensive renovation in existing buildings.
The alternative is a warm air system in which water runs through a ventilator driven water-to-air heat exchanger. Such a setup can either complement slower floor heating during warm up, or it can be a quick and economical way to implement a heat pump system into existing buildings. Oversizing the fans and ductwork can reduce the acoustic noise they produce. To efficiently distribute warm water or air from a heat pump, water pipes or air shafts must have significantly larger diameters than in conventional systems, and underfloor heaters should have much more pipes per square meter.[citation needed]
Solid state heat pumps
Magnetic refrigeration
In 1881, the German physicist Emil Warburg put a block of iron into a strong magnetic field and found that it increased very slightly in temperature. Some commercial ventures to implement this technology are underway, claiming to cut energy consumption by 40% compared to current domestic refrigerators.[14] The process works as follows: Powdered gadolinium is moved into a magnetic field, heating the material by 2 to 5 °C (4 to 9 °F). The heat is removed by a circulating fluid. The material is then moved out of the magnetic field, reducing its temperature below its starting temperature.[citation needed]
Thermoelectric heat pumps
Solid state heat pumps using the Thermoelectric Effect have improved over time to the point where they are useful for certain refrigeration tasks. Commercially available technologies have efficiencies that are currently well below that of mechanical heat pumps, however this area of technology is currently the subject of active research in materials science.
Thermoacoustic hot air engine
Near-solid-state heat pumps using Thermoacoustics are commonly used in cryogenic laboratories.[citation needed]
Historical development
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
Milestones:
- 1748: William Cullen demonstrates artificial refrigeration.
- 1834: Jacob Perkins builds a practical refrigerator with diethyl ether.
- 1852: Lord Kelvin describes the theory underlying heat pump.
- 1855–1857: Peter von Rittinger develops and builds the first heat pump.[15]
See also
- EcoCute domestic heat pump water heater
- Flash evaporation
- Geothermal heat pump
- Heat exchanger
- Renewable heat
- Thermoelectric heat pumps that use the Peltier effect
- Vapor-compression refrigeration
- Vortex tube
- IEA-ECBCS Annex 48 : Heat Pumping and Reversible Air Conditioning
References
- ^ Air-source heat pumps|url=http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy01osti/28037.pdf
- ^ http://www.mecanica.pub.ro/frigo-eco/R404A_DME.pdf 101110
- ^ BSRIA, "European energy legislation explained", www.bsria.co.uk, May 2010.
- ^ a b c d The Canadian Renewable Energy Network 'Commercial Earth Energy Systems', Figure 29. . Retrieved December 8, 2009.
- ^ Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences 'State of the Art of Air-source Heat Pump for Cold Region', Figure 5. . Retrieved April 19, 2008.
- ^ a b SINTEF Energy Research 'Integrated CO2 Heat Pump Systems for Space Heating and DHW in low-energy and passive houses', J. Steen, Table 3.1, Table 3.3. . Retrieved April 19, 2008.
- ^ http://www2.vlaanderen.be/economie/energiesparen/doc/brochure_warmtepomp.pdf
- ^ ROBUR heat pumps comparison
- ^ "Heat pumps sources including groundwater, soil, outside and inside air)" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-06-02.
- ^ Homeowners using heat pump systems[dead link]
- ^ EnergyIdeas.org, "Product & Technology Review: Acadia Heat Pump", Table 1, Dec 2007.
- ^ "the IPCC 4th Working Group III report" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-06-02.
- ^ Earth Temperature and Site Geology, http://www.geo4va.vt.edu/A1/A1.htm
- ^ Guardian Unlimited, December 2006 'A cool new idea from British scientists: the magnetic fridge'
- ^ Banks, David L. An Introduction to Thermogeology: Ground Source Heating and Cooling. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-7061-1.







